TRUSTED BY THE SMARTEST TEAMS IN THE WORLD FOR CERTIFIED CANDIDATES
SPOTO Blogs
Useful learning materials to become certified IT personnel
-
- 381
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-25 11:16
-
- 280
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-25 10:33
-
- 300
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-24 16:31
-
- 286
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-24 15:49
-
- 446
- SPOTO 2
- 2025-07-24 14:56
-
- 395
- SPOTO 2
- 2025-07-24 14:48
-
- 169
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-24 11:21
-
- 297
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-24 11:02
-
- 58
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-23 17:33
TRUSTED BY THE SMARTEST TEAMS IN THE WORLD FOR CERTIFIED CANDIDATES
SPOTO Blogs
Useful learning materials to become certified IT personnel
-
- 381
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-25 11:16
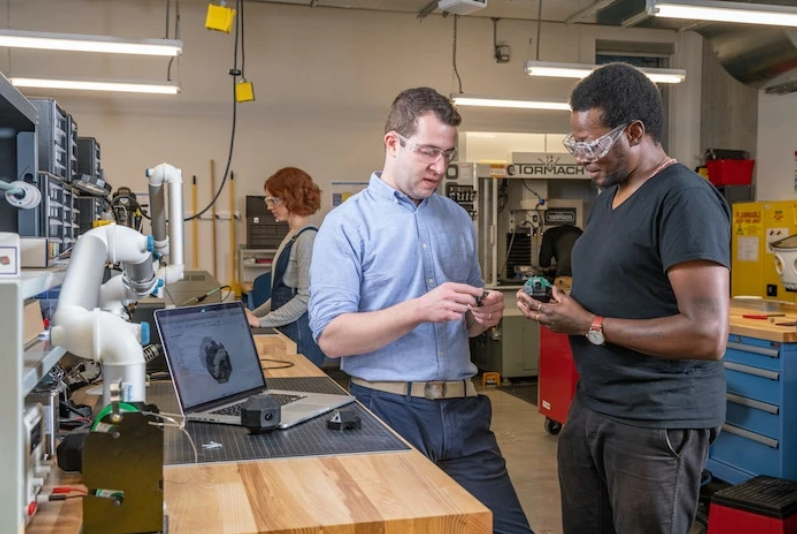
Table of Contents1. What are the primary responsibilities of a data center network engineer ?2. Why do you want to become a data center network engineer? What are the salary and career prospects?3. How to become a data center network engineer4. What certification is helpful in becoming a data center network engineer? With the rapid advancement of global data center construction and AI and cloud computing placing higher demands on network performance, data center network engineers will continue to be in short supply. Data center network engineers are professional technicians responsible for the construction, maintenance and implementation of data centers. They assist in maintaining the normal operation of enterprise infrastructure and play a multifaceted role in the daily operations of a unified network operation center (NOC). 1. What are the primary responsibilities of a data center network engineer ? The work of data center network engineers mainly revolves around the storage, use and maintenance of data resources in data centers. First of all, Data center network engineers are professional technicians responsible for the construction, maintenance and implementation of data centers. They assist in maintaining the normal operation of enterprise infrastructure and play a multifaceted role in the daily operations of a unified network operation center (NOC). They provide wide area network/local area network (WAN/LAN) network services, monitor the normal operation of data network infrastructure, and take into account customer satisfaction and regulatory compliance. Secondly, it is necessary to perform complex cross-departmental cooperation, lead the technical design and evaluation of various infrastructure projects, and serve as a senior technical resource to recommend appropriate technical designs and solutions that meet business needs and enterprise technology strategies. Finally, evaluate and implement the design of wide area network/local area network (WAN/LAN) architecture, supervise the operation of the organization's network, and recommend modifications to the network configuration based on cost-effectiveness. What skills are required to fulfill the above job responsibilities and become an excellent data center network engineer? The skills that data center network engineers need to have include the following aspects, mainly data management and infrastructure skills. Specifically, data center network engineers need to master programming language skills, including Python, Java, and C++. Secondly, proficiency in the use of big data tools is also one of the necessary skills, including Hadoop, Spark, Kafka, and Hive. Finally, because data center network engineers need to be able to manage databases, data center network engineers usually need to be proficient in data center infrastructure hardware, such as Nexus 5500/5000/3500, Fabric Extenders, F5 ADC, UCS Chassis, and UCS Fabric Interconnects. 2. Why do you want to become a data center network engineer? What are the salary and career prospects? The employment prospects of Data Center Network Engineers have continued to improve in recent years, driven by multiple factors such as the explosive growth of global data, the popularization of cloud computing, and the development of artificial intelligence. According to Statista 2024 data, the number of data centers in the world has exceeded 8,000, with the United States, China, and Germany ranking in the top three, and major cloud vendors (Alibaba Cloud, Huawei Cloud, AWS, Azure) are adding or expanding multiple hyperscale data centers (Hyperscale DC) around the world every year. At the same time, data center network engineers can not only work in large Internet companies, but also have a wide range of employment fields, including the financial field, cloud technology service providers, telecommunications operators, and government departments. This position will continue to be in high demand in the next 5-10 years. Those with CCNP Data Center, automated programming, virtualization and other capabilities will become high-quality talents in the job market. The average annual salary for a Data Center Network Engineer in the United States is $147,461. That works out to about $70.89 per hour. That works out to $2,835 per week or $12,288 per month. The highest earners in the country can make up to $196,000 per year. The average salary range for a Data Center Network Engineer varies greatly (as much as $112,000), which means there may be many opportunities for advancement and increased pay based on skill level, location, and years of experience. 3. How to become a data center network engineer The first step to becoming a data center network engineer is to have a bachelor's degree in computer science, data science, or a related field. It is worth noting that an advanced degree can further enhance your prospects and hopefully help you enter larger businesses and organizations. Secondly, gain practical experience through work or practical experience. Internships, freelance projects, or entry-level positions in data management can develop your practical skills. The improvement of practical skills can help you better get an offer from your favorite company. Secondly, get authoritative certification to help your internship and skills recognition. Professional certification can prove your professional skills and help you break through the application. Finally, data center network engineers also need to continue learning, because the field is developing rapidly, and it is crucial to keep up to date with new tools, frameworks, and best practices. 4. What certification is helpful in becoming a data center network engineer? CCNP Data Center certification is of great significance to those who want to become data center network engineers. It is not only a strong proof that you have mastered the core data center network technology, but also a "stepping stone" to enter this high-end technical position. Through the study and examination of CCNP Data Center, you will systematically master a set of skills closely related to modern data centers, such as Cisco Nexus switch configuration, VXLAN/EVPN virtual network technology, high-availability architectures such as vPC and FabricPath, Cisco UCS server integration, and data center automation deployment. Therefore, certification not only improves your practical operation ability, but also greatly enhances your competitiveness in the workplace. CCNP Data Center also lays a solid foundation for your future development to a higher level (such as network architect, cloud network engineer, data center technology director, etc.). -
- 280
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-25 10:33
Table of Contents1. What is an IT Service Manager? And what are the responsibilities of an IT Service Manager?2. Skills needed for an IT Service Manager3. IT Service Manager vs IT Project Manager4. IT Service Manager salary expectations5. Job Outlook for IT Service Managers6. What certification is helpful in becoming an IT Service Manager? With the increasing popularity of digital technology and computer technology in the office field, the workplace has become technology-dependent, and the maintenance and upgrade requirements of network infrastructure are getting higher and higher. Therefore, the necessary infrastructure needs to be properly installed, configured and maintained by professional technicians so that enterprises, organizations and companies can operate efficiently. In all these activities, IT Service Manager plays an indispensable role. This article will introduce you to the profession of IT Service Manager, as well as the employment prospects and key skills required for this profession. If you are interested in this profession, please continue reading. 1. What is an IT Service Manager? And what are the responsibilities of an IT Service Manager? IT Service Managers are professionals responsible for designing, delivering, managing, and improving the delivery of information and communications technology (ICT) services within an organization. Their job is to ensure that IT services meet business objectives, meet customer expectations, and operate efficiently and securely. In addition to dealing with technical issues, IT Service Managers are also responsible for overseeing service delivery, managing supplier relationships, designing service strategies, and participating in strategic planning. Whether managing cloud services, network infrastructure, cybersecurity measures, or end-user support, IT Service Managers ensure that technology supports broader business initiatives. Specifically, their job responsibilities focus on the following areas: The IT Service Manager needs to analyze the needs of their organization in terms of computer systems, determine the short-term and long-term personnel IT needs of their respective departments, and recommend possible upgrades to senior management. Secondly, the IT Service Manager needs to keep abreast of new technologies and upgrade the organization's computer systems, plan and be responsible for the installation and maintenance of computer software and hardware, and determine the best suppliers to obtain the highest quality services to meet the technical needs of their organization. Ensure that the organization's electronic documents are protected from cyber attacks. At the same time, the IT Service Manager also needs to be able to evaluate new projects from a cost and benefit perspective and explain the source of funds to management. Carry out division of labor within the team and between departments, plan and assign work to other IT professionals, such as computer support specialists, information security analysts, computer system analysts, and software developers. 2. Skills needed for an IT Service Manager First, IT Service Managers need to have technical knowledge in the IT field, including familiarity with network infrastructure, cloud services, network security, and ITIL framework. Second, IT Service Managers need to have leadership, communication, and problem-solving skills so that they can coordinate teams and clearly communicate technical concepts to quickly resolve problems and implement effective solutions. Finally, IT Service Managers need to have excellent project management skills and be able to effectively plan, execute, and monitor projects. Prioritize user satisfaction and align services with business needs. 3. IT Service Manager vs IT Project Manager IT Project Manager is the go-to for completing specific tasks on time. You have a start date, an end date, and clear goals. Whether you are implementing new software, migrating IT systems to new servers, or updating database systems, IT Project Management provides a framework to ensure that projects proceed smoothly. IT Project Managers are responsible for not only managing the planning of the tasks themselves, but also coordinating communications between the project team and stakeholders. The framework is designed to develop clear timelines and set clear, rapid goals to achieve a single goal, which is usually completed quickly. IT Service Manager focuses on IT Service Management (ITSM), a framework designed to continuously create value through the effective management of IT services. Unlike traditional IT Project Management, which focuses on completing specific tasks, ITSM is committed to continuously improving IT services to meet business needs. By following ITSM best practices, organizations can not only ensure that their IT services are reliable, but also that they are continuously updated to meet changing business needs. 4. IT Service Manager salary expectations The average annual salary for an IT Service Manager in the United States is $104,084. This is $2,001 per week or $8,673 per month. The highest earners can make $150,000 per year. The average salary range for an IT Service Manager varies greatly (as much as $46,500), which suggests there may be many opportunities for advancement and increased pay based on skill level, location and years of experience. 5. Job Outlook for IT Service Managers The job outlook for IT Service Managers is generally positive. On the one hand, technology is driving huge changes in the workplace. Unlike in the past, more and more companies and businesses are turning to information systems to improve operational efficiency. Although the advancement of technology may replace people to a certain extent and eat up certain jobs, the number of jobs for IT Service Managers who cater to the development of information technology and maintain the operation of corporate networks is increasing. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) predicts that the demand for IT Service Managers will increase by 15% from 2014 to 2024. Another major reason for the increase in demand is the increasing possibility of security threats. In fact, cybersecurity has become a major topic of discussion for companies that use information systems. Therefore, the possibility of increased cyber threats will only prompt companies to seek the professional services of information system managers. 6. What certification is helpful in becoming an IT Service Manager? CCNP Service Provider (Cisco Certified Network Professional for Service Providers) is a certification that is biased towards the technical field. It has very practical value for those who want to become or already serve as IT Service Managers. CCNP SP certification covers core technologies such as MPLS, BGP, QoS, and service provider network architecture, which are the key network foundations that many companies rely on daily. Mastering this knowledge can not only help you understand the network architecture and root causes of failures more deeply, but also promote problem solving more professionally and efficiently when encountering service interruptions, network performance problems, or supplier coordination. Therefore, it is recommended that IT service managers apply for CCNP Service Provider, which is not only an effective way to improve their own technical literacy and cross-team communication skills, but also an important step to build the ability to integrate technology and management and achieve career breakthroughs. Combined with management and general skills learning such as ITIL, cloud computing, and automation, it will greatly enhance your comprehensive competitiveness and future development potential. -
- 300
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-24 16:31
Table of Contents1. What is a Network support engineer ?2. What does a network support engineer do day-to-day?3. Average salary of a network support engineer.4. What is the job outlook for network support engineers?5. How to become a network support engineer?6. Essential certifications for network support engineers. 1. What is a Network support engineer ? Network support engineers are IT specialists responsible for designing, setting up, and maintaining corporate computer networks. They play a key role in keeping businesses connected, secure, and operational. Network support engineers are responsible for troubleshooting technical issues, monitoring system performance, and providing user support to ensure uninterrupted access to network services. In addition, they collect data from systems, routers, and other hardware to build and manage a fully operational network. 2. What does a network support engineer do day-to-day? Network support engineers play a key role in technical support and network management in the enterprise. Their responsibilities cover network maintenance, project management, and cross-departmental collaboration. Not only do they need to quickly provide backup solutions and troubleshooting support when a network failure occurs, they also need to conduct post-analysis of system failures and write trend reports to improve network stability and prevent future risks. At the same time, engineers are responsible for formulating proposals, identifying and assisting in the implementation of cost optimization strategies, and ensuring the efficient use of network resources. In addition, they also need to maintain paperwork related to network implementation, assist other departments in solving local technical problems, and coordinate with different departments to promote smooth Linux network design and operation. On the technical level, network support engineers must comprehensively manage the technical resources of the project and the enterprise, ensure that technical support services are always maintained at the best level, and provide professional consultation to customers when necessary to promote the timely and high-quality completion of the project. 3. Average salary of a network support engineer. The average annual salary for a network support engineer in the United States is $92,475, which is equivalent to approximately $44.46 per hour, $1,778 per week, and $7,706 per month. 4. What is the job outlook for network support engineers? The job outlook for network support specialists is bright and strong. According to statistics from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, overall employment of network support specialists is expected to grow 6% from 2023 to 2033, faster than the average growth rate for all occupations. It is expected that network job openings will average about 62,700 per year over the next decade. 5. How to become a network support engineer? First, you need to obtain a relevant degree and gain practical experience. Most network support engineers have a degree in a computer-related field, such as computer science or information technology. A solid academic foundation in STEM subjects (especially mathematics, computer science or physics) is essential to a career in network support engineering. Secondly, develop practical skills through technical training. Practical skills are essential to being competent for the job. For network support engineers, technical ability is not limited to theory, but also to apply knowledge in practical environments. Through practical training projects, experiments and simulations, you will gain critical experience in configuring network equipment, troubleshooting connection problems, and managing wired and wireless systems. Then, seek career opportunities in network support engineering to add to your work resume. Network support is a dynamic career development direction, and demand is growing in all walks of life. As companies rely more and more on powerful IT infrastructure, skilled professionals who can ensure network security, reliability, and high performance are essential. 6. Essential certifications for network support engineers. If you want to become a network support engineer but don't know what certificate to take, we recommend you to take the CCIE Service Provider certification. It is one of Cisco's top expert-level network certifications, focusing on providing high-performance, scalable, and highly available network solutions for telecom operators, ISPs (Internet service providers), large backbone networks, and cloud service platforms. For network support engineers who want to develop in this field, CCIE SP is a valuable "pass" that not only improves technical depth, but also significantly enhances professional competitiveness. -
- 286
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-24 15:49
Table of Contents1. Define Wireless Network Engineer2. Skills required for a Wireless Network Engineer3. How to become a Wireless Network Engineer4. What are the career prospects and salary of a wireless network engineer?5. Certifications for Wireless Network Engineers 1. Define Wireless Network Engineer Wireless network engineers are IT professionals who are responsible for designing, implementing, managing and troubleshooting wireless networks and wireless infrastructure. They specialize in wireless communication technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks and other radio frequency (RF)-based systems, maintain and optimize wireless networks and wireless network infrastructure, and solve potential and existing wireless network problems. Wireless network engineers are responsible for designing, deploying, managing, and optimizing wireless network systems to ensure that the network operates efficiently, securely, and stably, including managing firewalls such as Palo Alto, Juniper, or Cisco ASA. First, they use a variety of tools and techniques, such as network performance indicators (NPI), network scanning tools, SNMP, traffic analyzers, packet sniffers, and wireless site surveys, to test, evaluate, and troubleshoot network problems, and model network designs through simulation before deployment. Second, wireless network engineers need to work closely with vendors, enterprise managers, and other network engineers to participate in the planning and improvement of the network from project initiation to implementation to ensure that the business needs of customers are met and the optimized performance of VoIP and other wireless telecommunications equipment is ensured. Third, they are also responsible for configuring and managing various network devices, such as routers, switches, and firewall devices (such as Palo Alto, Juniper, and Cisco ASA). In addition, engineers also need to have radio frequency (RF) link design and verification capabilities to support the construction and optimization of WLAN and other wireless networks, and test and debug network equipment to achieve real-time monitoring and optimization of network performance. In addition, they are also required to write technical documentation, train other employees, and develop data backup and recovery strategies to ensure data integrity and reliability. Finally, the rules of the networking world change over time, and wireless network engineers also need to have a broad understanding of routing protocols (OSPF, EIGRP, and BGP). 2. Skills required for a Wireless Network Engineer The prerequisite for becoming an excellent Wireless Network Engineer is to have the skills required for this profession. As a Wireless Network Engineer, you need to have solid wireless network skills and knowledge. Specifically, wireless network engineers need to understand TCP/IP, including expertise in IP addressing, subnet division, and routing protocols such as OSPF and BGP, because Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is the basis of the Internet and most network infrastructure. Secondly, one of the core tasks of wireless network engineers is to maintain the security and stability of the organization's wireless network, so troubleshooting skills are one of the essential skills. Engineers must be proficient in using diagnostic tools such as packet analyzers, network performance monitors, and configuration management software to ensure smooth network operation. For example, use network monitoring tools to detect and solve potential problems before they worsen. It is worth noting that although technical skills are essential, wireless network engineers must also have excellent customer service capabilities. Engineers often work with customers or internal employees to provide them with necessary support for hardware, software, and network-related issues. Finally, skills such as network infrastructure design and router configuration and management are also important. Wireless network engineers must constantly understand the updates of technology so that the organization's network system and infrastructure can be updated and improved in a timely manner. However, with the emergence of software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) DevOps, the emergence of 5G, and the emergence and application of new technologies such as virtualization and cloud technology, it is necessary for wireless network engineers to receive new skills training as this may bring changes to the way they operate. 3. How to become a Wireless Network Engineer It usually takes 2 to 5 years to become a wireless network engineer, depending on your starting point and education path. Here is a brief breakdown: First, becoming a wireless network engineer requires a certain level of education, with a science degree in computer science often favored by employers. It may take 2 to 4 years to obtain an associate or bachelor's degree in computer networking, information technology, or a related field. Second, industry-recognized certifications can make your resume stand out, and industry-recognized certifications can be obtained in a few months to a year, usually at the same time or after formal education. Finally, having the right work experience in the workplace can make you more likely to get a job, and entry-level IT positions (such as help desk, network technician) provide the practical experience needed to advance to wireless network positions. This may take 1 to 3 years, depending on the content of the work and development opportunities. 4. What are the career prospects and salary of a wireless network engineer? The job outlook for wireless network engineers is expected to be very strong in the future. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of wireless network engineers is expected to grow 5% from 2019 to 2029, faster than the average for all occupations. The average annual salary for a senior wireless network engineer (CCNP certification) is about $87,772 to $106,566. The hourly wage for freelancers is only $24.57. Of course, the salary of a wireless network engineer is also affected by many other factors, such as work location, work experience, etc. 5. Certifications for Wireless Network Engineers CCIE Enterprise Wireless is an expert wireless network certification launched by Cisco. It is one of the most valuable technical certifications in the career of wireless network engineers. For professionals who want to become senior wireless network engineers or have deep capabilities in enterprise wireless network design, implementation and optimization, this certification can make people who obtain this certification stand out in job hunting and easily enter large multinational companies, governments, universities, medical and other high-end industries. It is also the recruitment threshold or priority condition for many senior positions in enterprises (such as wireless architects, senior network engineers, and technical consultants). -
- 446
- SPOTO 2
- 2025-07-24 14:56
Table of Contents1. What is Certified Information Privacy Professional certification?2. Global recognition of CIPP certification3. Benefits of CIPP certification4. CIPP vs CIPT certification 5. Alternative certifications like CIPP certification This article introduces the Certified Information Privacy Professional (CIPP) certification. Discover what the CIPP entails, its key details, and the eligibility criteria required to obtain it. Gain an in-depth understanding of the CIPP certification through this guide. 1. What is Certified Information Privacy Professional certification? Certified Information Privacy Professional (CIPP) is a globally recognized professional certification in the field of privacy protection launched by the International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP). It aims to measure an individual's mastery of privacy laws and regulations, industry practices and risk management, and is an important qualification for privacy compliance and data protection-related positions. CIPP certification focuses on privacy laws, regulatory frameworks and practical compliance. It is applicable to all industries involving data collection, processing, storage and transmission. 2. Global recognition of CIPP certification Certified Information Privacy Professional (CIPP) is an authoritative certification in the privacy field launched by the International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP). It has a very high degree of global recognition and is one of the most influential qualifications in the field of privacy compliance and data protection. The CIPP certification accurately covers the privacy regulatory systems of major economies in the world by segmenting the regional direction, so it is widely recognized in all regions. CIPP/E corresponds to the European direction and is a recognized privacy professional qualification in the EU and the European Economic Area. Due to the strong regulatory characteristics of the EU General Data Protection Regulation, companies often list CIPP/E as a priority when recruiting data protection officers and privacy compliance specialists, especially in the technology and financial industries in countries such as Germany, France, and the United Kingdom, where the recognition is almost "standardized." CIPP/US corresponds to the North American direction, covering the federal and state privacy laws in the United States, and is the core reference indicator for Silicon Valley technology companies and Wall Street financial institutions to recruit privacy compliance talents. According to IAPP statistics, more than 80% of Fortune 500 companies in the United States have core personnel responsible for privacy affairs holding CIPP certification. CIPP/A corresponds to the Asian direction. It has been rapidly rising in the Asia-Pacific market due to its inclusion in regional regulations such as China's "Personal Information Protection Law," India's "Digital Personal Data Protection Law," and Japan's "Personal Information Protection Law." In China, the proportion of CIPP certification holders in the privacy compliance teams of multinational companies' branches in China and Internet giants has increased year by year; in countries such as Singapore, India, and Japan, it has also become an important qualification for companies to deal with local data regulations. In Canada (CIPP/C), Australia, the Middle East and other regions, CIPP certification is also widely recognized by local companies, law firms, and consulting agencies. Especially in cross-border data transfer and cross-border compliance projects, professionals holding CIPP certification are regarded as "compliance experts with a global vision." 3. Benefits of CIPP certification It can help practitioners systematically master global or specific regional privacy regulations and provide companies with professional talent guarantees in data compliance, risk management, and privacy policy formulation. As one of the most recognized privacy certifications in the world, it is an important plus for professional competitiveness, especially in positions such as privacy officers, compliance managers, and data protection specialists. 4. CIPP vs CIPT certification Certified Information Privacy Professional (CIPP) and Certified Information Privacy Technologist (CIPT) are both authoritative privacy certifications launched by the International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP), but their positioning, focus and applicable population are significantly different. CIPP and CIPT belong to the IAPP system. Both are certified by IAPP, the world's largest privacy professional organization, and share IAPP's industry resources and recognition. They are authoritative proof of professional capabilities in the privacy field. Both revolve around "data privacy compliance," involving core content such as global or regional privacy regulations, data subject rights, and risk management, serving the data compliance and risk management goals of enterprises. And holding both certifications can enhance professional competitiveness in the privacy field. The difference between the two is that CIPP focuses on "law and management," focusing on privacy regulations, policy frameworks, compliance strategies and business implementation, and is a qualification certificate for "privacy compliance managers." CIPT focuses on "technology and practice," focusing on achieving privacy protection through technical means, and is a qualification certificate for "privacy technology implementers." The target groups of CIPP mainly include corporate privacy officers, data protection officers, compliance managers, legal specialists, privacy consultants, policy makers, etc. The target groups of CIPT mainly include data security engineers, IT architects, privacy technology solution developers, and technical team leaders responsible for privacy implementation, etc. The core test points of CIPP focus on regional privacy regulations and interpretations, privacy policy formulation, compliance audit process, cross-border data transfer rules, and business impact assessment of privacy risks, etc. The core test points of CIPT focus on privacy enhancement technology and technical implementation tools for privacy compliance, etc. CIPP has clear regional segmentation to accurately match the regulatory requirements of different regions. CIPT has no regional segmentation and is a global unified certification, focusing on the cross-regional application of general privacy technology. In summary, if your work focuses on "management, policy, and legal aspects of privacy compliance," you can consider CIPP; if your work focuses on "technical implementation and system implementation of privacy protection," you can consider CIPT. 5. Alternative certifications like CIPP certification Certified Information Privacy Manager (CIPM) Certified Information Privacy Technologist (CIPT) Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) ISO/IEC 27701 Privacy Information Management System (PIMS) -
- 395
- SPOTO 2
- 2025-07-24 14:48
Table of Contents1. What is a technical support specialist?2. What abilities does the technical support specialist require?3. Benefits of be a Technical Support Specialist4. Salary of a Technical Support Specialist5. Alternative careers like Technical Support Specialist Curious about Technical Support Specialist? Discover its components, requirements, and why this global project management credential matters. 1. What is a technical support specialist? Technical Support Specialists are professionals who are responsible for solving technical problems related to products and services for users or customers. They play a key role as a bridge between enterprises and users, ensuring that users can use products or services smoothly. 2. What abilities does the technical support specialist require? The core responsibilities of technical support include problem diagnosis and resolution, receiving technical consultations from users, locating the root causes of problems and providing solutions through telephone, email, online chat or remote control. It is also the responsibility of technical support specialists to explain the functions of products to users, provide guidance and training to users, remind users of operating methods and precautions, and conduct simple training when necessary to help users improve their efficiency. Technical Support Specialists also need to record users' problems, processing processes and results in detail to form a knowledge base; at the same time, they should give feedback on high-frequency problems, product defects, etc. to the R&D or product team to help optimize products. When problems are beyond their own handling scope, they should coordinate with R&D and operation and maintenance departments to solve them together to ensure that user problems are followed up in a timely manner. 3. Benefits of be a Technical Support Specialist Becoming a technical support specialist can bring many benefits, including the accumulation of professional skills and personal growth and development opportunities. (1) Quickly accumulate practical technical knowledge In daily work, you need to deal with various practical technical problems such as software failures, hardware debugging, network configuration, etc., and you can quickly master the practical experience of mainstream products, systems and tools in the industry to form a solid technical foundation. The problems encountered often cover multiple fields such as operating systems and databases, which helps to build a "broad-spectrum" technical cognition and lay the foundation for subsequent deep cultivation of subdivided fields to participate in system operation and maintenance and network engineering. (2) Improve communication and problem-solving skills You need to communicate frequently with users from different backgrounds, which can exercise the "translation ability" of converting complex technical problems into popular language, as well as the empathy ability of listening and understanding needs. When faced with sudden or unknown failures, you need to quickly disassemble the problem, perform logical analysis and find solutions. Long-term accumulation will significantly improve "troubleshooting" and emergency handling capabilities, and these abilities are crucial in almost all technical positions. (3) Broad industry adaptability Technical support positions exist in almost all industries involving technology products, with a wide range of career options and are not easily affected by fluctuations in a single industry. Whether it is internal or external support for customers, the core skills are universal and cross-industry transformation is relatively easy. (4) Close understanding of users and products, As a role that directly connects with users, it can most intuitively collect user feedback and improvement suggestions for products, and deeply understand the actual application scenarios and market needs of products. This is an important advantage for transitioning to positions such as product managers and product operations. The accumulated technical knowledge and user insights can support the transition to positions such as after-sales engineers and customer success managers, and even provide a practical foundation for entrepreneurship. (5) Stable career demand and competitiveness As long as an enterprise has technical products or systems, it needs technical support personnel to ensure user experience. Therefore, job demand is long-term and stable. Especially under the trend of digital transformation, the demand for technical support from various enterprises continues to grow. Compound talents with both technical capabilities and communication skills are highly competitive in the job market, and as experience accumulates, their salary and career recognition will steadily increase. 4. Salary of a Technical Support Specialist The salary of a technical support specialist varies depending on factors such as region, experience, skills, and industry. According to Payscale data, the average total salary of a junior technical support specialist with 1-4 years of experience in Saudi Arabia is 27,250 Saudi Riyals, and the average total salary of a mid-level technical support specialist with 5-9 years of experience is 69,634 Saudi Riyals. In Nordic countries, taking Italy as an example, the average salary of an Italian technical support specialist is 30,086 euros, with a salary range of 27K-36K euros. At the same time, the average salary of a technical support engineer in South Africa is 271,092 South African rand, with a salary range of 148K-449K South African rand. Education and experience will also affect the salary of a technical support specialist. Generally speaking, the more experience you have, the higher your salary. In China, the salary of a fresh graduate technical support specialist is about 8-12K, while a senior technical support specialist or technical expert with many years of experience can earn 15-30K or even higher. The salary level of technical support specialists who master professional skills such as troubleshooting and customer service will increase accordingly. In addition, people who master scarce technologies or multilingual skills will also have an advantage in salary. In general, education and salary are positively correlated. The income of a technical support specialist with a doctorate degree is often higher than that of a person with a secondary technical school degree. The treatment of different industries will also be different. The salary of technical support specialists in industries such as medical care, finance, and technology is usually higher, while the salary of some traditional industries may be relatively low. 5. Alternative careers like Technical Support Specialist Help Desk Technician IT Support Engineer Customer Success Manager Systems Administrator -
- 169
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-24 11:21
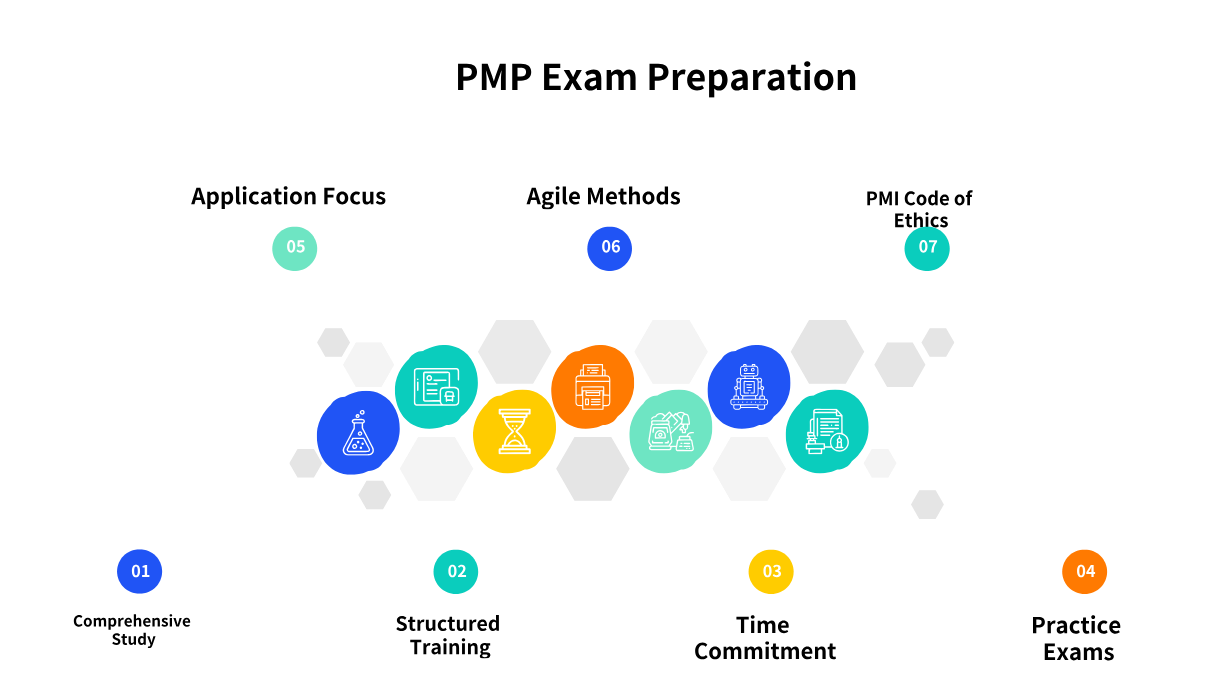
Table of ContentsThe PMP Exam: A Closer Look at Its DifficultyPMP vs. Other Project Management CertificationsStrategies to Conquer PMP Exam Difficulty The Project Management Professional (PMP) certification is a globally recognized credential that signifies a high level of expertise in project management. Many aspiring project managers often wonder about the difficulty of the PMP exam. While it is undoubtedly a rigorous assessment, with the right preparation and mindset, it is an achievable goal. The PMP Exam: A Closer Look at Its Difficulty The PMP exam is designed to test a candidate's comprehensive understanding of project management principles and their ability to apply these concepts in real-world scenarios. Its reputation for difficulty stems from several factors, including its broad syllabus, the application-based nature of its questions, and the stringent eligibility criteria set by the Project Management Institute (PMI). Exam Structure: Questions and Time Limit The PMP exam consists of 180 questions, and candidates are allotted 230 minutes (3 hours and 50 minutes) to complete it. The questions are a mix of various formats, including multiple-choice, multiple-response, matching, hotspot, and limited fill-in-the-blank. The exam includes two optional 10-minute breaks. Successfully navigating this structure requires not only knowledge but also strong time management skills, as the timer runs continuously for the entire exam duration. Average PMP Exam Score and Performance Domains PMI does not publish a fixed passing percentage for the PMP exam. Instead, it utilizes a sophisticated psychometric analysis to determine whether a candidate has passed. Results are reported in terms of proficiency levels across three performance domains: People (approximately 42% of the exam), Process (around 50%), and Business Environment (about 8%). Candidates receive a performance rating of "Above Target," "Target," "Below Target," or "Needs Improvement" for each domain. To pass, candidates generally need to demonstrate overall proficiency, typically achieving "Target" or "Above Target" in most domains. This scoring method emphasizes competency over simply memorizing facts. PMP Exam Pass Rate by Region and Country While PMI does not publicly disclose official global PMP exam pass rates, industry estimates from various training providers suggest that the first-time pass rate for well-prepared candidates typically falls within the 60-70% range. Some estimates indicate a failure rate for first-time test-takers between 40-50%. These figures underscore the exam's challenge, yet also highlight that success is within reach for dedicated individuals. Regional and country-specific pass rates can vary, often influenced by the quality and accessibility of training resources and the maturity of project management practices in those areas. For example, regions with a high concentration of PMI Authorized Training Partners may see higher success rates due to structured preparation. Understanding PMP Certification Requirements The PMP certification has strict eligibility criteria, which in themselves contribute to the perceived difficulty of obtaining the credential. Educational Background: Candidates must possess either a secondary degree (high school diploma, associate's degree, or global equivalent) with 60 months (five years) of non-overlapping professional project management experience, or a four-year degree (bachelor's degree or global equivalent) with 36 months (three years) of non-overlapping professional project management experience. Project Management Education: All candidates are required to complete 35 hours of project management education, which can be obtained through various training programs. This foundational requirement ensures that candidates have a structured understanding of project management principles before attempting the exam. Does PMP Exam Difficulty Vary by Industry? The PMP exam is designed to be industry-agnostic, meaning its difficulty does not inherently vary based on the candidate's industry background. The questions are scenario-based and focus on universal project management principles applicable across diverse sectors like IT, construction, healthcare, and finance. However, a candidate's practical experience in their specific industry can influence how easily they relate to and understand the situational questions. The quality of available training and the emphasis on formal project management within an industry can indirectly affect preparation levels and, consequently, individual success rates. PMP vs. Other Project Management Certifications Comparing the PMP to other project management certifications helps contextualize its difficulty and value. PMP Exam Difficulty vs. CAPM Exam The Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) is another certification offered by PMI, often considered an entry-level credential. Experience Level: The CAPM is geared towards individuals with less or no project management experience, while the PMP requires significant practical experience. Exam Content: The CAPM exam primarily focuses on foundational project management knowledge and memorization of terms from the PMBOK Guide. In contrast, the PMP exam is more comprehensive, featuring a higher proportion of scenario-based and application-oriented questions that require critical thinking and real-world judgment. Rigor: Consequently, the PMP exam is widely considered to be significantly more rigorous and challenging than the CAPM exam. While both require dedicated study, the PMP demands a deeper understanding and the ability to apply complex concepts. Identifying Difficult Topics While individual challenges may vary, many candidates find the application-based and situational questions to be the most difficult aspects of the PMP exam. These questions require more than rote memorization; they demand that candidates analyze a given scenario and apply the most appropriate project management principle or tool. The agile and hybrid methodologies, which constitute a significant portion (approximately 50%) of the exam content, can also be challenging for those with limited practical exposure to these approaches. Questions related to predictive, agile, and hybrid approaches often test a candidate's ability to choose the best method for a given project context. Strategies to Conquer PMP Exam Difficulty The PMP exam's difficulty can be overcome with a structured and dedicated approach to preparation. PMP Exam Study Tips for Beginners For those new to the PMP certification journey, a strategic approach is key to success. Comprehensive Study: Begin by understanding the PMP Exam Content Outline, which details the tasks, enablers, and knowledge areas covered. Utilize official PMI resources and high-quality study materials from PMI Authorized Training Partners. Structured Training: Enroll in a PMP exam prep course (which fulfills the 35-hour education requirement). These courses provide structured learning, often incorporating practice questions and real-world examples. Time Commitment: Allocate a substantial amount of time for preparation. Most successful candidates report dedicating between 150 to 300 hours of study over a period ranging from 2 to 6 months. Consistency in daily or weekly study sessions is more effective than sporadic cramming. Practice Exams: Regularly take full-length practice exams to familiarize yourself with the exam format, question types, and time constraints. Analyze your performance to identify weak areas and refine your strategy. Aim for consistent scores of 70-80% on practice tests before scheduling your exam. Focus on Application: Shift your mindset from memorization to understanding how to apply project management principles in various scenarios. The PMP exam heavily emphasizes situational judgment, requiring you to select the best course of action. Agile and Hybrid Focus: Given the current exam's emphasis, dedicate significant study time to agile and hybrid project management methodologies. Understand their principles, practices, and how they integrate with traditional project management. Review the PMI Code of Ethics: Familiarize yourself with the PMI Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct, as ethical considerations are often woven into exam questions. Required Preparation Time for the PMP Exam The time needed to prepare for the PMP exam varies significantly among individuals, largely depending on their prior project management experience, study habits, and the resources they utilize. Average Time: While some highly experienced individuals may prepare in a shorter timeframe, the consensus among successful candidates suggests an average preparation period of 2 to 6 months. This allows ample time to cover the extensive material, practice questions, and consolidate understanding. Hours of Study: Within this timeframe, the total study hours typically range from 150 to 300. This includes time spent on coursework, reading the PMBOK Guide and Agile Practice Guide, reviewing notes, and taking numerous practice exams. Consistency is Key: Consistent, focused study sessions, even for shorter durations daily, are often more effective than infrequent, long sessions. This approach helps in better retention and understanding of complex concepts. -
- 297
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-24 11:02
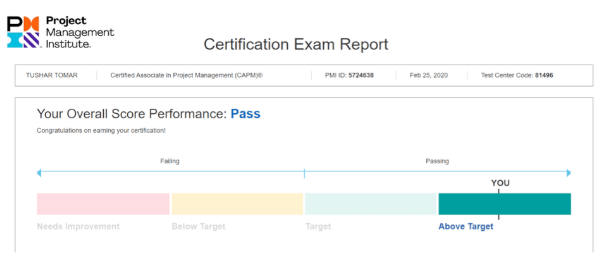
Table of ContentsWhat is the PMP Exam Pass Rate?PMP Exam DifficultyPMP exam pass rate by region and countryFactors Affecting PMP Exam Pass RatePMP exam pass rate vs. other project management certificationsHow to improve PMP exam pass rate The Project Management Professional (PMP) certification, offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI), is a globally recognized credential that signifies expertise in project management. For aspiring project managers, understanding the PMP exam pass rate is a crucial first step in their certification journey. It provides insights into the exam's difficulty and helps set realistic expectations. What is the PMP Exam Pass Rate? The PMP exam is a challenging assessment designed to test a candidate's proficiency across various project management domains. While PMI does not publicly disclose an official global PMP exam pass rate, industry estimates and data from various training providers suggest a general range. Many reputable training organizations report pass rates for their students, often indicating that around 60-70% of individuals who adequately prepare and take the exam successfully pass it on their first attempt. This figure can fluctuate based on the quality of preparation and individual aptitude. PMI PMP certification pass rate The PMP certification is highly sought after, with hundreds of thousands of certified professionals worldwide. As of early 2024, the number of active PMP credential holders surpassed 1.3 million, highlighting the widespread adoption and recognition of this certification. While an exact pass rate from PMI remains undisclosed, the robust number of certified professionals underscores the program's enduring appeal and the achievable nature of the certification with dedicated effort. PMP Exam Difficulty The PMP exam is widely considered a rigorous examination, primarily due to its comprehensive nature and the application-based questions. It evaluates not just theoretical knowledge but also the ability to apply project management principles in real-world scenarios. The exam consists of 180 questions, and candidates have 230 minutes to complete it. PMP exam passing score PMI employs a complex psychometric analysis to determine the passing score for the PMP exam, rather than a fixed percentage. This means the passing score can slightly vary over time to ensure fairness and consistency across different exam versions. Candidates receive a score report indicating their performance in each of the three performance domains: People, Process, and Business Environment. Performance is typically categorized as "Above Target," "Target," "Below Target," or "Needs Improvement." To pass, candidates generally need to demonstrate proficiency across all domains, with a strong performance in the "Target" or "Above Target" categories. There isn't a simple percentage equivalent for the passing score due to the weighted nature of the questions and the psychometric scaling. PMP exam pass rate by region and country While global pass rates are not explicitly provided by PMI, regional and country-specific pass rates can vary based on several factors, including the availability and quality of training resources, cultural approaches to test-taking, and the level of project management maturity within a given region. Regional Differences: Some reports from global training providers indicate slight variations in pass rates across continents. For instance, regions with well-established project management communities and extensive PMP training infrastructure, such as North America and parts of Europe, might see slightly higher average pass rates compared to emerging markets where formal project management training might be less prevalent. Country-Specific Variations: Within continents, individual countries can also exhibit different pass rates. Factors like economic development, educational standards, and the emphasis placed on professional certifications within a country's workforce can influence these figures. For example, some countries with a high number of PMP exam takers often have a developed ecosystem of training centers and study groups, potentially contributing to more consistent pass rates. Factors Affecting PMP Exam Pass Rate Several key factors significantly influence an individual's likelihood of passing the PMP exam. Understanding these can help aspiring candidates strategize their preparation. Quality of Study Materials and Training: Utilizing official PMI resources, reputable PMP exam prep books, and accredited training courses (from PMI Authorized Training Partners) demonstrably increases the chances of success. Data suggests that candidates who complete a structured PMP exam prep course are significantly more likely to pass. Study Hours and Consistency: The PMP exam requires substantial preparation. Most successful candidates report dedicating between 150 to 300 hours of study time over a period of 2 to 4 months. Consistent daily or weekly study habits are more effective than cramming. Prior Project Management Experience: While the PMP exam is not solely based on experience, having practical project management experience helps in understanding and applying the concepts tested. Candidates with more hands-on experience often find it easier to relate to the situational questions. Practice Exams and Mock Tests: Regularly taking full-length practice exams under timed conditions is crucial. This helps in familiarizing candidates with the exam format, identifying weak areas, and improving time management. Many successful candidates report taking 5-10 full-length mock exams. Understanding the PMI Lexicon: The PMP exam uses specific terminology and adheres strictly to the processes and knowledge areas outlined in the PMBOK Guide and other PMI publications. Candidates who immerse themselves in this lexicon tend to perform better. PMP exam pass rate vs. other project management certifications When considering project management certifications, the PMP stands out in terms of global recognition and perceived difficulty, which often correlates with its pass rate. PMP vs. CAPM: The Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) is also offered by PMI and is designed for entry-level project managers. Its exam is generally considered less challenging than the PMP, and consequently, its reported pass rates by training providers are often higher, sometimes reaching 75-85%. This reflects its foundational nature. PMP vs. PRINCE2: PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is another widely recognized project management certification, particularly strong in the UK and Europe. While direct pass rate comparisons are difficult due to differing reporting standards, the PMP is often viewed as requiring a deeper, more comprehensive understanding of project management principles, whereas PRINCE2 focuses more on process and framework. Anecdotal evidence suggests the PMP exam might have a slightly lower pass rate globally compared to PRINCE2 Foundation, while PRINCE2 Practitioner might be more comparable in difficulty to the PMP. PMP exam pass rate vs. first-time pass rate It's important to distinguish between the overall PMP exam pass rate and the first-time pass rate. While the overall pass rate may encompass individuals who have taken the exam multiple times, the first-time pass rate specifically refers to the percentage of candidates who succeed on their initial attempt. First-Time Pass Rate: Industry estimates for the first-time pass rate for well-prepared candidates typically hover around 60-70%. This indicates that while the exam is challenging, a significant majority of diligent candidates can achieve success on their first try. Impact of Multiple Attempts: Candidates who do not pass on their first attempt often learn from their experience, focus on their weak areas, and pass on subsequent attempts. This means the overall pass rate, if it were publicly available from PMI, might be slightly higher than the first-time pass rate, reflecting the persistence of candidates. How to improve PMP exam pass rate Improving your PMP exam pass rate is entirely within your control through strategic and diligent preparation. Enroll in a PMP Exam Prep Course: Taking a 35-hour PMP exam prep course from a PMI Authorized Training Partner (ATP) is highly recommended. These courses are designed to align with the current PMP exam content outline and provide structured learning. Master the PMBOK Guide and Agile Practice Guide: These are foundational texts. While not every detail needs to be memorized, a thorough understanding of the concepts, processes, and tools/techniques is essential. Focus on understanding the "why" and "how" behind the principles. Utilize Diverse Study Resources: Supplement your primary study materials with online forums, study groups, flashcards, and video lectures. Diverse resources can help clarify complex topics and reinforce learning. Practice, Practice, Practice: Take as many practice questions and full-length mock exams as possible. Aim for scores of 70-80% on practice tests before attempting the actual exam. Analyze your incorrect answers to understand the underlying concepts. Focus on Agile and Hybrid Methodologies: A significant portion of the current PMP exam (approximately 50%) covers agile and hybrid approaches. Ensure you have a strong grasp of agile principles, frameworks (Scrum, Kanban), and how they integrate into project management. Develop Strong Time Management Skills: During practice exams, work on your pace to ensure you can complete all 180 questions within the 230-minute time limit. Learn to quickly analyze situational questions and select the best answer. Simulate Exam Conditions: Take your final mock exams in an environment that mimics the actual testing center as closely as possible – quiet, uninterrupted, and timed. Understand PMI's Professional Responsibility: Familiarize yourself with the PMI Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct, as questions related to ethical considerations are often included. -
- 58
- SPOTO
- 2025-07-23 17:33
Table of ContentsWhat Is a Cloud Collaboration Engineer? Responsibilities of a Cloud Collaboration EngineerSkills RequiredTypical Job DescriptionHow to Become a Cloud Collaboration EngineerCloud Collaboration Engineer vs. Collaboration SpecialistDaily Tasks OverviewTools & Technologies UsedReal-World Project ExamplesWhy the Role Matters What Is a Cloud Collaboration Engineer? A Cloud Collaboration Engineer specializes in architecting, deploying, and optimizing cloud platforms that enable real-time teamwork—such as Microsoft Teams, Zoom, Slack, and Salesforce Chatter. They seamlessly integrate cloud infrastructure, networking, automation, and user experience to support secure and efficient collaboration for distributed teams. Responsibilities of a Cloud Collaboration Engineer Cloud Architecture & Deployment Design scalable, multi-region collaboration environments using AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Configure VMs, networking, firewalls, storage, and identity management. Security & Compliance Implement access controls, encryption, and compliance measures; ensure alignment with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Monitoring & Incident Response Continuously monitor system health and respond to alerts and outages in real time. Cost & Performance Optimization Global public cloud spending is projected to reach $723.4 billion in 2025. 32% of cloud budgets are typically wasted due to idle or overprovisioned resources. 60% of companies rank cost savings as their top cloud initiative. Cross-Team Collaboration Partner with developers, security, networking, and business teams to align infrastructure with organizational goals. Skills Required Technical Skills Cloud Expertise: 96% of companies use at least one public cloud; 50% of their workloads reside there. Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Tools like Terraform and CloudFormation. Networking: Fundamentals like IP, VPC, DNS, and load balancing. Containers & Orchestration: Docker, Kubernetes. Scripting & Automation: Python, Bash, PowerShell. Security & Governance: Identity and access management, encryption. Soft Skills Communication & Teamwork: Essential for cross-functional collaboration. Problem-Solving: Most in-demand soft skills proven essential for IT roles. Adaptability & Continuous Learning: Crucial in a rapidly evolving cloud landscape. Typical Job Description Position: Cloud Collaboration Engineer Key Duties: Build and maintain 24/7 cloud-based collaboration systems. Automate deployments and manage IaC. Monitor performance, ensure reliability, and optimize spend. Enforce compliance and manage audits. Document configurations and prepare SOPs. Qualifications: Bachelor’s in Computer Science, IT, or similar. Minimum 3 years of experience in cloud engineering or related roles. Certifications such as AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Azure Solutions Architect, Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect. Hands-on experience with scripting, IaC, networking, and security. How to Become a Cloud Collaboration Engineer Educational Foundation & Certifications: Obtain a relevant degree and cloud certifications. Technical Skill-Building: Learn Linux/Windows, networking, IaC, scripting, containers, and security. Hands-On Practice: Deploy collaboration tools, implement migrations, and handle cloud integrations. Develop Soft Skills: Hone communication, teamwork, and troubleshooting abilities. Build a Portfolio: Showcase real projects and pursue advanced certifications (e.g., CCNP Collaboration). Stay Engaged: Join cloud communities and stay updated with emerging technologies like serverless and FinOps. Cloud Collaboration Engineer vs. Collaboration Specialist Aspect Cloud Collaboration Engineer Collaboration Specialist Focus Backend deployment, automation, infrastructure End-user support, training, and adoption strategies Key Skills Cloud platforms, IaC, network, security User UX, communication, training Objective Build scalable, secure systems Increase user engagement and effective adoption Daily Tasks Overview Morning system health checks and incident reviews. Provision or adjust cloud configurations. Apply updates and security patches. Refine IaC templates and automation pipelines. Conduct stakeholder planning sessions. Analyze metrics for performance and cost. Troubleshoot emerging issues. Update documentation and SOPs. Tools & Technologies Used Cloud Platforms: AWS, Azure, GCP IaC: Terraform, CloudFormation Containers: Docker, Kubernetes CI/CD: Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps Monitoring/Security: CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, Splunk Collaboration Tools: Microsoft Teams, Zoom, Slack, Salesforce Chatter Real-World Project Examples Enterprise Teams Migration: Built a hybrid network infrastructure on Azure with SSO and compliance integration. Automated Slack Onboarding: Developed Terraform scripts to set up workspaces, channels, and permissions. Zoom DR Implementation: Engineered cross-region AWS configurations with auto-failover capabilities. Why the Role Matters With nearly all enterprises (94%) expected to use cloud services by 2025, and cloud costs often exceeding plans by 17%, the role of cloud collaboration engineers is essential. They ensure collaboration platforms are secure, reliable, cost-effective, and agile—enabling businesses to stay connected and compliant at scale.