TRUSTED BY THE SMARTEST TEAMS IN THE WORLD FOR CERTIFIED CANDIDATES
SPOTO Blogs
Useful learning materials to become certified IT personnel
-
- 717
- SPOTO 2
- 2026-02-26 14:42
-
- 514
- SPOTO 2
- 2026-02-06 09:52
-
- 583
- SPOTO 2
- 2026-01-26 14:28
-
- 2577
- SPOTOCLUB
- 2025-08-22 15:49
-
- 11158
- SPOTOCLUB
- 2025-08-22 15:33
-
- 511
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-29 15:20
-
- 520
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-24 11:21
-
- 4556
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-24 11:02
-
- 700
- SPOTO 2
- 2025-07-17 14:19
TRUSTED BY THE SMARTEST TEAMS IN THE WORLD FOR CERTIFIED CANDIDATES
SPOTO Blogs
Useful learning materials to become certified IT personnel
-
- 717
- SPOTO 2
- 2026-02-26 14:42
Table of Contents1. Quick overview of core exam information2. In depth analysis of the core changes in the 2026 PMP exam3. 2026 PMP Core Knowledge System (8th Edition Exam Outline)4. Golden Preparation Strategy and Time Planning In July 2026, the PMP exam will usher in the most comprehensive capability upgrade since the launch of PMP certification, with a focus on practical, digital, and strategic transformation from the proportion of exam areas, question design, to core exam points. This guide will provide a detailed explanation of the core changes, preparation focus, and coping strategies of the new version of the exam, helping you fully prepare for this important certification exam. 1. Quick overview of core exam information Implementation time: Global unified launch in July 2026; It is expected that the examination will be officially switched in September and December 2026 in Chinese Mainland, and the current syllabus will still be used on March 14 and June 14 of the first half of the year (1) Basic parameter changes: Number of questions: increased from 180 to 185 (including 10 non scoring prediction questions) Duration: Extended from 230 minutes to 240 minutes (only increased by 10 minutes) Rest time: Provide 2 mandatory 5-minute breaks (after completing questions 60 and 120, respectively). Question type: keep the traditional Single choice question and multiple choice questions, and add interactive questions such as graphic questions, hot topics and matching questions Methodology proportion: Agile and hybrid increased to 60%, traditional predictive decreased to 40% Passing criteria: PMI has not released specific scores and still adopts a binary scoring system of "pass/fail." 2. In depth analysis of the core changes in the 2026 PMP exam (1) Weight reconstruction in three major domains: from technical execution to strategic value Business environment: from 8% to 26% New organizational governance, AI applications ESG, frontier examination points such as financial compliance Focus on examining the alignment between the project and organizational strategy, business justification for value delivery, and risk and compliance management The question type focuses more on"How to use AI tools to optimize project critical paths and enhance business value? " Personnel: from 42% to 33% Simplify traditional team management content, strengthen agile leadership, virtual team management, and cross-cultural communication New modern team management concepts such as psychological safety, team health, and conflict resolution escalation have been added The question type focuses more on real-life decision-making scenarios: "Cross national and cross time zone teams have low morale. As a PM, what is your first reaction?" Process: From 50% to 41% No longer emphasizing process memory, but when/how to tailor processes to balance quality, cost, and delivery speed Strengthen the integration and application of predictive and agile methods, highlighting the practical ability of hybrid project management Add advanced exam points such as large-scale agility, remote agile collaboration, and balance between agility and governance (2) Methodological Revolution: Agile and Blended Becomes Absolute Mainstream The proportion of agile/hybrid methods has increased to 60%, while predictive methods have decreased to 40%, reflecting the comprehensive transformation of the industry from waterfall to agile Add enterprise level agile practices such as large-scale Scrum, SAFe framework, LeSS, etc. Strengthen the key capabilities of agile governance, value stream mapping, and continuous improvement for the integration of agility and organization How to balance customer value and team stability during mid sprint requirement changes (3) Frontier Exam Point Implantation: AI and Sustainable Development Become Essential Learning Content AI application Not focusing on technical principles, emphasizing scenario based applications: AI tools optimize project planning, risk prediction, performance monitoring Examining the practical value of AI in resource allocation, progress prediction, and quality control How to use AI risk prediction models to identify hidden risks in projects? " ESG Sustainable Development Combining ESG framework to analyze the impact of project carbon emissions on costs and green supply chain selection Examine sustainable project management practices, such as circular economy and strategies for achieving carbon neutrality goals Adapt to global corporate social responsibility strategies and enhance the long-term value of projects (4) Innovation in question type: from theoretical memory to practical ability Case analysis question: Based on real business scenarios (smart home development, cross-border team collaboration, digital transformation), it is required to comprehensively apply knowledge from three major fields to solve complex problems Graphic analysis question: Interpret project management tools such as burn out diagrams, RACI matrices, value stream diagrams, risk management matrices, etc., to enhance practical skills Multiple choice question: Shift from "best practices" to "situational adaptation," emphasizing the selection of tailored solutions. 3. 2026 PMP Core Knowledge System (8th Edition Exam Outline) (1) Core principles (6 principles replace 12 old principles) Value oriented: Project decision-making always focuses on delivering business value, balancing short-term outcomes with long-term strategies Embrace adaptability: flexibly choose predictive/agile/hybrid methods to adapt to project complexity and uncertainty Collaboration and Win win: Building a cross functional and cross organizational collaboration network to enhance stakeholder engagement Leading Change: Proactively managing organizational change, promoting the implementation of project results and continuous improvement Risk Intelligence: Integrating risk management into the entire project lifecycle, from passive response to proactive prevention System thinking: Understanding the relationship between projects and organizations, industries, and society, and optimizing overall solutions (2) Detailed content and key exam preparation points in the three major fields In the field of personnel management (33%), the core focus is on leadership, team performance, communication and collaboration, while weakening traditional management functions Leadership behavior adopts servant leadership, motivates the team, empowers and delegates, and resolves conflicts. In terms of team management, virtual team collaboration, multicultural management, agile team building and management, and talent development are utilized. Communication management involves establishing communication strategies and feedback mechanisms for different stakeholders, as well as eliminating communication barriers. Preparation focus: Understand the difference between leadership and management skills, master agile team management methods, and strengthen the practical application of conflict resolution and communication skills. The process management field (41%) focuses on value delivery, covering the entire project lifecycle and emphasizing the flexible application of methodologies. PMP integrates management, including project charter development, benefit management plan, stage checkpoint review, change control, and closure management. Collect requirements in scope management, manage product backlog, control scope boundaries, and map value streams. Focus on progress and cost, agile estimation, value driven prioritization, strategic application of earned value management, and conduct risk identification, qualitative/quantitative analysis, risk response strategies, agile risk dashboard, and continuous improvement of quality cost Preparation focus: Weaken ITTO memory, strengthen methodology selection ability, and master the core indicators and tools of value delivery. The business environment field (26%) has become the "strategic core" of the new exam, examining the ability to connect projects with organizations, markets, and society. Strategic alignment forms the connection between project and organizational strategic goals, business justification development and maintenance, and benefit realization management. Value management involves value identification, value stream optimization, value delivery monitoring, and value realization evaluation. Organizational governance implements project portfolio management, project portfolio management, governance framework application, and compliance management. The integration of external environmental ESG factors, market trend analysis, assessment of technological innovation impact, consideration of geopolitical risks and the application of AI/ML in project management, data-driven decision-making, and integration of digital tools are all key focuses of the exam. 4. Golden Preparation Strategy and Time Planning (1) Division of Preparation Stages (Recommended 4-6 Months) Basic stage (1-2 months): intensive reading of the PMBOK® Guide (8th edition) and Agile Practice Guide, understanding the core concepts and new principles of the three major fields, and establish a project management knowledge system framework. Enhancement phase (2-3 months): Conduct specialized exercises in three major areas, focusing on breaking through the business environment module, doing simulation questions, familiarizing oneself with new question types, and learning cutting-edge content such as AI applications and ESG. Sprint stage (1 month): Conduct a full set of simulated exams, strictly control the time, analyze mistakes, identify and fill in gaps, focus on reviewing business environment and agile content, familiarize oneself with the exam process and rest time arrangements. (2) Recommended Core Learning Resources Official textbook: PMBOK ® Guidelines (8th Edition), Agile Practice Guidelines (2021 Edition), PMP Exam Content Outline (2026 Edition) Supporting materials: PMI Study Hall (updated April 2026), Agile Framework Official Guide. SPOTO boasts abundant learning resources and a professional teaching team. Our experience can help you pass the PMP certification exam more effectively and efficiently on your first attempt. Come and learn more about SPOTO PMP courses! -
- 514
- SPOTO 2
- 2026-02-06 09:52
Table of Contents1. Core framework for value delivery2. Flexible application of prediction, agility, and hybrid methods3. Business environment aligned with strategy4. Integrated practical skills5. Emerging Trends and Compliance Requirements6. Professional ethics and professional qualities The focus of the 2026 PMP (Project Management Professional) exam will shift from "process compliance" to "value delivery," strengthening the application of agile and hybrid methods, and deeply adapting to the project management needs of digital transformation, cross regional collaboration, and sustainable development of European and American enterprises. The following is a detailed disassembly: 1. Core framework for value delivery This is the core theme of the 2026 PMP exam syllabus and also the core standard for European and American companies to measure project success. The project no longer aims to deliver on time and within budget, but rather to create business value. It requires: Identify how to mine the commercial value of projects based on organizational strategic goals Mastering value analysis tools such as cost-benefit analysis, ROI calculation, and stakeholder value proposition research is an essential ability for European and American companies during the project initiation stage. Break down business value into achievable project goals and develop a value delivery roadmap Master the hierarchical decomposition method of WBS to ensure that each work package is aligned with the value objectives Understand the core elements of the project charter, clarify the value boundaries and success criteria of the project. Track the progress of value realization throughout the project lifecycle, and verify the effectiveness of value delivery through stage reviews, user acceptance, and other methods Master the value adjustment mechanism, timely adjust the project scope or delivery priority when market demand or organizational strategy changes, and avoid ineffective work of "delivering the project but not creating value." After the project is completed, conduct a value review to evaluate the gap between the actual value of the project and the expected goals Summarizing experiences and lessons learned, forming organizational process assets, and providing value delivery references for subsequent projects are the core elements of knowledge management in European and American enterprises. 2. Flexible application of prediction, agility, and hybrid methods In the 2026 PMP exam syllabus, the proportion of agile and hybrid methods will increase to 60%, requiring mastery of the core logic and application scenarios of three types of methodologies: Predictive approach: suitable for traditional projects with clear requirements and stable scope. It is necessary to master the complete process of the five major process groups in the project lifecycle. Familiar with key tools such as Gantt chart, critical path method, resource balancing techniques, and risk matrix to ensure project delivery according to plan and budget. Agile methodology: suitable for projects with changing requirements and strong innovation, this is the mainstream methodology in the European and American technology industries. It is necessary to master the core agile framework, understand the core values of agile, as well as scope management, risk management, and stakeholder management in agile. Mixed method: suitable for complex projects of most European and American enterprises. Need to master how to combine the advantages of prediction and agility. Such as phased delivery, agile team embedding predictive project architecture, and dynamic priority adjustment mechanism. 3. Business environment aligned with strategy The 2026 syllabus will increase the weight of the business environment to 26%, emphasizing that projects must serve organizational strategy rather than exist in isolation. You need to understand the logic behind formulating organizational strategies and master how to align project goals with organizational strategic objectives Being able to identify the impact of strategic changes on projects, adjust project direction in a timely manner, and ensure that projects always create value for the organization. European and American project management attaches great importance to the participation of stakeholders. It is necessary to master stakeholder identification and analysis tools, develop targeted communication strategies, manage the expectations of different types of stakeholders, and especially master cross-cultural and cross-border stakeholder communication skills to adapt to the global project scenarios of European and American enterprises. Understand the impact of organizational structure types of European and American companies on projects; Master the core principles of project governance, such as decision-making processes, compliance supervision, and change control mechanisms. Understand the role and functions of the Project Management Office (PMO), and how to leverage PMO resources to drive project success. 4. Integrated practical skills In predictive projects, master the process of scope definition, WBS decomposition, and scope change control. In agile projects, mastering the sorting, prioritization, and control of iteration scope of product to-do lists can enable the development of a reasonable schedule plan based on project characteristics and address the risk of schedule delays. Master project cost estimation methods; Develop a cost budget and implement cost control measures to avoid overspending. Mastering skills in resource planning, allocation, and conflict resolution, especially in coordinating and managing resources across teams and regions, is a high-frequency requirement for remote/distributed projects in Europe and America. Understand the definition of quality and master the tools of quality planning, quality assurance, and quality control. Mastering the entire process of risk management enables the development of proactive risk response strategies, rather than passively responding to risks. Master the method of developing project communication plans and choose appropriate communication channels; Ensure the timeliness, accuracy, and effectiveness of communication. Master the process of procurement management, be familiar with commonly used contract types in Europe and America, and the core requirements of contract compliance. Master the change control process and be able to evaluate the impact of changes on project scope, schedule, cost, and quality. Develop change requests and obtain approval; Mastering the methods of problem identification and resolution, being able to quickly locate the root cause of the problem, develop solutions, and track execution effectiveness, avoiding problem escalation and affecting project delivery. 5. Emerging Trends and Compliance Requirements ESG integration: European and American companies have increasingly strict requirements for sustainable development, and need to master how to integrate ESG principles into the entire project lifecycle. Digitization and AI application: Master the application of digital tools in project management, such as project management software and collaboration tools; Understand the application scenarios of AI technology in project management.. Compliance and ethical standards: Familiar with the core compliance requirements of the European and American markets, such as data privacy protection and industry security standards; Strictly adhere to PMI's Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct for Project Management. Professionals, with core principles including honesty, responsibility, respect, and fairness. This is a mandatory requirement for PMP certification and a core assessment point for recruitment in European and American companies. 6. Professional ethics and professional qualities The four principles of PMI Code of Ethics are honesty, responsibility, respect, and fairness. Leadership and team management skills: able to motivate team members and enhance team cohesion; master conflict management skills to resolve conflicts within or across teams; being able to cultivate the abilities of team members and help the team grow is a key skill for promoting project managers in European and American companies. Summary: The core knowledge system of PMP certification in 2026 is essentially an integrated framework of "value orientation + comprehensive methodology coverage + strategic alignment + practical skills + compliance literacy," which fully meets the core requirements of European and American enterprises for project managers. Not only should one be able to 'do projects,' but also to 'do valuable projects.' -
- 583
- SPOTO 2
- 2026-01-26 14:28
Table of Contents1. The industry gold standard in project management in the United States, with no official endorsement from PMI2. The salary of project management positions is significantly higher, and the competitiveness of certified personnel far exceeds that of unlicensed personnel3. Adapt to the urgent needs of AI+ digital projects in the United States in 2026, and align the exam syllabus with the latest industry trends4. Hard recruitment indicators for American companies are highly recognized by both Fortune 500 and small and medium-sized enterprises5. A cross industry universal competency certificate that adapts to the cross disciplinary/career transition needs of the US workplace6. Connect with local PMI resources in the United States, unlock exclusive job search and networking opportunities7. Strengthen systematic project management skills and bid farewell to scattered work experience8. The basic threshold for promotion in project management in the US workplace is difficult to enter the core promotion channel without a certificate9. Adapt to the trend of remote project collaboration in the United States and fit the actual work scenario10. The certification is long-term and highly value-added, suitable for the long-term career development of the American workplace PMP is launched by PMI in the United States and is an authoritative certification in the field of global project management. It is also a golden certificate for project management talents in the domestic workplace in the United States. In 2026, the deepening of digital transformation in the United States, the large-scale implementation of AI projects, and distributed collaboration will become the norm in the workplace. Coupled with the increasing demand for standardized project management in various industries, the value of PMP has not been diluted, but has become the core lever for American professionals to enter the project management track and achieve career advancement. The following are the top 10 core reasons for obtaining PMP in 2026, which are in line with the actual needs of employment, promotion, and cross industry development in the United States: 1. The industry gold standard in project management in the United States, with no official endorsement from PMI PMP is a certification system developed by the authoritative American organization PMI, which fully conforms to the project management processes and standards of American enterprises. It is recognized as a core endorsement of project management capabilities in the American workplace by 2026. Compared to other niche project management certifications, PMP has an absolute leading position in recognition and credibility in the United States, becoming the primary reference indicator for American companies to judge job seekers' project management abilities. 2. The salary of project management positions is significantly higher, and the competitiveness of certified personnel far exceeds that of unlicensed personnel According to the 2026 US labor market data, among various project management related positions, PMP certificate holders earn 15%-40% more than unlicensed individuals with equivalent work experience. In high paying industries such as technology, finance, healthcare, and high-end manufacturing, this premium ratio will further increase. PMP is widely regarded by American companies as an important reference for salary grading and performance evaluation, and holding a certificate directly becomes a bargaining chip for salary increases in the workplace. 3. Adapt to the urgent needs of AI+ digital projects in the United States in 2026, and align the exam syllabus with the latest industry trends The PMP exam outline for PMI in 2026 has completed a new round of iteration, removing outdated single process management content and adding core content such as AI project management foundation, digital project landing methodology, agile and waterfall mixed management mode, fully meeting the landing needs of AI projects and digital transformation projects in industries such as technology, e-commerce, and fintech in the United States. 4. Hard recruitment indicators for American companies are highly recognized by both Fortune 500 and small and medium-sized enterprises By 2026, over 90% of Fortune 500 companies in the United States will prioritize PMP as a project manager, project coordinator, and product delivery position. Silicon Valley technology companies, Wall Street financial institutions, and healthcare groups will also consider PMP as the "entry threshold" for core project positions. Even for small and medium-sized enterprises in the United States, standardized project management can reduce project failure rates and gradually include PMP in recruitment requirements, making it difficult for unlicensed individuals to enter core project teams. 5. A cross industry universal competency certificate that adapts to the cross disciplinary/career transition needs of the US workplace The core methodology of PMP is not limited to a single industry. In the US market by 2026, PMP certification will be recognized in all fields that require project implementation, including technology, finance, manufacturing, healthcare, e-commerce, real estate, and non-profit organizations. 6. Connect with local PMI resources in the United States, unlock exclusive job search and networking opportunities After obtaining PMP certification, you can join PMI branches across the United States and have access to PMI's official talent pool in the United States, directly matching the recruitment needs of enterprise project management positions. At the same time, it is possible to participate in PMI's offline industry exchange meetings, meet project management practitioners from different fields such as Silicon Valley and Wall Street, and accumulate industry connections in the American workplace. These networking resources are an important help for job hunting and promotion in the American workplace. 7. Strengthen systematic project management skills and bid farewell to scattered work experience The core requirements for project management in American companies are "standardization, replicability, and low risk," while the project experience of most professionals is often scattered and lacks a systematic approach. The PMP preparation process in 2026 can help learners build a complete knowledge system from project initiation, planning, execution to monitoring and closure, master the three mainstream management methods of agile, hybrid, and waterfall in the American workplace, and transform scattered experience into practical and systematic abilities, adapting to the project management process requirements of American enterprises. 8. The basic threshold for promotion in project management in the US workplace is difficult to enter the core promotion channel without a certificate In the career advancement system of American companies in 2026, PMP is the basic threshold for almost all promotion nodes, from junior project coordinators to project managers, project portfolio managers, project directors, and enterprise level project management leaders. Even with years of project work experience, it is difficult to enter the core management promotion channel of American companies without PMP certification, and this rule is particularly evident in large enterprises. 9. Adapt to the trend of remote project collaboration in the United States and fit the actual work scenario By 2026, the proportion of remote projects in the US workplace had exceeded 60%, with cross time zone collaboration, remote team management, and online project delivery becoming the norm. Obtaining the PMP exam can directly master these essential skills and solve the core pain points of remote project management. 10. The certification is long-term and highly value-added, suitable for the long-term career development of the American workplace PMP is not a one-time certification, and renewal can be completed by completing the Professional Development Unit (PDU) required by PMI. There are abundant channels for accumulating PDUs in the United States. In 2026, PMI also launched a specialized certification pathway for PMP holders in the United States, allowing them to seamlessly transition to higher-level certifications after obtaining PMP certification, paving the way for long-term career development. Summary: The PMP application process is in line with American workplace habits and can be completed online throughout the entire process. Pearson VUE test centers are located in major cities in the United States, providing flexible exam times; At the same time, there are abundant PMP learning resources in the United States, so even if you enter the project management track with zero foundation, you can quickly find a suitable learning path. -
- 2577
- SPOTOCLUB
- 2025-08-22 15:49
Table of ContentsWhy Is the PMP Exam So Difficult?What Are the PMP Prerequisites and Costs?How Can You Prepare for the PMP Exam Successfully?Is the PMP Certification Really Worth the Effort?Conclusion The Project Management Professional (PMP)® certification, offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI)®, is widely recognized as the gold standard for project management professionals worldwide. As its reputation for prestige and value grows, so do the questions about its difficulty. For aspiring project managers, the primary concern is often not whether they can earn the credential, but rather, how hard is the PMP exam? The short and honest answer is that it is a rigorous, challenging test that stands apart from many other professional certifications. However, the difficulty is a deliberate feature, designed to protect the integrity and value of the credential itself. This report will provide a definitive, data-driven breakdown of what makes the exam so challenging, what it truly takes to pass, and why the effort is a worthwhile investment in a professional's career. The PMP exam is widely considered one of the hardest professional certification exams due to its complex, scenario-based questions and rigorous time constraints.1 It tests a candidate’s ability to apply project management principles to real-world situations, rather than simply recalling memorized facts.1 With an unofficial failure rate estimated at 40-50% for first-time test-takers, success requires a strategic approach and dedicated preparation.4 To truly understand the PMP exam's difficulty, one must look beyond a simple pass-or-fail metric. It is a multi-faceted challenge that includes stringent eligibility requirements, a significant financial investment, and a unique test format designed to evaluate critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By addressing each of these components, this report will demystify the PMP and provide a clear roadmap for the certification journey. Blog Claim: The PMP exam is a significant but surmountable challenge whose difficulty is a direct reflection of the certification's high value and global recognition. Blog Claim: The PMP exam is a significant but surmountable challenge whose difficulty is a direct reflection of the certification's high value and global recognition. Why Is the PMP Exam So Difficult? The difficulty of the PMP exam is not arbitrary; it is a direct result of its structure, content, and the unique way it evaluates a candidate's abilities. Unlike knowledge-based exams that reward memorization, the PMP is a test of applied wisdom and strategic thinking.3 It is designed to ensure that only those professionals who have an excellent understanding of project management concepts are awarded the certification, maintaining its credibility.7 The PMP exam’s difficulty stems from its focus on applying project management principles to situational scenarios, rather than rote memorization.1 It requires candidates to understand the "PMI mindset," manage time effectively, and overcome mental fatigue.1 This emphasis on practical application is reflected in the high percentage of questions centered on real-world problems. The exam consists of 180 questions that must be answered within a total time of 230 minutes, or just over 1 minute and 16 seconds per question.9 This high-speed environment is a key factor in the exam's rigor, especially as test-takers must contend with the significant mental fatigue that comes from concentrating for nearly four hours straight.1 Two optional 10-minute breaks are provided during the exam, but they do not pause the overall countdown, requiring candidates to manage their time strategically.10 Once a section of 60 questions is completed and submitted, it cannot be revisited.10 This pressure-cooker environment is a key factor in the exam's rigor. The vast majority of PMP questions are situational, presenting a hypothetical project scenario and asking what a project manager should do next.3 The challenge is that multiple answers may seem correct, but only one is considered the "PMI best answer".1 This "PMI mindset" is a core concept that cannot be learned from simple memorization; it is a deep understanding of how PMI principles should be applied in a given context.1 A candidate's ability to discern the single most optimal response from a set of plausible options is what the exam truly measures. A significant shift in the exam content since 2021 is the approximately 50/50 split between predictive (waterfall) and agile/hybrid methodologies.12 This is not just a change in topics; it reflects a fundamental evolution in the industry's best practices. The PMP, once seen as a traditional "waterfall" certification, has adapted to remain relevant in a modern, dynamic business environment. A candidate who fails to prepare for the agile content is essentially preparing for an outdated exam. This signals that the PMP is a living document that evolves with the industry, and staying current with its content outline is non-negotiable for success.14 The exam is structured around three core domains: People (42% of the questions), Process (50%), and Business Environment (8%).9 This focus on "People" and the "Business Environment" reflects a modern emphasis on leadership, communication, and strategic alignment, moving beyond just the technical aspects of project management.13 While PMI does not publish official pass rates, unofficial estimates suggest that 40-50% of first-time test-takers do not pass.4 This statistic alone confirms the exam’s reputation as a formidable challenge. The high failure rate is not a design flaw but a deliberate choice. The exam's structure and questions act as a rigorous filter, ensuring that only highly skilled and dedicated professionals can earn the PMP. This protects the credential's value and makes it a credible signal of expertise to employers who are looking for proficient project managers.1 Sub-heading claims: The exam's difficulty is intentional, designed to test a candidate's practical application of knowledge, critical time management, and ability to handle a high-stakes, high-pressure environment. What Are the PMP Prerequisites and Costs? Before one can even sit for the PMP exam, a specific set of eligibility requirements must be met. These are designed to ensure a foundation of education and real-world experience.16 This is a critical first step, as a significant portion of the challenge is simply qualifying for the exam itself. To qualify for the PMP exam, candidates must have either a four-year bachelor's degree and 36 months of experience leading projects or a high school diploma and 60 months of experience.18 Both paths require a mandatory 35 hours of project management education.17 The experience must be non-overlapping and earned within the last eight years.18 A crucial detail is that PMI no longer requires a specific number of project hours (e.g., 4,500 or 7,500 hours), focusing instead on the number of months leading projects.18 A candidate's application must document this experience and is subject to a random audit.16 The 35-hour training requirement is mandatory for all candidates 19 and can be fulfilled through a formal course offered by a PMI Authorized Training Partner (ATP), a university, or other qualifying training providers.16 A significant benefit is that holding PMI's Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM)® certification automatically satisfies this requirement.17 The costs associated with the PMP are multi-layered and can vary significantly. The most significant costs are for the exam itself and the required training. Type of Fee PMI Member Price Non-Member Price PMP Exam Fee $405 9 $555 23 PMP Re-examination Fee $275 4 $375 4 PMI Membership (1st Year) $164 24 N/A PMI Membership (Renewal) $154 24 N/A 35-Hour Training $45 - $3,000 25 $45 - $3,000 25 A PMI membership costs $164 for the first year, but it reduces the PMP exam fee by $150, making the total cost for a member just $14 more than for a non-member.9 This is a small price to pay for the additional benefits of membership, such as free access to the PMBOK® Guide and other valuable resources.24 The ability to access these resources at no extra cost makes membership a smart, strategic move for almost all candidates. While the costs can be significant, many employers recognize the value of the credential and will reimburse their employees for the exam and study materials.23 The fact that companies are willing to invest thousands of dollars in their employees' PMP journey underscores the credential's direct link to enhanced business acumen and organizational efficiency.28 The PMP's financial and experiential prerequisites act as a primary filter, ensuring a baseline of serious commitment and professional competence before a candidate even attempts the exam. Sub-heading claims: The PMP's financial and experiential prerequisites act as a primary filter, ensuring a baseline of serious commitment and professional competence before a candidate even attempts the exam. How Can You Prepare for the PMP Exam Successfully? With a clear understanding of the exam's difficulty and the prerequisites, the next logical step is to build a winning strategy. The PMP is not a test one can "wing" on experience alone; it requires a disciplined and structured approach to studying.1 Effective preparation for the PMP exam involves a multi-pronged approach: creating a structured study plan (typically 100-200 hours over 2-6 months), using high-quality resources, and taking multiple full-length practice exams to build stamina and identify knowledge gaps.1 A key distinction between the PMP and PMI’s other certifications, such as the CAPM, helps clarify the required preparation. The Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM)® is described as a "knowledge-based exam" that tests fundamental terminology and processes from the PMBOK® Guide.6 In contrast, the PMP is an "experience-based exam" that tests a candidate's ability to handle "real-world project management scenarios".6 This is a vital differentiation because it means the PMP is not about how much is memorized, but rather, how well a professional can apply their knowledge to solve complex problems. Certification Target Audience Prerequisites Exam Focus Exam Difficulty PMP Experienced Project Managers (3-5 years) Bachelor's degree + 36 months experience OR High school diploma + 60 months experience, plus 35 hours of project management education. Applying principles to real-world scenarios (situational) Rigorous and challenging CAPM Entry-level Professionals 23 hours of project management education Foundational knowledge and terminology Less rigorous (knowledge-based) Experts recommend dedicating 100-200 hours of study time for the PMP exam.1 For most working professionals, this translates to 3 to 6 months of consistent, focused effort.30 A crucial part of this is to align one's study plan with the official PMI Exam Content Outline (ECO), which serves as the exam's blueprint and details the weighting of each domain.14 One of the most common reasons for failure is not taking enough practice exams.5 These mock exams are crucial for several reasons: they help with time management 31, build the necessary stamina to sit for nearly four hours 1, and, most importantly, train the test-taker to think in the "PMI mindset" and apply concepts to scenarios.1 Aiming for a score of 75-80% on practice exams is a strong indicator of readiness.31 The path to PMP certification is also littered with avoidable pitfalls.31 One of the biggest is underestimating the agile and hybrid content, which now makes up 50% of the exam.14 Another common mistake is passive studying—simply reading books without active practice.14 Conversely, active learning, such as taking mock exams, engaging in study groups, and applying concepts to scenarios, is repeatedly cited as a key to success.1 This suggests that a higher quality of preparation, not just a higher quantity, directly leads to a higher probability of passing. Sub-heading claims: Strategic, disciplined preparation, anchored by practice exams and a focus on application, is the single most important factor in overcoming the PMP exam's difficulty. Is the PMP Certification Really Worth the Effort? The difficulty of the PMP exam, combined with the time and financial investment, naturally leads to the ultimate question: is it all worth it? The data and industry consensus provide a resounding answer: yes, absolutely.33 The most compelling benefit is the significant increase in earning potential. According to the Project Management Institute (PMI), PMP-certified professionals earn a median salary that is 33% higher than their non-certified counterparts across 21 countries.28 Other sources cite a 25% increase.33 This financial return on investment alone makes the PMP a highly valuable credential. The PMP certification can open doors to new job opportunities and career advancement.33 Many organizations specifically prefer or even require PMP-certified candidates for senior project management roles, making it a direct pathway to more lucrative positions.28 The certification proves a candidate's ability to lead projects in a wide range of industries, from IT and healthcare to construction and finance.34 The value of the PMP is not just in boosting a salary but in maintaining professional viability and access to the most desirable jobs in the field. One source states that "in today's market, it is simply expected that a project manager (especially in senior roles) is PMP certified".34 The PMP is internationally recognized and respected, demonstrating expertise and commitment to the project management profession.9 It serves as a testament to a professional's knowledge, skills, and experience, distinguishing them from their peers in a competitive job market.33 The credential also provides access to PMI’s global network of over 700,000 members, offering unparalleled networking opportunities.28 The PMP exam tests skills across three domains: People, Process, and Business Environment. By requiring mastery in all three areas, the certification ensures its holders can deliver tangible value to their employers, which, in turn, justifies the increased salary and demand for certified professionals.28 Sub-heading claims: The professional and financial rewards of PMP certification are substantial and widely recognized, making the initial difficulty a worthy long-term investment. Conclusion The journey to PMP certification is undeniably challenging, requiring a significant investment of time, money, and mental energy. The difficulty is embedded in the exam's structure, which prioritizes the application of knowledge over rote memorization, and its prerequisites, which filter for experienced and committed professionals. However, as this guide has shown, the rewards far outweigh the costs. The PMP credential is a powerful catalyst for career advancement, providing a substantial increase in earning potential, a wealth of new job opportunities, and global professional credibility. By approaching the exam with a strategic study plan, a firm grasp of the "PMI mindset," and the right resources, the PMP becomes not an impossible hurdle, but a definitive and achievable milestone on the path to project management mastery. External Links Recommendation Project Management Institute (PMI): The official source for all PMP information, including the Exam Content Outline, handbooks, and eligibility requirements.9 Pearson VUE: The authorized provider for PMP exam registration and scheduling.37 A reputable PMI Authorized Training Partner (ATP): For fulfilling the mandatory 35 contact hours of education with verified, up-to-date content.38 Online forums or communities: Such as the Reddit PMP subreddit, where test-takers share real-world experiences, tips, and strategies.1 PMP Exam Simulator or Practice Test Provider: To access full-length mock exams and build stamina and time management skills.1 Referen links: Is it Hard to Get the PMP Certification in 2026? - Project Management Academy Project Management | How Difficult is the PMP® Exam? - DCM Learning Types of PMP® Exam Questions You Can Expect on the Real Test What Happens if You Fail the PMP Exam? (PMI Failure Rate) [2025] What is the PMP exam failure rate? Get updated stats now - iCert Global What is the difference between the CAPM® and PMP® Exam? - The PM PrepCast How Hard Is the PMP Exam and How to Crack in 2026? - KnowledgeHut Just took the PMP exam, ridiculous difficulty - Reddit Project Management Professional (PMP)® Certification | PMI PMP Exam Structure and Breaks: Clarifications Needed! - Reddit Free Top 70+ PMP Exam Questions And Answers Project Management Professional (PMP)® Examination Content Outline – January 2021 - PMI Changes to the Project Management Professional PMP® Exam - Cprime -
- 11158
- SPOTOCLUB
- 2025-08-22 15:33
Table of ContentsWhat Are the Core PMP Exam Fees?How Much Do PMP Prep and Training Materials Cost?Is a PMI Membership Worth the Cost?What is the Financial ROI of PMP Certification?Conclusion The Project Management Professional (PMP)® certification stands as a globally recognized standard for project managers, demonstrating mastery of the people, processes, and business priorities critical to successful project delivery.1 For professionals considering this credential, the financial investment is a primary concern. The question of the exam's cost, however, is not a simple one, as the total financial outlay extends far beyond the singular price of the examination. It is a multi-faceted sum of fees, training expenses, and study materials that collectively represent a significant career investment. The core cost of the PMP certification is divided into a tiered exam fee based on whether a candidate is a member of the Project Management Institute (PMI). The initial exam fee is $405 for PMI members and $655 for non-members. This financial difference is a central consideration, as is the cost of mandatory project management training, which can range from an inexpensive e-learning course to a costly, immersive bootcamp. The true total investment, therefore, is highly personalized and depends on the preparation path a candidate chooses. This report will transition from a high-level overview of the PMP's financial requirements into a detailed, component-by-component breakdown of every potential cost. It will analyze the fees associated with the examination and retakes, evaluate the varied expenses for education and study materials, and perform a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis of PMI membership. Finally, it will present a strong argument for the PMP as a strategic, high-return investment, justifying the initial financial commitment with concrete data on salary and career growth. The cost of PMP certification is not a simple expense but a strategic, high-ROI investment, as the demonstrable return in career advancement and increased earning potential consistently outweighs the initial financial outlay. What Are the Core PMP Exam Fees? The most direct and unavoidable cost of the PMP certification is the exam fee itself. The Project Management Institute, the body that administers the exam, employs a tiered pricing structure that heavily favors its members. This pricing model is a critical element of the certification's financial landscape and one of the first decisions a candidate must make. The cost of the initial exam is $405 for those who hold a PMI membership and a substantially higher $655 for non-members.1 This price difference is not merely a small discount; it is a fundamental aspect of PMI's strategy to incentivize membership. In the unfortunate event of a failed attempt, a candidate must also consider the cost of retaking the exam. The retake fee is also tiered, with PMI members paying $275 and non-members facing a cost of $375 per attempt.3 This re-examination policy allows for up to three attempts within a one-year eligibility window, with a mandatory 30-day waiting period between each failed attempt.3 This policy underscores the importance of adequate preparation. A single failed attempt introduces a significant financial burden of at least $275 to a candidate's total cost, and a second adds another layer of expense, emphasizing that the most cost-effective path is a first-time pass. The decision to invest in quality preparation is therefore not just about learning; it's a financial calculation to mitigate the risk of accumulating additional fees. The table below provides a clear comparison of the core exam fees. Fee Type PMI Member Cost Non-Member Cost Initial Exam $405 $655 First Retake $275 $375 Second Retake $275 $375 The primary financial costs of PMP certification are the exam fees, and a PMI membership offers a clear and immediate financial advantage. How Much Do PMP Prep and Training Materials Cost? The financial commitment to PMP certification extends beyond the exam fee to the mandatory educational component. The Project Management Institute requires that all candidates complete 35 hours of project management education or training before they are eligible to apply for the exam.1 This prerequisite is an essential part of the certification journey and one of the most variable cost factors, with options ranging from highly affordable self-study to premium, instructor-led courses. The most budget-friendly options are typically self-paced e-learning courses. Some providers offer comprehensive packages that satisfy the 35-hour requirement for as little as $30 5 or approximately $350 for a full year of access to an online program that includes an exam simulator and thousands of practice questions.6 These e-learning platforms are a popular choice for self-motivated individuals who can study independently and at their own pace. A candidate can also fulfill the education requirement by enrolling in a PMP bootcamp or live, instructor-led course. These programs offer a more structured learning environment and often come with a higher price tag. Costs can range from $995 to $1,995 for online courses 7 and can exceed $2,995 for intensive virtual bootcamps.9 These higher-priced options often include a guaranteed-to-run schedule, direct access to certified instructors, and extensive study materials. The decision to choose a particular preparation path involves more than just a preference for learning style; it is a form of financial risk management. As a candidate, spending more on a reputable, structured course can be a strategic move to secure a first-time pass. A candidate who opts for a more expensive but comprehensive training program, such as one costing $995 7, may be more likely to pass on their first attempt, thereby avoiding a $375 retake fee and the associated stress and time. In this way, a seemingly larger upfront investment in preparation can ultimately result in a lower total cost of certification. The choice to invest in quality preparation is not about overpaying but about making a calculated decision to save money and time in the long run. The cost of PMP preparation is the most flexible component of the total investment, and choosing the right study method can significantly increase the chances of a first-time pass. Is a PMI Membership Worth the Cost? A thorough analysis of the total cost of PMP certification must consider the value of a Project Management Institute membership. For many candidates, joining PMI is a financially sound decision that delivers benefits far beyond a simple discount on the exam. The first-year PMI membership fee for a professional is $154 plus a one-time $10 application fee, for a total of $164.10 While this is an additional expense, the savings on the exam fee alone typically offset this initial cost. When combining the first-year membership fee with the member-exclusive exam price, the total cost for a member to take the PMP exam is $569 ($164 for membership + $405 for the exam).1 This represents a direct savings of $86 compared to the non-member exam fee of $655.1 This financial advantage is even more pronounced if a candidate needs to retake the exam, as members pay $275 per retake compared to the non-member fee of $375.3 The value of a PMI membership, however, is not limited to these immediate savings. It is a long-term investment that provides continuous access to a vast professional ecosystem. Members receive a complimentary digital copy of the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK®) Guide, which is a foundational resource for the PMP exam.11 They also gain access to a global network of over 700,000 peers, local chapters, and exclusive resources that support career progression and continuing education.12 This access to professional development units (PDUs) and community support is vital for maintaining the PMP credential and staying current in the field. Furthermore, the membership offers substantial long-term savings on the PMP renewal fee, which is $60 for members versus $150 for non-members every three years.11 The decision to join PMI is therefore a strategic financial and professional decision that provides both immediate savings and long-term value, making it a worthwhile investment. The table below provides a comprehensive comparison of the total PMP certification cost for a candidate who chooses the PMI member path versus the non-member path. It synthesizes the data points discussed and offers a clear view of the overall financial outlay. Cost Component PMI Member Path Non-Member Path PMI Membership (First Year) $164 $0 Initial Exam Fee $405 $655 Total Initial Cost $569 $655 Retake Fee (if needed) $275 $375 3-Year Renewal Fee $60 $150 PMI membership is a strategic financial and professional decision that provides both immediate savings and long-term value, making it a worthwhile investment. What is the Financial ROI of PMP Certification? The most compelling argument for the PMP certification is not the cost of the exam but the significant return on investment (ROI) it can provide over a professional's career. The PMP credential is a gateway to increased earning potential, career advancement, and professional credibility. Multiple industry studies confirm a substantial salary premium for PMP-certified professionals. The Project Management Institute’s "Earning Power: Project Management Salary Survey" found that PMP-certified individuals report a median salary that is 33% higher than their non-certified counterparts across 21 countries.14 In the United States, this translates to a median salary increase of $25,000 for those with the PMP.16 This data suggests that the PMP certification is not just a badge but a quantifiable asset that directly contributes to a higher salary. Beyond salary, the PMP certification can unlock a path to more senior and lucrative roles within an organization. A PMP credential can position a professional for high-paying positions such as Project Executive, PMO Lead, or Cybersecurity Project Manager, which often command six-figure salaries.12 These are not entry-level roles; they are positions of leadership and strategic importance that require a proven track record of managing complex projects. The PMP credential serves as a validation of this experience, signaling to employers that a candidate possesses the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in a leadership capacity.13 While some may argue that PMP certification has become a mere baseline requirement for senior project management roles, this perspective only reinforces its value. The PMP acts as a critical filter for recruiters and hiring managers, allowing a candidate to be considered for a higher-paying bracket where salaries are inherently greater due to the complexity and responsibility of the work. Without the PMP, a candidate might be overlooked for these opportunities, regardless of their experience. Thus, the PMP is not just a direct cause of a salary increase but a key that unlocks the door to a higher earning bracket. It demonstrates a commitment to the profession and instills confidence in employers and peers, serving as an asset that contributes to a professional's total value. The PMP is a financially savvy career move that demonstrates a commitment to the profession and leads to increased earning potential and enhanced career opportunities. Conclusion The PMP certification is a significant, multi-faceted investment that extends beyond a singular exam fee. A comprehensive financial analysis reveals that the total cost for a candidate can range from as little as a few hundred dollars for a self-paced e-learning path to several thousand for a premium, instructor-led bootcamp. The single most effective way to reduce the overall financial outlay is to become a member of the Project Management Institute, as the savings on the initial exam fee alone typically exceed the first-year membership cost. This decision also provides access to a wealth of resources and a professional network that are invaluable for career advancement and recertification. Ultimately, the PMP certification is not a simple expense to be minimized but a strategic investment in a professional’s career. The data overwhelmingly supports this view, with certified professionals reporting a median salary that is a substantial 33% higher than their non-certified counterparts. The PMP is a credential that validates a candidate's skills and experience, positioning them for higher-paying, senior-level roles and proving their dedication to the craft of project management. The financial and intangible returns on this investment consistently and demonstrably outweigh the initial costs, making the PMP a wise and essential step for any serious project management professional. External links recomendation Project Management Institute (PMI) Official Website: This is the definitive source for the most current PMP certification requirements, exam fees, and official study materials. Pearson VUE: As the official testing partner for PMP exams, this site is used to schedule, reschedule, and manage all exam appointments. Reputable PMP Training Providers: Authoritative training partners such as Project Management Academy, Simplilearn, or university programs can be consulted for course details, pricing, and schedules. PMI's "Earning Power: Project Management Salary Survey": This document provides the foundational salary data that underpins the PMP's financial value, offering a transparent view of the professional landscape. Reference link: How Much Does The PMP Exam Cost in 2026? What Happens if You Fail the PMP Exam? (PMI Failure Rate) [2025] PMP Certification Requirements 2026: Eligibility, Process, & Exam Guide PMP Exam Prep E-Learning 35 Hour Class PMP® Exam Prep | Boost Your Certification Success - Brain Sensei PMP® Certification Online | PMI Approved PMP Online Training Course - Project Management Academy Payment - Project Management Certification Online at Purdue University PMM800 Project Management Professional (PMP)® Bootcamp - SLU Workforce Center What Is The PMI Membership Cost In 2026 - Gururo PMP Certification Cost: Breaking Down the Cost in 2026 - KnowledgeHut Benefits of PMP Certification & Training in 2026 - Project Management Academy PMP Salary Guide 2024: Earnings, Opportunities & Comparisons - PM Training School Project Manager Salary: Your 2026 Guide - Coursera -
- 511
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-29 15:20
Table of Contents1. What is the PMP certification?2. How PMP certification aids individuals in starting part-time IT careers?3. How to get PMP certified?4. Realistic Earnings: What Can You Make?5. Conclusion Project Management Professional (PMP) certification is a globally recognized qualification signifying a high level of expertise in project management. In today's competitive job market, professional certification is a golden ticket to career advancement and financial success. Among the many certifications available, the Project Management Professional (PMP) certification stands out as a preeminent qualification. Awarded by the Project Management Institute (PMI), the globally recognized PMP certification has become the benchmark for excellence in project management. But what value does this coveted certification bring to professionals? And how can it help them earn a part-time income? This article will provide a deeper understanding of whether the PMP certification is worth pursuing, drawing on real-life examples, real-world data, and practical insights. Let's explore the reasons. 1. What is the PMP certification? The Project Management Professional (PMP) certification, offered by the globally renowned Project Management Institute (PMI), comprehensively validates your knowledge, skills, and experience in project management. It demonstrates your ability to effectively lead and direct projects while ensuring adherence to PMI-advocated project management best practices, processes, methodologies, and professional ethics. 2. How PMP certification aids individuals in starting part-time IT careers? The PMP certification is more than just a line on your resume; it signifies mastery of project management principles, methodologies, and best practices. To qualify for the PMP exam, candidates must possess extensive practical project management experience—at least 4,500 hours of project leadership and direction—as well as 35 hours of formal project management education. The exam itself is rigorous and covers a wide range of topics, including planning, execution, monitoring, and risk management. By earning the PMP certification, professionals can demonstrate to employers their superior skills, strong work ethic, and commitment to delivering successful projects. This level of expertise is highly sought after in industries such as technology, healthcare, finance, and construction, where effective project management is crucial. Real Case Study 1: Leveraging PMP Certification to Generate PMO Part-Time Income Thomas Walenta (Global Project Economics Expert | Ego Hackenheim, Germany): I worked on an 18-month, two-day-a-week project to establish a project management office (PMO). The key was mentoring an inexperienced PMO leader (despite years of experience working on large projects). Most of the work was done on-site, but some was done remotely (for example, writing concepts, presentations, and estimates), with two part-timers involved. Part-time home working is very popular in Germany.A PMP (Project Management Professional) certification demonstrates your comprehensive project management knowledge and practical skills, meeting the core requirements of a PMO within an enterprise. If you hold a PMP and possess expertise in processes, data, and cross-departmental coordination, then a PMO is a career path well worth considering. 3. How to get PMP certified? Passing the PMP exam is no easy feat and requires in-depth study. Below, we'll share tips and practical tips for passing the PMP certification. (1) Comprehensive learning: First, understand the PMP exam content outline, which details the exam tasks, enablers, and knowledge areas covered. Make full use of PMI official resources and high-quality learning materials provided by PMI authorized training partners. (2) Structured training: Take a PMP exam prep course (meet the 35-hour education requirement). These courses provide structured learning content and usually include practice questions and real-life examples. (3) Time investment: Set aside sufficient time for preparation. Most successful candidates report that they invest 150 to 300 hours of study time over a period of 2 to 6 months. Consistent daily or weekly study is more effective than sporadic cramming. (4) Practice exams: Regularly take full practice exams using the SPOTO question bank to familiarize yourself with the exam format, question types, and time limits. Analyze your performance, identify weak areas, and improve your strategies. Aim to achieve a consistent score of 70-80% on practice exams before scheduling the exam. (5) Focus on application: Shift your mindset from rote memorization to understanding how to apply project management principles in a variety of scenarios. The PMP exam places heavy emphasis on situational judgment, requiring you to choose the best course of action. (6) Review the PMI Code of Ethics: Become familiar with the PMI Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct, as ethical considerations are often incorporated into exam questions. Real Case Study 2: How can working professionals use SPOTO's PMP question bank to prepare for the exam efficiently? Neha Bhimrajka is working as a Procurement Category Manager at GPRO Services India Pvt Ltd (Maersk). With 13 years of rich experience across strategic sourcing, procurement consulting, e-procurement, commercial negotiations, stakeholder management, supplier relations, expatriate management, and procurement and sales functions in multiple sectors such as shipping, finance, and retail. He shares: I started studying 5-6 hours a day with dedication. I started with SPOTO's material and the sixth edition of PMBOK a few times to build my foundation. Mock tests are a must. The more mock tests you attempt, the clearer you will get. Mock tests also help you assess the gap between your actual preparation and your goals, which helps you work towards specific improvement opportunities while being more confident in the areas you excel in. It is imperative to attempt the full four-hour test to get an idea of what the actual exam is like. It is imperative to have at least 7-10 days available for mock tests before your scheduled exam. Before taking the exam, I completed all the mock tests provided by SPOTO, covering no less than 3000+ questions. 4. Realistic Earnings: What Can You Make? According to PMI's salary survey, PMP-certified professionals earn significantly more than their non-certified counterparts. In the United States, the median annual salary for PMP-certified project managers in 2022 is $121,000, and annual salaries often exceed six figures depending on industry, experience, and location. In contrast, non-PMP-certified project managers often earn much less, often below the six-figure threshold. Of course, if you simply want to earn a part-time income through PMP certification, this is also a viable path. This article also provides actual salary data based on relevant research. With a PMP certification, your income can vary depending on the type of part-time job you choose. This article provides some examples of potential income opportunities. Online PMP Course Instructor/Training Assistant: $40–$150/hr Freelance Project Manager (PM): $500–$3000/project Project Management Consultant/Process Optimization Consultant: $50–$120/hr Part-time Instructor for In-House Training: ($600–$2000/day Real Case Study 3: Leverage PMP certification endorsement to achieve additional part-time income Giro shared, "I'm a Project Management Professional (PMP) currently working as an Enterprise Architect. My side hustle is proposal writing. I live in a low-income area, but proposal writing is in high demand. I primarily handle responses to government Requests for Proposals (RFPs). I typically work for three to four weeks at a time. My weekly hours are limited to around 10 to 15 hours, as I'm also working a 40-hour shift. My hourly rate ranges from $75 to $150, depending on the complexity of the proposal. It's a good part-time income for me, and I can do it after getting off work, at home, or on weekends. To be honest, I even do a little while I'm at work." 5. Conclusion With project management's growing importance across industries, the Project Management Professional (PMP) certification has become an essential qualification for ambitious professionals. A PMP certification not only enhances your professional capabilities but also offers the opportunity to pursue a side hustle, supplement your income, and thrive in both your primary and secondary careers. SPOTO understands the career aspirations of project managers and the challenges they face in preparing for the PMP exam. Through our professional PMP application agency services, reliable PMP exam question banks, or PMP exam prep services, we can help you quickly obtain the coveted PMP certification. Our dedicated team is ready to provide personalized consultations, answer your questions about the PMP certification, and customize your study plan. We encourage all professionals interested in advancing their project management skills and qualifications to take action now. Act now and take a crucial step in your career development and expand your part-time opportunities with SPOTO's services. Contact us to quickly obtain your PMP certification and embark on a rewarding new chapter in your project management career. -
- 520
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-24 11:21
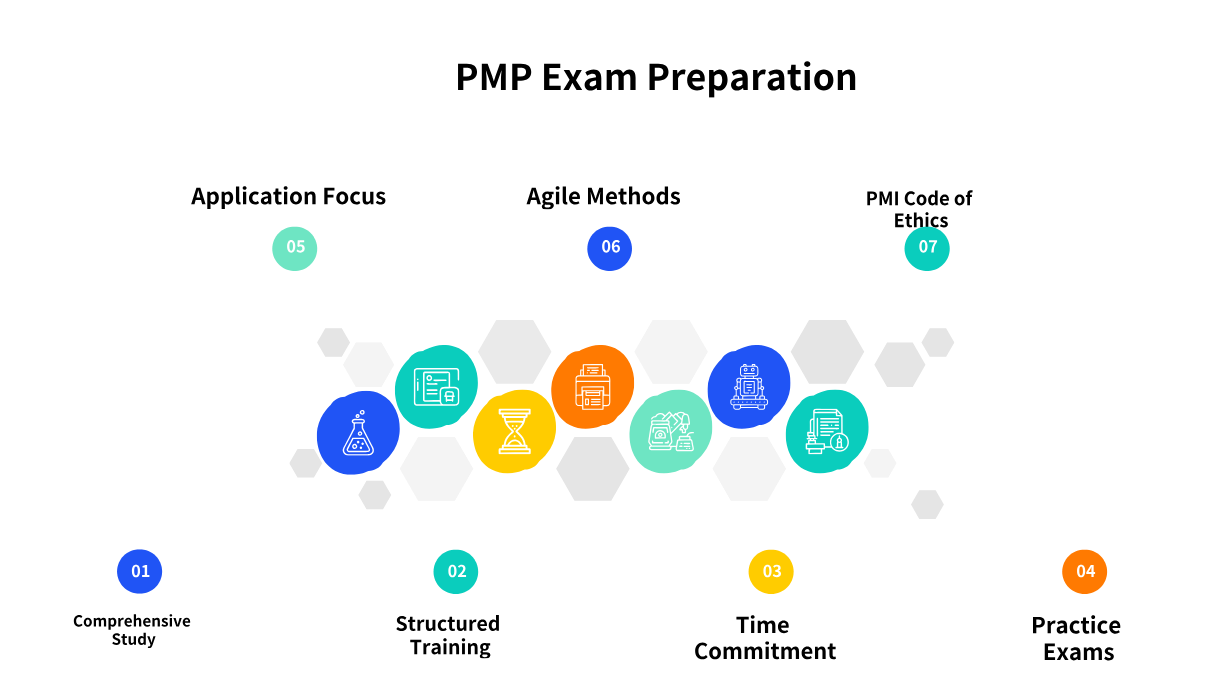
Table of ContentsThe PMP Exam: A Closer Look at Its DifficultyPMP vs. Other Project Management CertificationsStrategies to Conquer PMP Exam Difficulty The Project Management Professional (PMP) certification is a globally recognized credential that signifies a high level of expertise in project management. Many aspiring project managers often wonder about the difficulty of the PMP exam. While it is undoubtedly a rigorous assessment, with the right preparation and mindset, it is an achievable goal. The PMP Exam: A Closer Look at Its Difficulty The PMP exam is designed to test a candidate's comprehensive understanding of project management principles and their ability to apply these concepts in real-world scenarios. Its reputation for difficulty stems from several factors, including its broad syllabus, the application-based nature of its questions, and the stringent eligibility criteria set by the Project Management Institute (PMI). Exam Structure: Questions and Time Limit The PMP exam consists of 180 questions, and candidates are allotted 230 minutes (3 hours and 50 minutes) to complete it. The questions are a mix of various formats, including multiple-choice, multiple-response, matching, hotspot, and limited fill-in-the-blank. The exam includes two optional 10-minute breaks. Successfully navigating this structure requires not only knowledge but also strong time management skills, as the timer runs continuously for the entire exam duration. Average PMP Exam Score and Performance Domains PMI does not publish a fixed passing percentage for the PMP exam. Instead, it utilizes a sophisticated psychometric analysis to determine whether a candidate has passed. Results are reported in terms of proficiency levels across three performance domains: People (approximately 42% of the exam), Process (around 50%), and Business Environment (about 8%). Candidates receive a performance rating of "Above Target," "Target," "Below Target," or "Needs Improvement" for each domain. To pass, candidates generally need to demonstrate overall proficiency, typically achieving "Target" or "Above Target" in most domains. This scoring method emphasizes competency over simply memorizing facts. PMP Exam Pass Rate by Region and Country While PMI does not publicly disclose official global PMP exam pass rates, industry estimates from various training providers suggest that the first-time pass rate for well-prepared candidates typically falls within the 60-70% range. Some estimates indicate a failure rate for first-time test-takers between 40-50%. These figures underscore the exam's challenge, yet also highlight that success is within reach for dedicated individuals. Regional and country-specific pass rates can vary, often influenced by the quality and accessibility of training resources and the maturity of project management practices in those areas. For example, regions with a high concentration of PMI Authorized Training Partners may see higher success rates due to structured preparation. Understanding PMP Certification Requirements The PMP certification has strict eligibility criteria, which in themselves contribute to the perceived difficulty of obtaining the credential. Educational Background: Candidates must possess either a secondary degree (high school diploma, associate's degree, or global equivalent) with 60 months (five years) of non-overlapping professional project management experience, or a four-year degree (bachelor's degree or global equivalent) with 36 months (three years) of non-overlapping professional project management experience. Project Management Education: All candidates are required to complete 35 hours of project management education, which can be obtained through various training programs. This foundational requirement ensures that candidates have a structured understanding of project management principles before attempting the exam. Does PMP Exam Difficulty Vary by Industry? The PMP exam is designed to be industry-agnostic, meaning its difficulty does not inherently vary based on the candidate's industry background. The questions are scenario-based and focus on universal project management principles applicable across diverse sectors like IT, construction, healthcare, and finance. However, a candidate's practical experience in their specific industry can influence how easily they relate to and understand the situational questions. The quality of available training and the emphasis on formal project management within an industry can indirectly affect preparation levels and, consequently, individual success rates. PMP vs. Other Project Management Certifications Comparing the PMP to other project management certifications helps contextualize its difficulty and value. PMP Exam Difficulty vs. CAPM Exam The Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) is another certification offered by PMI, often considered an entry-level credential. Experience Level: The CAPM is geared towards individuals with less or no project management experience, while the PMP requires significant practical experience. Exam Content: The CAPM exam primarily focuses on foundational project management knowledge and memorization of terms from the PMBOK Guide. In contrast, the PMP exam is more comprehensive, featuring a higher proportion of scenario-based and application-oriented questions that require critical thinking and real-world judgment. Rigor: Consequently, the PMP exam is widely considered to be significantly more rigorous and challenging than the CAPM exam. While both require dedicated study, the PMP demands a deeper understanding and the ability to apply complex concepts. Identifying Difficult Topics While individual challenges may vary, many candidates find the application-based and situational questions to be the most difficult aspects of the PMP exam. These questions require more than rote memorization; they demand that candidates analyze a given scenario and apply the most appropriate project management principle or tool. The agile and hybrid methodologies, which constitute a significant portion (approximately 50%) of the exam content, can also be challenging for those with limited practical exposure to these approaches. Questions related to predictive, agile, and hybrid approaches often test a candidate's ability to choose the best method for a given project context. Strategies to Conquer PMP Exam Difficulty The PMP exam's difficulty can be overcome with a structured and dedicated approach to preparation. PMP Exam Study Tips for Beginners For those new to the PMP certification journey, a strategic approach is key to success. Comprehensive Study: Begin by understanding the PMP Exam Content Outline, which details the tasks, enablers, and knowledge areas covered. Utilize official PMI resources and high-quality study materials from PMI Authorized Training Partners. Structured Training: Enroll in a PMP exam prep course (which fulfills the 35-hour education requirement). These courses provide structured learning, often incorporating practice questions and real-world examples. Time Commitment: Allocate a substantial amount of time for preparation. Most successful candidates report dedicating between 150 to 300 hours of study over a period ranging from 2 to 6 months. Consistency in daily or weekly study sessions is more effective than sporadic cramming. Practice Exams: Regularly take full-length practice exams to familiarize yourself with the exam format, question types, and time constraints. Analyze your performance to identify weak areas and refine your strategy. Aim for consistent scores of 70-80% on practice tests before scheduling your exam. Focus on Application: Shift your mindset from memorization to understanding how to apply project management principles in various scenarios. The PMP exam heavily emphasizes situational judgment, requiring you to select the best course of action. Agile and Hybrid Focus: Given the current exam's emphasis, dedicate significant study time to agile and hybrid project management methodologies. Understand their principles, practices, and how they integrate with traditional project management. Review the PMI Code of Ethics: Familiarize yourself with the PMI Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct, as ethical considerations are often woven into exam questions. Required Preparation Time for the PMP Exam The time needed to prepare for the PMP exam varies significantly among individuals, largely depending on their prior project management experience, study habits, and the resources they utilize. Average Time: While some highly experienced individuals may prepare in a shorter timeframe, the consensus among successful candidates suggests an average preparation period of 2 to 6 months. This allows ample time to cover the extensive material, practice questions, and consolidate understanding. Hours of Study: Within this timeframe, the total study hours typically range from 150 to 300. This includes time spent on coursework, reading the PMBOK Guide and Agile Practice Guide, reviewing notes, and taking numerous practice exams. Consistency is Key: Consistent, focused study sessions, even for shorter durations daily, are often more effective than infrequent, long sessions. This approach helps in better retention and understanding of complex concepts. -
- 4556
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-24 11:02
Table of ContentsWhat is the PMP Exam Pass Rate?PMP Exam DifficultyPMP exam pass rate by region and countryFactors Affecting PMP Exam Pass RatePMP exam pass rate vs. other project management certificationsHow to improve PMP exam pass rate The Project Management Professional (PMP) certification, offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI), is a globally recognized credential that signifies expertise in project management. For aspiring project managers, understanding the PMP exam pass rate is a crucial first step in their certification journey. It provides insights into the exam's difficulty and helps set realistic expectations. What is the PMP Exam Pass Rate? The PMP exam is a challenging assessment designed to test a candidate's proficiency across various project management domains. While PMI does not publicly disclose an official global PMP exam pass rate, industry estimates and data from various training providers suggest a general range. Many reputable training organizations report pass rates for their students, often indicating that around 60-70% of individuals who adequately prepare and take the exam successfully pass it on their first attempt. This figure can fluctuate based on the quality of preparation and individual aptitude. PMI PMP certification pass rate The PMP certification is highly sought after, with hundreds of thousands of certified professionals worldwide. As of early 2024, the number of active PMP credential holders surpassed 1.3 million, highlighting the widespread adoption and recognition of this certification. While an exact pass rate from PMI remains undisclosed, the robust number of certified professionals underscores the program's enduring appeal and the achievable nature of the certification with dedicated effort. PMP Exam Difficulty The PMP exam is widely considered a rigorous examination, primarily due to its comprehensive nature and the application-based questions. It evaluates not just theoretical knowledge but also the ability to apply project management principles in real-world scenarios. The exam consists of 180 questions, and candidates have 230 minutes to complete it. PMP exam passing score PMI employs a complex psychometric analysis to determine the passing score for the PMP exam, rather than a fixed percentage. This means the passing score can slightly vary over time to ensure fairness and consistency across different exam versions. Candidates receive a score report indicating their performance in each of the three performance domains: People, Process, and Business Environment. Performance is typically categorized as "Above Target," "Target," "Below Target," or "Needs Improvement." To pass, candidates generally need to demonstrate proficiency across all domains, with a strong performance in the "Target" or "Above Target" categories. There isn't a simple percentage equivalent for the passing score due to the weighted nature of the questions and the psychometric scaling. PMP exam pass rate by region and country While global pass rates are not explicitly provided by PMI, regional and country-specific pass rates can vary based on several factors, including the availability and quality of training resources, cultural approaches to test-taking, and the level of project management maturity within a given region. Regional Differences: Some reports from global training providers indicate slight variations in pass rates across continents. For instance, regions with well-established project management communities and extensive PMP training infrastructure, such as North America and parts of Europe, might see slightly higher average pass rates compared to emerging markets where formal project management training might be less prevalent. Country-Specific Variations: Within continents, individual countries can also exhibit different pass rates. Factors like economic development, educational standards, and the emphasis placed on professional certifications within a country's workforce can influence these figures. For example, some countries with a high number of PMP exam takers often have a developed ecosystem of training centers and study groups, potentially contributing to more consistent pass rates. Factors Affecting PMP Exam Pass Rate Several key factors significantly influence an individual's likelihood of passing the PMP exam. Understanding these can help aspiring candidates strategize their preparation. Quality of Study Materials and Training: Utilizing official PMI resources, reputable PMP exam prep books, and accredited training courses (from PMI Authorized Training Partners) demonstrably increases the chances of success. Data suggests that candidates who complete a structured PMP exam prep course are significantly more likely to pass. Study Hours and Consistency: The PMP exam requires substantial preparation. Most successful candidates report dedicating between 150 to 300 hours of study time over a period of 2 to 4 months. Consistent daily or weekly study habits are more effective than cramming. Prior Project Management Experience: While the PMP exam is not solely based on experience, having practical project management experience helps in understanding and applying the concepts tested. Candidates with more hands-on experience often find it easier to relate to the situational questions. Practice Exams and Mock Tests: Regularly taking full-length practice exams under timed conditions is crucial. This helps in familiarizing candidates with the exam format, identifying weak areas, and improving time management. Many successful candidates report taking 5-10 full-length mock exams. Understanding the PMI Lexicon: The PMP exam uses specific terminology and adheres strictly to the processes and knowledge areas outlined in the PMBOK Guide and other PMI publications. Candidates who immerse themselves in this lexicon tend to perform better. PMP exam pass rate vs. other project management certifications When considering project management certifications, the PMP stands out in terms of global recognition and perceived difficulty, which often correlates with its pass rate. PMP vs. CAPM: The Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) is also offered by PMI and is designed for entry-level project managers. Its exam is generally considered less challenging than the PMP, and consequently, its reported pass rates by training providers are often higher, sometimes reaching 75-85%. This reflects its foundational nature. PMP vs. PRINCE2: PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is another widely recognized project management certification, particularly strong in the UK and Europe. While direct pass rate comparisons are difficult due to differing reporting standards, the PMP is often viewed as requiring a deeper, more comprehensive understanding of project management principles, whereas PRINCE2 focuses more on process and framework. Anecdotal evidence suggests the PMP exam might have a slightly lower pass rate globally compared to PRINCE2 Foundation, while PRINCE2 Practitioner might be more comparable in difficulty to the PMP. PMP exam pass rate vs. first-time pass rate It's important to distinguish between the overall PMP exam pass rate and the first-time pass rate. While the overall pass rate may encompass individuals who have taken the exam multiple times, the first-time pass rate specifically refers to the percentage of candidates who succeed on their initial attempt. First-Time Pass Rate: Industry estimates for the first-time pass rate for well-prepared candidates typically hover around 60-70%. This indicates that while the exam is challenging, a significant majority of diligent candidates can achieve success on their first try. Impact of Multiple Attempts: Candidates who do not pass on their first attempt often learn from their experience, focus on their weak areas, and pass on subsequent attempts. This means the overall pass rate, if it were publicly available from PMI, might be slightly higher than the first-time pass rate, reflecting the persistence of candidates. How to improve PMP exam pass rate Improving your PMP exam pass rate is entirely within your control through strategic and diligent preparation. Enroll in a PMP Exam Prep Course: Taking a 35-hour PMP exam prep course from a PMI Authorized Training Partner (ATP) is highly recommended. These courses are designed to align with the current PMP exam content outline and provide structured learning. Master the PMBOK Guide and Agile Practice Guide: These are foundational texts. While not every detail needs to be memorized, a thorough understanding of the concepts, processes, and tools/techniques is essential. Focus on understanding the "why" and "how" behind the principles. Utilize Diverse Study Resources: Supplement your primary study materials with online forums, study groups, flashcards, and video lectures. Diverse resources can help clarify complex topics and reinforce learning. Practice, Practice, Practice: Take as many practice questions and full-length mock exams as possible. Aim for scores of 70-80% on practice tests before attempting the actual exam. Analyze your incorrect answers to understand the underlying concepts. Focus on Agile and Hybrid Methodologies: A significant portion of the current PMP exam (approximately 50%) covers agile and hybrid approaches. Ensure you have a strong grasp of agile principles, frameworks (Scrum, Kanban), and how they integrate into project management. Develop Strong Time Management Skills: During practice exams, work on your pace to ensure you can complete all 180 questions within the 230-minute time limit. Learn to quickly analyze situational questions and select the best answer. Simulate Exam Conditions: Take your final mock exams in an environment that mimics the actual testing center as closely as possible – quiet, uninterrupted, and timed. Understand PMI's Professional Responsibility: Familiarize yourself with the PMI Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct, as questions related to ethical considerations are often included. -
- 700
- SPOTO 2
- 2025-07-17 14:19
Table of Contents1. What is PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification?2. Benefits of having PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification3. Details of the PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification4. What Are the Qualifications to get a PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification?5. How much does it cost to pass the PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification?6. Similar certifications of PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification This article will introduce you to what a PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification is, the details information of PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification and the necessary conditions to get a PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification. By reading this article, you will gain an in-depth understanding of the PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification. 1. What is PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification? PMI Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP® ) is a professional certification launched by the Project Management Institute (PMI) that focuses on agile practices. It aims to verify the comprehensive ability of the holder to apply multiple agile methods in agile project management. It is one of the most influential certifications in the agile field worldwide and is suitable for all practitioners who participate in or lead agile projects and teams. The PMI Agile Certified Practitioner is different from the certification of a single agile framework. It emphasizes "universal practices across agile methods" and focuses on the flexible application of agile principles in different scenarios, rather than mechanically applying a certain framework. The core goals of the PMI Agile Certified Practitioner are to establish unified standards for agile practices, covering core elements such as agile values, teamwork, iterative delivery, and continuous improvement, and to prove that the holder has the ability to choose appropriate agile methods in complex projects and balance agile flexibility and project constraints; to help organizations identify professionals who can effectively promote agile transformation and coordinate agile teams with business goals. 2. Benefits of having PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification PMI-ACP® is a certification launched by PMI that complements PMP. PMP focuses on integrated management, while PMI-ACP® focuses on agile practices. It has a high degree of global recognition and is highly recognized in multinational companies, IT, Internet, software development and other fields. PMI-ACP® covers a variety of agile methods, proving that the holder can choose the most appropriate practice based on the characteristics of the project rather than being limited to a single framework. With the development of enterprises, the demand for agile talents continues to grow. PMI-ACP® is an important plus for job hunting and promotion, especially in organizations undergoing agile transformation. Certified holders are more likely to obtain management positions, which can help job seekers or existing workers who hope to further develop their work have more career options. This certification has a high degree of practical guidance. The preparation process can systematically sort out agile principles and tools to help practitioners solve practical problems. 3. Details of the PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification The PMI-ACP® exam lasts a total of 3 hours, with 120 multiple-choice questions. Candidates can choose to take the online computer test at home or at a designated test center through Pearson VUE's OnVUE platform or take the offline written test at an authorized test center in some regions. The exam content is based on PMI's "Agile Practice Guide," covering 7 major knowledge areas, with a total score of 200 points and a passing score of 150 points. "Pass/Fail" will be displayed immediately after the exam, and the detailed score report can be checked on the PMI official website about 5 working days later. The exam focuses on modules such as agile principles and thinking, value-driven delivery, stakeholder participation, team performance, adaptive planning, problem discovery and resolution, and agile practice tools. 4. What Are the Qualifications to get a PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification? (1) Submit an application Fill out the online application on the PMI official website and upload project experience certificates, training certificates and other materials. The review period is about 5-10 working days. (2) Pass the exam After passing the review, make an appointment for an online or offline exam at the Pearson VUE test center. PMI uses a standard score system and requires a score of 150 or above to pass. (3) Maintain certification The certification is valid for 3 years. Within 3 years, you need to accumulate 30 professional development units and pay a renewal fee of US$150. 5. How much does it cost to pass the PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification? The initial registration fee for the PMI-ACP® exam is $435 for PMI members and $535 for non-PMI members. To become a PMI member, you need to pay an additional annual fee, which is $139/year globally, and $39/year for student members. Members can enjoy discounts on exam fees and other resource benefits. If you fail the first exam, you can retake it within 1 year of the registration validity period: PMI members will spend $250 and non-PMI members will spend $375. In addition, the PMI-ACP® certification requires candidates to complete at least 21 hours of agile training. The training fee varies depending on the institution, course format and region, usually between $500-1500. The certificate is valid for 3 years. When renewing the certificate, you need to pay a renewal management fee of $150 and accumulate 30 professional development units. 6. Similar certifications of PMI Agile Certified Practitioner certification ICAgile Certified Professional (ICP) Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) SAFe Agilist (SA) AgilePM Foundation