TRUSTED BY THE SMARTEST TEAMS IN THE WORLD FOR CERTIFIED CANDIDATES
SPOTO Blogs
Useful learning materials to become certified IT personnel
-
- 2231
- circle
- 2025-01-06 11:00
-
- 1534
- circle
- 2025-01-03 11:56
-
- 3028
- circle
- 2025-01-02 14:39
-
- 1548
- circle
- 2025-01-02 10:25
-
- 1409
- SPOTO
- 2024-11-29 15:20
-
- 1414
- SPOTO
- 2024-06-20 16:02
-
- 1545
- SPOTO
- 2024-06-20 15:54
-
- 3138
- SPOTO
- 2024-06-20 15:47
-
- 1786
- SPOTO
- 2024-06-20 15:47
TRUSTED BY THE SMARTEST TEAMS IN THE WORLD FOR CERTIFIED CANDIDATES
SPOTO Blogs
Useful learning materials to become certified IT personnel
-
- 2231
- circle
- 2025-01-06 11:00
The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification is a globally respected credential that proves your knowledge in networking basics, device configuration, and troubleshooting. With the IT industry's demand for certified professionals steadily increasing, many candidates wonder: Can I prepare for and pass the CCNA exam in just three months? The answer is yes! With a structured study approach, the right resources, and consistent effort, achieving CCNA certification within three months is entirely possible. Let's explore the factors that influence success and craft an efficient preparation strategy for this timeframe. Factors That Influence CCNA Preparation 1. Your Prior Knowledge and Experience Experienced IT Professionals If you have a background in networking, familiarity with Cisco devices, or IT fundamentals, you'll likely find the material less challenging. Key concepts like subnetting, IP addressing, and basic device setup might already be part of your skillset, reducing the time needed for preparation. Beginners For those new to networking, the learning curve will be steeper. Building foundational knowledge might take additional time, but with focus and effort, it's still achievable in three months. 2. Study Commitment Full-Time Learners Dedicating 4–6 hours a day to studying can make a 3-month timeline highly realistic. Working Professionals Juggling work and study requires efficient time management. Even with fewer daily hours available, disciplined planning can help you succeed. 3. Study Resources Using reliable, up-to-date materials is crucial for understanding CCNA topics. Outdated content can slow your progress and lead to confusion, so choose resources like Cisco's official guides, top-rated video tutorials, and trusted practice exams. 4. Learning Style Visual Learners Videos and animations simplify complex topics, making them easier to grasp. Hands-On Learners Practicing in a simulated lab environment ensures concepts are not just learned but applied effectively. A Three-Month Study Plan for CCNA Month 1: Building the Basics Focus on networking fundamentals and basic device configurations. Key Topics: Networking models (OSI and TCP/IP), IP addressing, subnetting, and basic commands. Resources: Cisco's official CCNA study guide. Video tutorials from platforms like CBT Nuggets or Udemy. Actions: Dedicate time to mastering foundational concepts. Use Cisco Packet Tracer or GNS3 for initial hands-on practice. Month 2: Core Concepts and Labs Deep dive into advanced networking topics and start intensive lab practice. Key Topics: VLANs, routing protocols (OSPF, EIGRP), switching concepts, and security basics. Resources: Practice labs simulating real-world scenarios. Troubleshooting exercises to build problem-solving skills. Actions: Dedicate extra time to subnetting and VLAN configuration. Use mock scenarios to replicate challenges you might face in the exam. Month 3: Exam Readiness Focus on review, testing, and fine-tuning weak areas. Key Topics: Comprehensive troubleshooting, exam strategies, and time management. Resources: High-quality practice exams from platforms like SPOTO. Virtual labs for real-time practice. Actions: Take full-length mock exams regularly to identify gaps. Focus on improving speed and accuracy under exam-like conditions. Tips for a Successful 3-Month Plan 1. Consistency Is Key Study daily, even if for short periods, to maintain steady progress. Break down complex topics into manageable sections and review them often. 2. Leverage Practical Experience CCNA emphasizes real-world application. Simulate networks, practice configurations, and troubleshoot issues using tools like Cisco Packet Tracer or GNS3. 3. Engage With the Community Join online forums such as Reddit's r/ccna or the Cisco Learning Network. These platforms provide valuable insights, study tips, and answers to questions. 4. Tackle Weak Areas First Identify topics that are challenging, such as subnetting or routing protocols, and dedicate extra time to mastering them early in your study plan. 5. Use Practice Exams Strategically Mock exams not only test your knowledge but also help you practice time management. Aim for consistently high scores to build confidence before attempting the actual exam. Overcoming Challenges Balancing Work and Study Finding time to study can be difficult if you're working full-time. Solution: Create a structured schedule and stick to it. Utilize short breaks for quick reviews or flashcards. Complex Topics Some concepts, like routing protocols or VLAN configurations, might feel overwhelming. Solution: Break them into smaller, digestible parts. Use visuals and diagrams to clarify abstract ideas. Maintaining Motivation Sustaining focus over three months can be tough. Solution: Set milestones and reward yourself for achieving them. Study groups or an accountability partner can also keep you engaged. Is a 3-Month CCNA Preparation Worth It? Achieving CCNA certification within three months showcases your ability to focus, learn quickly, and stay disciplined — traits that employers value highly. It opens doors to roles like Network Administrator or Support Engineer and lays a solid foundation for advanced certifications like CCNP or CCIE. While challenging, the rewards are significant. A concentrated effort over three months can set you up for long-term success in IT. Conclusion Passing the CCNA exam in three months is a realistic goal for determined candidates. With a structured study plan, hands-on practice, and the right resources, you can confidently master the material and ace the exam. Whether you're starting fresh or building on existing skills, this certification is a worthwhile investment in your IT career. -
- 1534
- circle
- 2025-01-03 11:56
Table of ContentsKey Factors Affecting Study TimeGeneral Preparation TimelineEffective Strategies for CCNA PreparationOvercoming Common ChallengesWhy is CCNA Worth the Effort?Conclusion The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification is a significant milestone for IT professionals aiming to excel in networking. Recognized globally, this credential validates the ability to configure, manage, and troubleshoot networks. A common query among those aspiring to achieve this certification is: How much time should you dedicate to studying for CCNA? The answer depends on several factors, such as prior experience, the study approach, and available time. This article breaks down these considerations to provide IT professionals with a roadmap for their CCNA preparation. Key Factors Affecting Study Time 1. Previous Knowledge and Experience Seasoned IT Professionals: Those with a solid foundation in networking, familiarity with Cisco devices, or related roles may only need 1-2 months of preparation. Beginners: Those new to networking typically require 3-4 months to build the necessary understanding of core concepts like IP addressing, subnetting, and network protocols. 2. Study Commitment Full-Time Students: Individuals dedicating substantial daily hours to their studies can prepare in a shorter timeframe, often within 1-2 months. Part-Time Students: Professionals juggling work and studies may need 3-6 months, depending on the consistency and intensity of their efforts. 3. Quality of Study Materials Using the right resources significantly influences preparation time. Cisco's official study guides, video tutorials, and lab simulations provide focused and reliable content that accelerates learning. 4. Learning Style Visual Learners: Benefit from video content that breaks down complex topics into digestible visuals. Hands-On Learners: Practical lab exercises, requiring additional setup and repetition, are crucial for mastering CCNA's technical aspects. General Preparation Timeline While individual circumstances vary, most professionals' study journeys for CCNA can be categorized into three distinct phases: 1. Building the Basics Start with foundational networking topics, including the OSI and TCP/IP models, device configurations, and basic network communication. This phase typically lasts a few weeks to a couple of months, depending on prior knowledge. 2. Mastering Advanced Topics Move on to more challenging areas like routing protocols, VLANs, IP addressing, and subnetting. These are critical for passing the exam and demand rigorous practice. Expect to spend 1-2 months in this phase. 3. Applying Knowledge Through Practice The final stage involves mock exams, lab simulations, and review. Tools like Cisco Packet Tracer, GNS3, and SPOTO's virtual labs simulate real-world scenarios and solidify practical skills. Allocate 3-4 weeks for this phase to identify and address any gaps. Effective Strategies for CCNA Preparation 1. Prioritize Practical Learning CCNA emphasizes hands-on skills, so invest time in lab simulations. Tools like Cisco Packet Tracer, GNS3, and SPOTO's virtual labs provide environments to replicate real-world scenarios. 2. Leverage Online Resources Video tutorials from platforms such as Udemy and CBT Nuggets simplify complex concepts. Engage with online forums like Reddit's r/ccna or Cisco Learning Network for peer advice and additional resources. 3. Take Mock Exams Mock tests help simulate the exam environment and gauge readiness. Aim for consistent scores of 85% or higher before scheduling your actual test. 4. Focus on Weak Points Pay extra attention to challenging areas like subnetting, routing protocols, or troubleshooting. Regular practice and revisiting these topics ensure steady improvement. 5. Create a Study Plan Organize your study time by setting weekly goals. Divide topics into manageable sections to prevent burnout and track progress effectively. Overcoming Common Challenges 1. Balancing Work and Study IT professionals often struggle to find sufficient study time. Solution: Establish a fixed schedule with dedicated study sessions. Utilize small time slots during breaks or commutes for quick reviews. 2. Handling Complex Topics Concepts like subnetting and routing protocols can be daunting. Solution: Break these down into smaller sections. Use visual aids and tutorials to reinforce understanding. 3. Staying Motivated Lengthy preparation periods can lead to waning enthusiasm. Solution: Celebrate small wins and join study groups for motivation. Peer discussions can also clarify doubts and enhance learning. Why is CCNA Worth the Effort? Achieving the CCNA certification validates your skills and enhances career prospects in roles such as Network Administrator or Junior Network Engineer. Furthermore, it lays a robust foundation for pursuing advanced Cisco certifications like CCNP or CCIE. While preparation time varies, the career growth and opportunities it unlocks make the investment of time and effort worthwhile. Conclusion The duration IT professionals should spend studying for CCNA depends on experience, study habits, and resource availability. With a structured approach, most candidates can prepare effectively within 2-6 months. Whether you're new to networking or looking to solidify your expertise, CCNA is an investment in your future. Dedicate time and effort, and you'll be well-equipped to succeed in the exam and advance in your IT career. -
- 3028
- circle
- 2025-01-02 14:39
Table of Contents1. Subnetting2. Routing Protocols3. Access Control Lists (ACLs)4. Network Address Translation (NAT)5. Wireless Networking6. Automation and ProgrammabilityGeneral Tips for Tackling Tough TopicsConclusion The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification is a significant milestone for aspiring networking professionals. It covers a wide range of topics, from networking fundamentals to more advanced areas like security and automation. While rewarding, many candidates find certain topics especially challenging. This article highlights some of the hardest topics in the CCNA syllabus and provides practical strategies to master them, ensuring you're well-prepared to pass the exam and excel in your networking career. 1. Subnetting Why It's Challenging Subnetting requires mathematical precision and a deep understanding of binary numbers, IP addressing, and network classes. Many learners struggle with converting between binary and decimal, calculating subnet masks, and determining the number of usable hosts. How to Defeat It Understand the Basics: Start with the fundamentals of binary math and how IP addressing works. Practice with Subnetting Problems: Use tools like subnetting calculators or practice websites to solve multiple subnetting scenarios. Memorize Key Values: Learn common subnet mask values and their corresponding CIDR notations (e.g., /24, /26). Time Yourself: In the CCNA exam, you'll need to subnet quickly. Practice solving problems within a time limit to simulate exam conditions. 2. Routing Protocols Why It's Challenging The CCNA exam covers several routing protocols, including OSPF, EIGRP, and RIP. Understanding how these protocols function, their metrics, and their configuration can be overwhelming for beginners. How to Defeat It Focus on OSPF: Since OSPF is emphasized in the CCNA, prioritize understanding its states, metrics, and how it calculates the shortest path. Visualize the Process: Draw diagrams to illustrate how routing tables are updated and routes are exchanged. Lab Practice: Use tools like Packet Tracer or GNS3 to configure and troubleshoot routing protocols. Real-world practice solidifies theoretical knowledge. 3. Access Control Lists (ACLs) Why It's Challenging ACLs are critical for controlling network traffic, but their syntax and application can be tricky. Understanding the difference between standard and extended ACLs, as well as configuring them correctly, often confuses candidates. How to Defeat It Learn the Syntax: Memorize the structure of ACL commands and the differences between standard and extended ACLs. Practice Scenarios: Work on various examples, such as permitting or denying specific IP addresses or protocols. Experiment in Labs: Implement ACLs in lab environments to see how they affect traffic flow. 4. Network Address Translation (NAT) Why It's Challenging NAT involves translating private IP addresses to public IP addresses, which can be conceptually complex. Understanding different types of NAT (static, dynamic, and PAT) and their configurations can be daunting. How to Defeat It Master the Concepts: Understand why NAT is used and how each type differs. Focus on Configuration: Practice configuring NAT on Cisco devices, paying attention to details like access lists and pool definitions. Simulate Real-World Use Cases: Create scenarios in labs where NAT is essential, such as enabling internet access for a private network. 5. Wireless Networking Why It's Challenging Wireless concepts in CCNA include security protocols (WPA, WPA2), standards (802.11a/b/g/n/ac), and basic wireless architecture. For many, this is a less familiar topic compared to wired networking. How to Defeat It Understand the Standards: Focus on the differences between the 802.11 standards and their capabilities. Learn Wireless Security: Understand the security mechanisms used in wireless networks and their implications. Hands-On Practice: Use wireless routers and access points to set up networks and experiment with configurations. 6. Automation and Programmability Why It's Challenging Automation is a newer addition to the CCNA syllabus. It requires understanding programming concepts, APIs, and tools like Python. For those without a programming background, this can feel intimidating. How to Defeat It Learn Basic Python: Familiarize yourself with Python syntax and concepts like loops and conditionals. Resources and tutorials on SPOTO and YouTube are great starting points. Understand APIs: Learn how REST APIs work and how to use tools like Postman to interact with them. Use Cisco's DevNet: Cisco's DevNet platform offers excellent resources to get started with network automation. General Tips for Tackling Tough Topics 1. Break Down the Topics Complex subjects can be overwhelming, but breaking them into smaller chunks makes them more manageable. Focus on one aspect at a time and build your knowledge gradually. 2. Leverage Online Resources Platforms like Cisco Networking Academy, YouTube channels, SPOTO, and forums like Reddit's r/ccna provide valuable insights and community support. 3. Practice, Practice, Practice The CCNA is a practical exam, so hands-on experience is critical. Tools like Cisco Packet Tracer, GNS3, and physical lab equipment can help you gain real-world skills. 4. Join a Study Group Collaborating with peers can help you learn faster and keep you motivated. Join online communities, forums, or local study groups. 5. Use a Structured Study Plan Create a study plan that allocates time for each topic. Dedicate more time to areas you find challenging, and review regularly to reinforce your knowledge. Conclusion The CCNA certification is challenging, but it's also a rewarding journey that lays the foundation for a successful networking career. While topics like subnetting, routing protocols, and network automation may seem daunting at first, they become manageable with the right approach. By leveraging hands-on practice, breaking topics into digestible parts, and using online resources, you can overcome the hardest parts of the CCNA syllabus and emerge as a confident, certified networking professional. -
- 1548
- circle
- 2025-01-02 10:25
Table of Contents1. What is the CCNA Certification?2. Can Beginners Learn CCNA Without Prior Experience?3. Steps for Beginners to Self-Study for CCNA4. Challenges for Beginners Learning CCNA5. Conclusion For those new to networking, earning a Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification might seem daunting. With its emphasis on foundational networking concepts, the CCNA certification is a popular starting point for aspiring IT professionals. But is it possible for an amateur with no prior experience to study and pass the CCNA exam independently? The answer is yes—with focus, persistence, and the right strategy, beginners can successfully self-study for CCNA. Let's explore how. 1. What is the CCNA Certification? The CCNA certification is Cisco's entry-level credential in networking. It validates your knowledge of core networking concepts, including: Networking Basics: Understanding how devices communicate within a network, IP addressing, and subnetting. Routing and Switching: Configuring routers and switches to manage network traffic effectively. Network Security: Protecting networks from unauthorized access using firewalls, VPNs, and access control. Basic Automation: Introducing concepts like Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and basic programming for network tasks. As of now, the CCNA exam which includes both theoretical and practical components, covers a broad range of topics, making it an excellent foundation for any networking career. 2. Can Beginners Learn CCNA Without Prior Experience? While the CCNA exam is comprehensive, it's designed to be approachable for those starting their networking careers. Here's why beginners can tackle CCNA successfully: It assumes no prior experience in networking. Study materials are beginner-friendly, breaking down complex topics into manageable concepts. Practical tools like simulators allow learners to gain hands-on experience without expensive equipment. With the right resources and a structured approach, even complete beginners can achieve CCNA certification. 3. Steps for Beginners to Self-Study for CCNA 3.1 Start with Networking Basics If you're completely new to networking, start by learning the fundamentals. Understand key concepts like: What is a network? How do devices communicate? What is an IP address? Resources like Cisco's Packet Tracer or free online courses on platforms like YouTube can be invaluable. 3.2 Use Official Cisco Study Materials Cisco provides beginner-friendly resources, such as: Cisco Learning Network: Offers tutorials, forums, and free resources for CCNA aspirants. Official Cert Guide: This book explains concepts step-by-step, with examples tailored for new learners. These materials ensure you're learning from accurate and reliable sources. 3.3 Explore Beginner-Focused Online Courses Platforms like SPOTO offer courses designed specifically for amateurs. These courses include: Video tutorials explaining concepts visually. Quizzes to test your understanding. Hands-on practice labs for real-world skills. 3.4 Practice Hands-On Skills Practical experience is crucial for CCNA preparation. Beginners can: Use Packet Tracer: Cisco's free network simulation tool. Explore tools like GNS3 for more advanced simulations. Opt for cloud-based labs from providers like SPOTO, which offer guided practice in a virtual environment. 3.5 Create a Study Plan Structure your study sessions to avoid feeling overwhelmed. Allocate time for: Learning Concepts: Focus on one topic at a time, such as IP addressing or routing protocols. Hands-On Practice: Apply what you've learned in a simulated environment. Review and Testing: Use mock exams to track your progress and improve weak areas. 3.6 Join Beginner-Friendly Communities Online communities can be an excellent source of motivation and support. For beginners, forums like the Cisco Learning Network, Reddit's ccna, and networking-focused Discord groups provide opportunities to: Ask questions and clarify doubts. Share resources and tips. Learn from others' experiences. 4. Challenges for Beginners Learning CCNA While self-studying for CCNA as a beginner is achievable, there are challenges: Overwhelming Information: Networking concepts can initially seem complex. Staying Consistent: Without a structured classroom environment, it's easy to lose focus. Lack of Practical Experience: Beginners may find it challenging to understand how theoretical knowledge applies in real-world scenarios. To overcome these obstacles, beginners should take it slow, seek help from mentors or forums, and focus on hands-on practice. 5. Conclusion For beginners wondering if they can learn CCNA on their own, the answer is a resounding yes. The CCNA certification is designed to be approachable, even for those without prior networking experience. With a structured approach, beginner-friendly resources, and consistent practice, you can build the foundational skills needed to pass the exam and kickstart your networking career. Start your journey today and take your first steps into the exciting world of IT networking! -
- 1409
- SPOTO
- 2024-11-29 15:20
Table of ContentsCisco Command Set – Routing Protocols and Troubleshooting Cisco: To clear the configuration, use: erase startup-config (which deletes the contents of NVRAM), then reboot the router with: reload. Huawei: To clear the configuration, use: reset saved-configuration, then reboot the router with: reboot. Cisco Router and Switch Password Recovery: Selective Routing Advertisement: For example, in RIP configuration, configure the S0 interface to only receive but not send RIP advertisements. Router(config)#router rip Router(config-router)#passive-interface serial 0 About Keyboard Shortcuts: Ctrl+B (backward): Move the cursor one character to the left. Ctrl+F (forward): Move the cursor one character to the right. Ctrl+A (A stands for "beginning"): Move the cursor to the beginning of the command. Ctrl+E (end): Move the cursor to the end of the command. Esc+B (backward): Move the cursor one word to the left. Esc+F (forward): Move the cursor one word to the right. Ctrl+Z: Exit privileged mode at once (Router#). About Modes: User Mode (User Execution Mode): The initial mode when connecting to a router, characterized by the ">" prompt. In this mode, you can only view the configuration and status of the router but cannot make changes. To configure the router, you must enter Privileged Mode. Privileged Mode (Privilege Execution Mode): To enter this mode, use the command enable. If a password is set, you will need to enter the correct password. This mode is characterized by the "#" prompt. Global Configuration Mode: From Privileged Mode, you can enter this mode by using the command configure terminal. In this mode, you can make global configurations. Specific Configuration Modes: These include router interface configuration mode, router sub-interface configuration mode, routing protocol configuration mode, line configuration mode, and more. Mode Transitions: After connecting to the router, you first enter User Mode, which is characterized by the ">" symbol. In this mode, you can only view the router's configuration and status, but you cannot configure it. To make configurations, you must enter Privileged Mode. Use the command enable to enter, and if a password is set, it must be entered correctly. In Privileged Mode, the prompt will change to "#". To enter Global Configuration Mode from Privileged Mode, use the command configure terminal. Commands to Enter Specific Configuration Modes from Global Configuration Mode: Privileged Mode → Router Interface Configuration Mode: For serial interface: interface serial ?? For Ethernet interface: interface ethernet ?? Privileged Mode → Router Sub-interface Configuration Mode: subinterface Privileged Mode → Routing Protocol Configuration Mode: router rip Privileged Mode → Line Configuration Mode: line vty ?? Commands and Usage in Different Modes: User Mode (Router>): show ping, telnet, connect: These commands are used the same way as in Privileged Mode. Privileged Mode (Router#): show users: View all users connected to the router. show hosts: View the IP-to-name mapping table. show arp: View the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) table. show protocol: View the router's protocol status. show version: View the version of the IOS and memory information. show flash: View the flash memory usage. show clock: View the current time of the router. show history: View the last ten commands entered. show ip interface brief: View the IP settings and status of router interfaces. show interfaces: View the status of all router interfaces. show interfaces [specific interface]: View the status of a specific router interface. show running-config: View the configuration file in RAM. show startup-config: View the configuration file in NVRAM. show cdp: View CDP information. show cdp entry ??: View information about a specific neighboring router. show cdp neighbors: View all neighboring routers. show cdp neighbors detail: View detailed information about all neighboring routers. show cdp traffic: View information about CDP packets. show cdp ?? (port number): View CDP information for a specific port. show session: View the status of the original router during a remote login session. clear cdp counters: Clear CDP counters. clear cdp table: Clear the CDP information. copy running-config startup-config: Copy the configuration file in RAM to NVRAM. copy startup-config running-config: Copy the configuration file in NVRAM to RAM. copy tftp running-config: Copy the configuration file from a TFTP server to RAM. copy running-config tftp: Copy the configuration file from RAM to a TFTP server. ping ?? (hostname or IP): Test the connectivity between the router and a remote router. telnet ?? (hostname or IP): Log in to a remote router (requires login password). connect ?? (hostname or IP): Similar to telnet for remote login. traceroute ?? (hostname or IP): Trace the route to a destination router. Commands in Global Configuration Mode: hostname ?? (name): Change the router's hostname. enable password ??: Change the password for entering Privileged Mode. enable secret ??: Change the secret password for entering Privileged Mode (this password is encrypted). clock set hour:minute:second day month year: Set the router's time. ip host ?? (name) ?? (IP address): Add a hostname-to-IP address mapping. service password-encryption: Enable encryption for all passwords (the enable secret password is already encrypted). cdp run: Enable CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol) on all interfaces. cdp timer: Set the CDP advertisement timer. cdp holdtime: Set the CDP hold time. end: Exit from Global Configuration Mode to User Mode. exit: Exit one level at a time (use multiple exit commands to progressively step out). Commands in Interface Configuration Mode: ip address ?? (IP address): Set the IP address for the interface. no shutdown: Enable the interface (bring it up). shutdown: Disable the interface (bring it down). clock rate ??: Set the clock rate for the DCE (Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment) side (DTE does not need this). cdp enable: Enable CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol) on the interface. Commands in Line Configuration Mode: line vty 0 4password ??login: Enable login for the virtual terminal lines using the configured password. Most Common Cisco Command Categories: 1. Switch Configuration Commands: Mode Transition Commands: User Mode → Privileged Mode: Use the command enable. Privileged Mode → Global Configuration Mode: Use the command config t. Global Configuration Mode → Interface Mode: Use the command interface [interface type] [interface number]. Global Configuration Mode → Line Configuration Mode: Use the command line [interface type] [interface number]. Note: User Mode: Used to view initialization information. Privileged Mode: Used to view all information, debug, and save configuration information. Global Configuration Mode: Used to configure overall settings for the router or switch, affecting all interfaces. Interface Mode: Used to configure settings for a specific interface. Line Configuration Mode: Used to configure control settings for the router's interfaces. Configuration Commands: show running-config: Display all configurations. show version: Display version number and register values. shutdown: Disable the interface. no shutdown: Enable the interface. ip address [IP address]: Configure an IP address for the interface. secondary [IP address]: Configure a secondary IP address for the interface. show interface [interface type] [interface number]: View the interface status and configuration. show controllers [interface]: Check if the interface has a DCE cable connected. show history: View the history of commands entered. show terminal: View terminal settings, including terminal buffer size. hostname [hostname]: Configure the router or switch hostname. config memory: Modify the startup configuration saved in NVRAM. exec-timeout 0 0: Set the console session timeout to zero (no timeout). service password-encryption: Encrypt all passwords manually. enable password [password]: Configure a plaintext password for Privileged Mode. enable secret [password]: Configure a secret (encrypted) password for Privileged Mode. line vty 0 4/15: Enter the configuration mode for telnet lines. password [password]: Configure a password for telnet access. line aux 0: Enter the configuration mode for the AUX (Auxiliary) port. password [password]: Configure a password for the AUX port. line con 0: Enter the configuration mode for the console port. password [password]: Configure a password for the console port. bandwidth [number]: Configure the bandwidth for an interface. no ip address: Remove the configured IP address from the interface. show startup-config: View the configuration in NVRAM (startup configuration file). show running-config: View the current configuration in RAM. copy running-config startup-config: Save the current configuration to the startup configuration file, so that it is used next time the router starts up. write: Save the current configuration to NVRAM (startup configuration file). erase startup-config: Clear the configuration stored in NVRAM, essentially clearing the startup configuration file. show ip interface brief: View the essential information of all interfaces. banner motd # [message] #: Configure the router or switch message-of-the-day (MOTD) banner. description [message]: Add a description to an interface. vlan database: Enter VLAN database mode. vlan [vlan number] [name]: Create a VLAN and assign a name to it. switchport access vlan [vlan number]: Assign a VLAN to an interface (access mode). interface vlan [vlan number]: Enter VLAN interface configuration mode. ip address [IP address]: Configure an IP address for a VLAN interface. vtp [service/client/transparent]: Configure the VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol) mode for the switch. vtp domain [domain name]: Configure the VTP domain for the switch. vtp password [password]: Configure the VTP password for the switch. switchport mode trunk: Enable trunking mode on the interface. no vlan [vlan number]: Delete a VLAN. show spanning-tree vlan [vlan number]: View the spanning tree status for a specific VLAN. Router Configuration Commands: ip route [non-direct network] [subnet mask] [next-hop address]: Configure static/default route. show ip route: View the routing table. show protocols: Display all passive routing protocols and which protocols are configured on each interface. show ip protocols: Display routing protocols configured on the router and provide information about timers used in the routing protocols. router rip: Activate the RIP (Routing Information Protocol). network [directly connected network]: Advertise a directly connected network in RIP. interface loopback 0: Activate the loopback interface. passive-interface [interface type] [interface number]: Configure an interface to be passive (used for protocols like RIP). debug ip [protocol]: Dynamically view routing update information for a specific protocol. undebug all: Disable all debugging output. router eigrp [AS number]: Activate the EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol). network [network] [subnet mask]: Advertise a directly connected network in EIGRP. show ip eigrp neighbors: View the EIGRP neighbor table. show ip eigrp topology: View the EIGRP topology table. show ip eigrp traffic: View the number of packets sent by EIGRP. router ospf [process ID]: Activate the OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) protocol. network [directly connected network] area [area number]: Advertise a directly connected network in OSPF. show ip ospf: Display OSPF process ID and Router ID. encapsulation [encapsulation format]: Change the encapsulation format of the interface. no ip domain-lookup: Disable domain name lookup on the router. ip routing: Enable routing functionality on a Layer 3 switch. show users: View online users on the switch. clear line [line number]: Clear a specific line on the switch. Layer 3 Switch Configuration Commands: Configure a group of Layer 2 ports: configure terminal: Enter configuration mode. interface range {port-range}: Enter range configuration mode to configure multiple ports. Configure Layer 3 ports: configure terminal: Enter configuration mode. interface {fastethernet | gigabitethernet} interface-id | vlan vlan-id | port-channel port-channel-number: Enter port configuration mode for specific interfaces or VLANs. no switchport: Convert the physical port to a Layer 3 port. ip address [ip_address] [subnet_mask]: Configure IP address and subnet mask for the Layer 3 port. no shutdown: Activate the port. Example: Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet0/2 Switch(config-if)# no switchport Switch(config-if)# ip address 192.20.135.21 255.255.255.0 Switch(config-if)# no shutdown Configure VLAN: configure terminal: Enter configuration mode. vlan [vlan-id]: Enter VLAN configuration mode, and specify a VLAN ID (new or existing). name [vlan-name]: Optionally assign a name to the VLAN (default name is VLAN followed by the VLAN number). mtu [mtu-size]: Optionally change the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) size. Example: Switch# configure terminal Switch(config)# vlan 20 Switch(config-vlan)# name test20 Switch(config-vlan)# end Alternatively: Switch# vlan database Switch(vlan)# vlan 20 name test20 Switch(vlan)# exit Assign ports to a VLAN: configure terminal: Enter configuration mode. interface [interface-id]: Enter the interface to which you want to assign the VLAN. switchport mode access: Define the port as a Layer 2 access port. switchport access vlan [vlan-id]: Assign the interface to a VLAN. Example: Switch# configure terminal Switch(config)# interface fastethernet0/1 Switch(config-if)# switchport mode access Switch(config-if)# switchport access vlan 2 Switch(config-if)# end VLAN Trunk Configuration Commands Enter Configuration Mode: configure terminal: Enter global configuration mode. Configure Trunk Port: interface interface-id: Enter the port configuration mode (e.g., FastEthernet0/4). switchport trunk encapsulation {isl | dot1q | negotiate}: Configure Trunk encapsulation type (ISL, 802.1Q, or negotiate). switchport mode {dynamic {auto | desirable} | trunk}: Configure port trunk mode. switchport access vlan vlan-id: Optionally, specify the default VLAN if the port is not in trunk mode. switchport trunk native vlan vlan-id: Configure the Native VLAN for 802.1Q. Example: Switch(config)# interface fastethernet0/4 Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q Switch(config-if)# end Define Allowed VLANs on Trunk: switchport trunk allowed vlan {add | all | except | remove} vlan-list: Configure the allowed VLANs on the trunk port. no switchport trunk allowed vlan: Remove VLAN restrictions and allow all VLANs. Example: Switch(config)# interface fastethernet0/1 Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan remove 2 Switch(config-if)# end Configure Native VLAN for 802.1Q: switchport trunk native vlan vlan-id: Configure the Native VLAN for 802.1Q trunks. no switchport trunk native vlan: Restore to the default Native VLAN. Example: Switch(config)# interface fastethernet0/2 Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 10 Switch(config-if)# end Configure Load Balancing based on Port Priorities: spanning-tree vlan vlan-id port-priority priority: Configure port priority for specific VLANs. Example: Switch(config)# interface fastethernet0/1 Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree vlan 8 port-priority 10 Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree vlan 9 port-priority 10 Switch(config-if)# end Verify and Save Configuration: show vlan: Verify VLAN configuration. show running-config: View current configuration. copy running-config startup-config: Save configuration. Load Balancing by Configuring STP Path Cost Trunk1 carries VLANs 8-10, Trunk2 carries VLANs 2-4 Enter Switch 1 configuration mode: configure terminal Enter interface FastEthernet 0/1: interface fastethernet 0/1 Configure trunk encapsulation: switchport trunk encapsulation {isl | dot1q | negotiate} Set the port mode to trunk (default is ISL encapsulation): switchport mode trunk Exit the interface configuration mode: exit Repeat steps 2-4 for interface FastEthernet 0/2: interface fastethernet 0/2 switchport trunk encapsulation {isl | dot1q | negotiate} switchport mode trunk exit Verify the running configuration: show running-config Verify the VLANs learned by Switch 1: show vlan Enter configuration mode again: configure terminal Enter interface FastEthernet 0/1 again: interface fastethernet 0/1 Set the spanning-tree path cost for VLAN 2: spanning-tree vlan 2 cost 30 Set the spanning-tree path cost for VLAN 3: spanning-tree vlan 3 cost 30 Set the spanning-tree path cost for VLAN 4: spanning-tree vlan 4 cost 30 Exit configuration mode: end Repeat steps 9-14 for interface FastEthernet 0/2 to configure spanning-tree path cost for VLANs 8, 9, and 10. Save the configuration: copy running-config startup-config Cisco Command Set – Routing Protocols and Troubleshooting ip route Command The ip route command is used to configure static routes: Router(config)# ip route <network address or subnet> [subnet mask] <next hop IP address | exit address from local router> [administrative distance 0-255, default is 1] Note: Static address configuration ip default-network Command The ip default-network command is used to define a default network, typically with a dynamic routing protocol: Router(config)# ip default-network <destination network> Note: Used with routing protocols to configure a default route based on one of the dynamic route numbers. Router(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 <next hop IP address | exit address from local router> Note: Only used on the exit router when there is a single public IP address. Interior Routing Protocols Use the router and network commands to enable routing protocols: Router(config)# router <routing protocol: rip | igrp | eigrp | ospf | is-is etc.> [AS number] Router(config-router)# network <directly connected network that will use the routing protocol> Router(config-router)# network <another directly connected network that will use the routing protocol> Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Router(config)# router rip Router(config-router)# network <directly connected network with RIP> Router# show ip protocols Router# show ip route Router# debug ip rip Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) Router(config)# router igrp <AS number> Router(config-router)# network <directly connected network with IGRP> Router# show ip interface Router# show ip protocols Router# show ip route Router# debug ip rip ip route Command The ip route command is used to configure static routes: Router(config)# ip route <network address or subnet> [subnet mask] <next hop IP address | exit address from local router> [administrative distance 0-255, default is 1] Note: Static address configuration ip default-network Command The ip default-network command is used to define a default network, typically with a dynamic routing protocol: Router(config)# ip default-network <destination network> Note: Used with routing protocols to configure a default route based on one of the dynamic route numbers. Router(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 <next hop IP address | exit address from local router> Note: Only used on the exit router when there is a single public IP address. Interior Routing Protocols Use the router and network commands to enable routing protocols: Router(config)# router <routing protocol: rip | igrp | eigrp | ospf | is-is etc.> [AS number] Router(config-router)# network <directly connected network that will use the routing protocol> Router(config-router)# network <another directly connected network that will use the routing protocol> Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Router(config)# router rip Router(config-router)# network <directly connected network with RIP> Router# show ip protocols Router# show ip route Router# debug ip rip Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) Router(config)# router igrp <AS number> Router(config-router)# network <directly connected network with IGRP> Router# show ip interface Router# show ip protocols Router# show ip route Router# debug ip rip -
- 1414
- SPOTO
- 2024-06-20 16:02
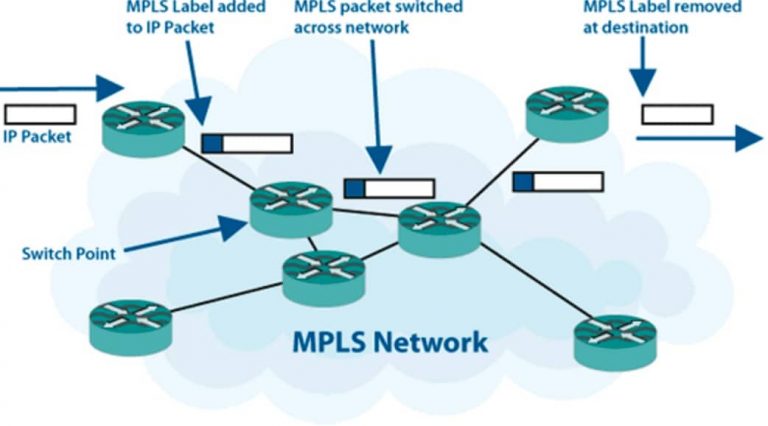
Table of ContentsWhat is MPLS Traffic Engineering?MPLS Traffic Engineering MechanismsDesigning MPLS Traffic Engineering NetworksMPLS Traffic Engineering Terminology As the demand for efficient, scalable, and high-performance network solutions grows, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Traffic Engineering (TE) has become a pivotal technology in modern networking. Chapter 12 of the CCIE Routing and Switching v5.0 Official Cert Guide delves into the complexities and applications of MPLS Traffic Engineering, offering a comprehensive overview of its principles, mechanisms, and design considerations. This blog post aims to break down these concepts and provide a clear understanding of MPLS TE for networking professionals and enthusiasts. What is MPLS Traffic Engineering? MPLS Traffic Engineering is a technique used to optimize the flow of network traffic. It allows network operators to control the path that data packets take through the network, ensuring efficient use of available bandwidth and improving overall network performance. MPLS TE is particularly useful in large-scale networks where traffic patterns can vary significantly, and efficient resource utilization is critical. Key Components of MPLS Traffic Engineering Label Switched Path (LSP) An LSP is a predetermined path through an MPLS network that data packets follow from an ingress node to an egress node. Each LSP is established using a signaling protocol such as RSVP-TE (Resource Reservation Protocol-Traffic Engineering), which sets up the path and reserves the necessary resources. Traffic Engineering Database (TED) The TED is a specialized database that stores information about the network topology, including available bandwidth and link characteristics. It is used by the path computation element (PCE) to calculate optimal paths for LSPs. Path Computation Element (PCE) The PCE is responsible for determining the best path for an LSP based on the network topology and traffic engineering constraints. It uses algorithms like Constrained Shortest Path First (CSPF) to find paths that meet specific criteria such as minimum bandwidth or maximum delay. Resource Reservation Protocol-Traffic Engineering (RSVP-TE) RSVP-TE is a signaling protocol used to establish and maintain LSPs in an MPLS network. It handles the reservation of resources along the path and ensures that the necessary bandwidth is available for the LSP. MPLS Traffic Engineering Mechanisms Explicit Route Objects (ERO) EROs are used to define the specific path that an LSP should take through the network. They provide the flexibility to override the default routing decisions and direct traffic through preferred routes based on various constraints. Administrative Groups (Link Coloring) Administrative groups, also known as link colors, are used to categorize network links based on certain attributes like geographical location or link type. This categorization helps in path selection by allowing or disallowing certain links for specific LSPs. Bandwidth Constraints MPLS TE allows for the specification of bandwidth requirements for each LSP. This ensures that the paths selected can accommodate the required bandwidth, preventing congestion and improving the quality of service. Fast Reroute (FRR) Fast Reroute provides a mechanism for rapid recovery from link or node failures. By precomputing backup paths and immediately switching traffic to these paths upon failure, FRR minimizes traffic disruption and enhances network reliability. Designing MPLS Traffic Engineering Networks Network Topology and LSP Design Designing an MPLS TE network starts with understanding the network topology and traffic patterns. This involves identifying key traffic flows and determining the optimal paths to ensure efficient use of network resources. Constraint-Based Path Selection Path selection in MPLS TE is driven by constraints such as bandwidth, delay, and administrative policies. These constraints must be carefully defined and implemented to achieve the desired network performance. Scalability Considerations As networks grow, the scalability of MPLS TE becomes crucial. This includes managing the number of LSPs, the complexity of the TED, and the computational load on the PCE. Techniques like hierarchical LSPs and aggregation of traffic flows can help manage scalability. Monitoring and Optimization Continuous monitoring of LSP performance and network conditions is essential for maintaining optimal traffic engineering. Tools like MPLS ping and traceroute are used to verify LSP integrity and troubleshoot issues. Optimization involves adjusting LSPs and network configurations based on real-time data and performance metrics. MPLS Traffic Engineering Terminology Constrained Shortest Path First (CSPF) CSPF is an algorithm used to compute the shortest path for an LSP while considering various constraints like bandwidth and administrative groups. It extends the basic shortest path first (SPF) algorithm by incorporating additional criteria into the path computation process. Link-State Advertisement (LSA) LSAs are used by routing protocols like OSPF and IS-IS to distribute information about the network topology. In the context of MPLS TE, LSAs carry additional information such as available bandwidth and link attributes, which are used by the TED. Tunnel Tail-End The tunnel tail-end refers to the destination node of an LSP. It is the point where the MPLS labels are removed, and the original IP packet is forwarded to its final destination. Preemption Preemption is a mechanism that allows higher-priority LSPs to take over resources from lower-priority LSPs. This ensures that critical traffic can be accommodated even during periods of high network congestion. MPLS Traffic Engineering is a powerful tool for optimizing network performance and ensuring efficient use of resources. By understanding its key components, mechanisms, and design principles, network operators can implement effective MPLS TE solutions that meet the demands of modern networking environments. Whether you're managing a large-scale service provider network or an enterprise WAN, MPLS Traffic Engineering provides the flexibility and control needed to deliver high-quality, reliable network services. -
- 1545
- SPOTO
- 2024-06-20 15:54
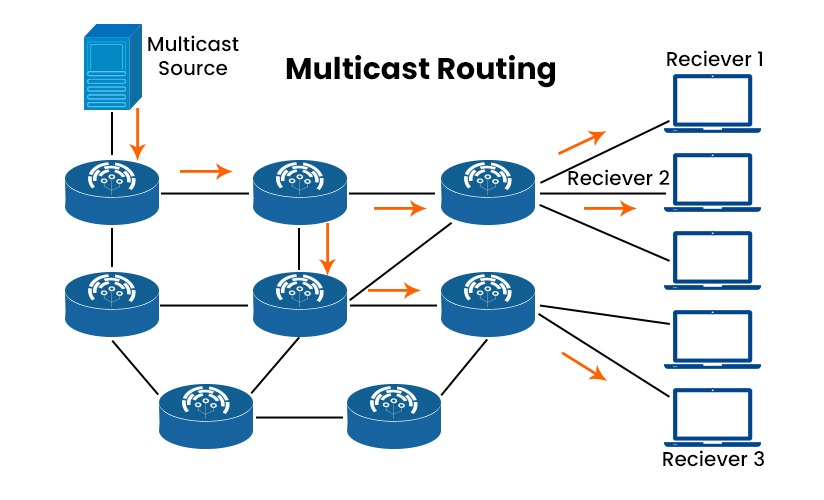
Table of ContentsIntroduction to Multicast RoutingMulticast BasicsInternet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM)Multicast Border Gateway Protocol (MBGP)Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP)Bidirectional PIM (BIDIR-PIM) Introduction to Multicast Routing Multicast routing is an essential concept in modern network communication, particularly for efficiently distributing data to multiple recipients. Unlike unicast (one-to-one) or broadcast (one-to-all), multicast routing allows the delivery of information to a group of destinations simultaneously, reducing bandwidth consumption and improving network performance. In this blog, we'll explore key technical terms and concepts related to multicast routing as covered in Chapter 11 of the Cisco CCIE Routing and Switching v5.0 Official Cert Guide. Multicast Basics What is Multicast? Multicast is a method of communication where data is transmitted from one sender to multiple receivers. Unlike broadcast, which sends data to all devices on a network, multicast targets a specific group of receivers. This approach is highly efficient for applications like video conferencing, online streaming, and real-time data feeds. Multicast Addressing Multicast uses a specific range of IP addresses (224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 for IPv4) to identify multicast groups. Devices interested in receiving multicast traffic must join the corresponding multicast group. The communication happens at both the network and data link layers, utilizing IP multicast addresses and MAC addresses designed for multicast. Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) What is IGMP? Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is used by IPv4 systems to report their multicast group memberships to adjacent routers. IGMP plays a crucial role in managing multicast group membership on a local network, ensuring that routers know which devices want to receive specific multicast streams. IGMP Versions IGMPv1: The simplest form, allowing hosts to join multicast groups but not leave them explicitly. IGMPv2: Introduced the leave group message, enabling more efficient management of group membership. IGMPv3: Added support for source-specific multicast (SSM), allowing hosts to specify which sources they want to receive traffic from. Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) Overview of PIM Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) is a family of multicast routing protocols that provide efficient routing of multicast packets. PIM is called "protocol independent" because it can operate over various underlying unicast routing protocols. PIM Dense Mode (PIM-DM) PIM-DM is suitable for environments where multicast group members are densely distributed. It uses a flood-and-prune mechanism to build the multicast distribution tree. Initially, multicast traffic is flooded to all parts of the network, and then branches without receivers are pruned back. Flooding: Multicast traffic is sent to all routers. Pruning: Routers without group members send prune messages to stop receiving unwanted traffic. PIM Sparse Mode (PIM-SM) PIM-SM is designed for environments where multicast group members are sparsely distributed. It uses a rendezvous point (RP) to manage group membership and build multicast distribution trees more efficiently. Rendezvous Point (RP): A router that acts as the meeting point for multicast sources and receivers. Join/Prune Mechanism: Routers send join messages towards the RP to indicate interest in a multicast group. Prune messages are sent to stop receiving traffic when there are no interested members. Multicast Border Gateway Protocol (MBGP) What is MBGP? Multicast Border Gateway Protocol (MBGP) extends BGP to support multicast routing. It allows the exchange of multicast routing information between different autonomous systems, ensuring efficient delivery of multicast traffic across the internet. MBGP Functionality MBGP maintains separate routing tables for unicast and multicast routes, ensuring that multicast traffic follows optimal paths. This separation allows for more flexible and efficient routing of multicast traffic, especially in complex network environments. Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) Overview of MSDP Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) is used in conjunction with PIM-SM to enable multiple RPs to share information about active multicast sources. This helps in creating a seamless and efficient multicast routing infrastructure across multiple domains. MSDP Mechanics Source Advertisement (SA) Messages: Used by RPs to announce the presence of active multicast sources to other RPs. SA Caching: Routers cache received SA messages to quickly forward join messages to the appropriate sources. Bidirectional PIM (BIDIR-PIM) What is BIDIR-PIM? Bidirectional PIM (BIDIR-PIM) is a variant of PIM-SM that simplifies the multicast routing process by allowing traffic to flow bidirectionally on a single multicast distribution tree. This approach reduces the complexity and overhead associated with managing multiple unidirectional trees. Advantages of BIDIR-PIM Simplified Tree Management: Single bidirectional tree reduces the need for maintaining separate source-specific trees. Scalability: Better suited for large-scale multicast deployments with numerous group members and sources. Multicast routing is a powerful and efficient method for distributing data to multiple recipients in a network. Understanding the various protocols and mechanisms, such as IGMP, PIM, MBGP, MSDP, and BIDIR-PIM, is essential for designing and managing modern multicast-enabled networks. By leveraging these technologies, network engineers can optimize bandwidth usage and enhance the overall performance of multicast applications. Incorporating multicast routing into your network can significantly improve the delivery of data-intensive applications, ensuring a seamless and efficient user experience. As multicast technology continues to evolve, staying updated with the latest protocols and best practices will be crucial for any communications engineer working in today's dynamic networking landscape. -
- 3138
- SPOTO
- 2024-06-20 15:47
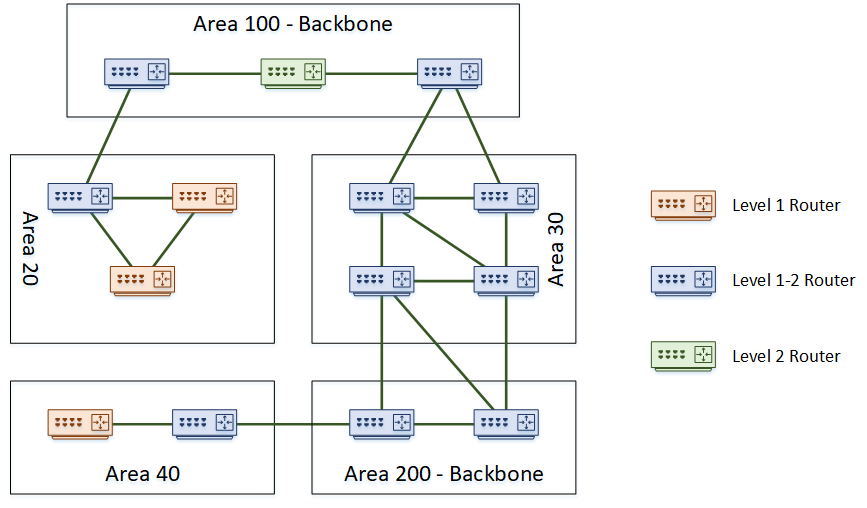
Table of ContentsWhat is IS-IS?IS-IS Network StructureIS-IS Metrics and Path Selection Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) is a powerful and versatile routing protocol that plays a crucial role in the networking world. Originating from the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, IS-IS has become a staple in modern IP routing due to its robust features and adaptability. This blog post explores the fundamental concepts of IS-IS, its operation, and key technical terms to help you gain a comprehensive understanding of this essential protocol. What is IS-IS? IS-IS stands for Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System, a routing protocol designed for moving information efficiently within a computer network, typically within an autonomous system such as a corporate network or an internet service provider (ISP). Unlike many protocols that are derived from the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP), IS-IS originated from the OSI protocol suite, making it a bit unique in its operation and terminology. Key Components of IS-IS Intermediate Systems (IS): These are the routers in the IS-IS network. IS-IS refers to routers as Intermediate Systems, distinguishing between End Systems (ES), which are typically user devices like computers or smartphones. Network Service Access Point (NSAP) Addressing: IS-IS uses NSAP addresses for identifying systems and interfaces within the network. This addressing scheme is more flexible and hierarchical compared to traditional IP addressing. Link-State Protocol: IS-IS is a link-state routing protocol, meaning each router maintains a map of the network and uses algorithms to calculate the best path to each destination. This is in contrast to distance-vector protocols like RIP (Routing Information Protocol). IS-IS Network Structure IS-IS operates by dividing the network into areas. These areas help manage large networks by limiting the scope of routing updates, which improves efficiency and scalability. Areas: The IS-IS network can be divided into multiple areas. Each router belongs to an area, and areas are interconnected by backbone routers that share routing information. Levels: IS-IS supports a two-level hierarchy: Level 1: Intra-area routing. Routers in the same area exchange information. Level 2: Inter-area routing. Routers in different areas exchange information through Level 2 routers. Designated Intermediate System (DIS): In multi-access networks, such as Ethernet, a Designated Intermediate System is elected to manage the communication and reduce the overhead by sending out link-state information on behalf of all routers on that network segment. IS-IS Operation IS-IS routers exchange information using Protocol Data Units (PDUs). There are several types of PDUs, but the most important ones are: Hello PDUs (IIH - IS-IS Hello): These are used to establish and maintain neighbor relationships. Routers send Hello PDUs to identify themselves and discover other routers on the network. Link State PDUs (LSPs): These contain information about the router’s links and are used to build a complete picture of the network’s topology. Each router generates its own LSPs, which are then flooded throughout the network. Sequence Number PDUs (SNPs): These are used to ensure the reliability and synchronization of LSPs. They help routers manage and verify the LSPs they have received. Key Features of IS-IS Scalability: IS-IS is highly scalable, making it suitable for very large networks. Its hierarchical structure and efficient handling of routing updates allow it to perform well in extensive deployments. Flexibility: Originally designed for the OSI stack, IS-IS has been adapted for use with IP, making it versatile and flexible. It supports both IPv4 and IPv6, making it future-proof. Fast Convergence: IS-IS typically converges quickly, which is crucial for maintaining network stability and performance. This means that the network can rapidly adapt to changes, such as link failures or topology changes. IS-IS Metrics and Path Selection IS-IS uses cost metrics to determine the best path to a destination. These metrics can be configured based on various parameters like bandwidth, delay, and reliability. The protocol calculates the shortest path first (SPF) using the Dijkstra algorithm, ensuring optimal routing. Wide Metrics: IS-IS supports both narrow and wide metrics. Wide metrics provide a larger range of values, allowing for more granular control over path selection and better support for modern high-speed networks. Traffic Engineering: IS-IS can be used in conjunction with MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) for traffic engineering. This allows network operators to optimize the flow of traffic through the network based on specific requirements and constraints. Security in IS-IS Security is a critical aspect of modern networks. IS-IS includes several features to enhance security, including: Authentication: IS-IS supports plain text and cryptographic authentication of routing updates. This helps ensure that only legitimate routers can participate in the routing process. Route Filtering: Network administrators can implement route filtering to control the propagation of routing information. This can prevent unauthorized or incorrect routes from affecting the network. IS-IS is a robust, scalable, and flexible routing protocol that plays a vital role in modern networking. Its hierarchical structure, efficient handling of routing updates, and support for both IPv4 and IPv6 make it an excellent choice for large and complex networks. Understanding the fundamental concepts and operations of IS-IS is essential for network engineers and administrators looking to optimize and secure their network infrastructure. Whether you are working in a service provider environment or managing an enterprise network, IS-IS offers the tools and features needed to maintain a reliable and efficient routing architecture. -
- 1786
- SPOTO
- 2024-06-20 15:47
Table of ContentsDevNet Associate Certification OverviewWhat Jobs Can You Get with DevNet Associate Certification?Conclusion In 2026, the networking industry is undergoing rapid transformation. As digital transformation accelerates, the demand for advanced network technology is growing, particularly in the areas of automation, intelligence, and security. Emerging technologies like cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G communication, and the application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in network management are driving innovation and development in the network industry. In this fast-paced environment, cybersecurity professionals need to continuously update their skills and knowledge to keep up with these technological advancements and industry needs. It is within this context that the DevNet Associate certification was introduced. DevNet is a platform launched by Cisco to help network professionals expand their skill set by leveraging network automation, programming, and DevOps practices. DevNet Associate Certification Overview The DevNet Associate certification is a professional credential offered by Cisco that recognizes the expertise of network professionals in network automation, programming, and DevOps practices. This certification focuses on the innovative application of networking technologies, particularly at the intersection of software development and network engineering. The DevNet Associate certification covers not only the fundamental networking concepts, but also the ability to leverage modern tools and frameworks for network automation, enabling professionals to design, build, and maintain more intelligent and efficient network systems. Value of DevNet Associate Certification The DevNet Associate certification provides a platform for network professionals to demonstrate their expertise in the field of network automation and programming. As network environments become increasingly complex, professionals with this certification are able to: Improve employability: Stand out in the job market and attract more employers. Advance your career: Support career advancement or transformation, especially in today's increasingly automated technology landscape. Expand your skills: Deepen your understanding of network automation and programming through the certification learning and exam process. Gain industry recognition: Demonstrate professional abilities and enhance your personal brand value. Adapt to technological change: Stay ahead of the ever-evolving technological landscape and adapt to new job requirements. How to get a DevNet certification To earn the DevNet Associate certification, candidates must pass the 200-901 exam. 200-901 Exam Overview This exam tests a candidate's knowledge of software development and design, including understanding and using APIs, Cisco platforms and development, application development and security, and infrastructure and automation. Exam Code: DEVASC 200-901 Exam Fee: $300 Exam Duration: 120minutes Exam Format: Multiple choice questions Passing Score: 800-850 out of 1000 points (depending on the exam) Exam Topics: Software Development and Design —— 15% Understanding and Using APIs —— 20% Cisco Platforms and Development —— 15% Application Deployment and Security —— 15% Infrastructure and Automation ——20% Network Fundamentals —— 15% Get SPOTO's 200-901 Exam Dumps and Ace the DevNet Associate Certification! What Jobs Can You Get with DevNet Associate Certification? The DevNet Associate certification opens up a variety of career paths, from technology implementation to strategic planning, security analysis to education and training. Here are some of the job roles that you can pursue with this certification: 1. Network Automation Engineer As a Network Automation Engineer, you will be responsible for developing and implementing automation solutions that simplify network configuration and management tasks. This role requires you to apply your programming skills and in-depth understanding of network devices to design efficient automation scripts and tools. 2. DevOps Engineer The rise of a DevOps culture requires networking professionals to have interdisciplinary skills. As a DevOps Engineer, you'll work closely with development teams to enable continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) of network services. The DevNet Associate certification provides you with the foundation you need to communicate and collaborate with developers. 3. Cloud Solution Architect The popularity of cloud computing has provided a new arena for networking professionals. As a Cloud Solution Architect, you will design and deploy cloud-based web services and applications. This role typically requires a deep understanding of cloud platforms and the ability to leverage APIs for automation. 4. Cybersecurity Analyst Cybersecurity is a core concern in today's IT landscape. As a Cybersecurity Analyst, you'll leverage the knowledge and skills gained through the DevNet Associate certification to identify and mitigate cyber threats, ensuring the security of your organization's network. 5. IT Consultant DevNet Associate certified professionals can also become IT consultants, providing consulting services to businesses on network automation and digital transformation. This role requires you to have extensive technical knowledge and excellent communication skills. 6. Technical Trainer If you're passionate about sharing knowledge, consider becoming a technical trainer. Use your certification and experience to provide training and mentorship to other professionals, helping them develop their skills. 7. Product or Solution Sales Engineer In the field of technical sales, professionals with deep technical backgrounds are in high demand. As a Product or Solution Sales Engineer, you will be responsible for introducing and selling network-related products and services to customers. Conclusion In conclusion, the DevNet Associate certification can open up a wide range of job opportunities in the field of network automation and programmability. This credential demonstrates your proficiency in leveraging modern tools and frameworks to design, build, and maintain intelligent and efficient network systems. However, for those seeking higher salaries and more advanced career prospects, pursuing higher-level certifications such as the DevNet Professional or Expert may be beneficial. These more comprehensive certifications can provide a deeper understanding of network automation and programmability, leading to more lucrative roles within the industry. By continually developing your skills and knowledge in network automation and programming, you can position yourself for greater success and growth within the rapidly evolving networking landscape. The DevNet Associate certification serves as a solid foundation, and further advancing your expertise through higher-level certifications can open the door to more specialized and senior-level positions. Ultimately, the DevNet Associate certification is a valuable credential that can significantly enhance your career opportunities. However, it is essential to maintain a commitment to ongoing learning and skill development to stay ahead of the curve in this dynamic industry.