Table of Contents
The Project Management Professional (PMP) certification, offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI), is a globally recognized credential that signifies expertise in project management. For aspiring project managers, understanding the PMP exam pass rate is a crucial first step in their certification journey. It provides insights into the exam's difficulty and helps set realistic expectations.
What is the PMP Exam Pass Rate?
The PMP exam is a challenging assessment designed to test a candidate's proficiency across various project management domains. While PMI does not publicly disclose an official global PMP exam pass rate, industry estimates and data from various training providers suggest a general range. Many reputable training organizations report pass rates for their students, often indicating that around 60-70% of individuals who adequately prepare and take the exam successfully pass it on their first attempt. This figure can fluctuate based on the quality of preparation and individual aptitude.
PMI PMP certification pass rate
The PMP certification is highly sought after, with hundreds of thousands of certified professionals worldwide. As of early 2024, the number of active PMP credential holders surpassed 1.3 million, highlighting the widespread adoption and recognition of this certification. While an exact pass rate from PMI remains undisclosed, the robust number of certified professionals underscores the program's enduring appeal and the achievable nature of the certification with dedicated effort.
PMP Exam Difficulty
The PMP exam is widely considered a rigorous examination, primarily due to its comprehensive nature and the application-based questions. It evaluates not just theoretical knowledge but also the ability to apply project management principles in real-world scenarios. The exam consists of 180 questions, and candidates have 230 minutes to complete it.
PMP exam passing score
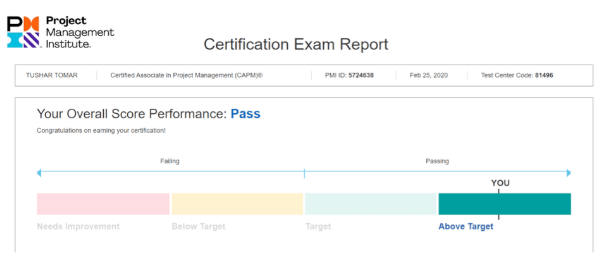
PMI employs a complex psychometric analysis to determine the passing score for the PMP exam, rather than a fixed percentage. This means the passing score can slightly vary over time to ensure fairness and consistency across different exam versions. Candidates receive a score report indicating their performance in each of the three performance domains: People, Process, and Business Environment. Performance is typically categorized as "Above Target," "Target," "Below Target," or "Needs Improvement." To pass, candidates generally need to demonstrate proficiency across all domains, with a strong performance in the "Target" or "Above Target" categories. There isn't a simple percentage equivalent for the passing score due to the weighted nature of the questions and the psychometric scaling.
PMP exam pass rate by region and country
While global pass rates are not explicitly provided by PMI, regional and country-specific pass rates can vary based on several factors, including the availability and quality of training resources, cultural approaches to test-taking, and the level of project management maturity within a given region.
-
Regional Differences: Some reports from global training providers indicate slight variations in pass rates across continents. For instance, regions with well-established project management communities and extensive PMP training infrastructure, such as North America and parts of Europe, might see slightly higher average pass rates compared to emerging markets where formal project management training might be less prevalent.
-
Country-Specific Variations: Within continents, individual countries can also exhibit different pass rates. Factors like economic development, educational standards, and the emphasis placed on professional certifications within a country's workforce can influence these figures. For example, some countries with a high number of PMP exam takers often have a developed ecosystem of training centers and study groups, potentially contributing to more consistent pass rates.
Factors Affecting PMP Exam Pass Rate
Several key factors significantly influence an individual's likelihood of passing the PMP exam. Understanding these can help aspiring candidates strategize their preparation.

-
Quality of Study Materials and Training: Utilizing official PMI resources, reputable PMP exam prep books, and accredited training courses (from PMI Authorized Training Partners) demonstrably increases the chances of success. Data suggests that candidates who complete a structured PMP exam prep course are significantly more likely to pass.
-
Study Hours and Consistency: The PMP exam requires substantial preparation. Most successful candidates report dedicating between 150 to 300 hours of study time over a period of 2 to 4 months. Consistent daily or weekly study habits are more effective than cramming.
-
Prior Project Management Experience: While the PMP exam is not solely based on experience, having practical project management experience helps in understanding and applying the concepts tested. Candidates with more hands-on experience often find it easier to relate to the situational questions.
-
Practice Exams and Mock Tests: Regularly taking full-length practice exams under timed conditions is crucial. This helps in familiarizing candidates with the exam format, identifying weak areas, and improving time management. Many successful candidates report taking 5-10 full-length mock exams.
-
Understanding the PMI Lexicon: The PMP exam uses specific terminology and adheres strictly to the processes and knowledge areas outlined in the PMBOK Guide and other PMI publications. Candidates who immerse themselves in this lexicon tend to perform better.
PMP exam pass rate vs. other project management certifications
When considering project management certifications, the PMP stands out in terms of global recognition and perceived difficulty, which often correlates with its pass rate.
-
PMP vs. CAPM: The Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) is also offered by PMI and is designed for entry-level project managers. Its exam is generally considered less challenging than the PMP, and consequently, its reported pass rates by training providers are often higher, sometimes reaching 75-85%. This reflects its foundational nature.
-
PMP vs. PRINCE2: PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is another widely recognized project management certification, particularly strong in the UK and Europe. While direct pass rate comparisons are difficult due to differing reporting standards, the PMP is often viewed as requiring a deeper, more comprehensive understanding of project management principles, whereas PRINCE2 focuses more on process and framework. Anecdotal evidence suggests the PMP exam might have a slightly lower pass rate globally compared to PRINCE2 Foundation, while PRINCE2 Practitioner might be more comparable in difficulty to the PMP.
PMP exam pass rate vs. first-time pass rate
It's important to distinguish between the overall PMP exam pass rate and the first-time pass rate. While the overall pass rate may encompass individuals who have taken the exam multiple times, the first-time pass rate specifically refers to the percentage of candidates who succeed on their initial attempt.
-
First-Time Pass Rate: Industry estimates for the first-time pass rate for well-prepared candidates typically hover around 60-70%. This indicates that while the exam is challenging, a significant majority of diligent candidates can achieve success on their first try.
-
Impact of Multiple Attempts: Candidates who do not pass on their first attempt often learn from their experience, focus on their weak areas, and pass on subsequent attempts. This means the overall pass rate, if it were publicly available from PMI, might be slightly higher than the first-time pass rate, reflecting the persistence of candidates.
How to improve PMP exam pass rate
Improving your PMP exam pass rate is entirely within your control through strategic and diligent preparation.
-
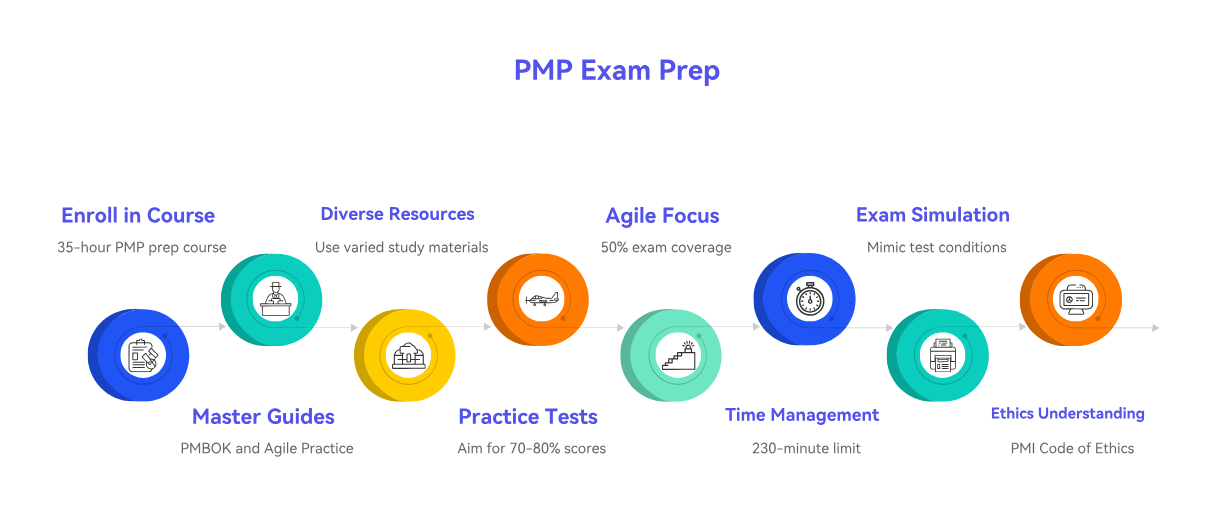
Enroll in a PMP Exam Prep Course: Taking a 35-hour PMP exam prep course from a PMI Authorized Training Partner (ATP) is highly recommended. These courses are designed to align with the current PMP exam content outline and provide structured learning.
-
Master the PMBOK Guide and Agile Practice Guide: These are foundational texts. While not every detail needs to be memorized, a thorough understanding of the concepts, processes, and tools/techniques is essential. Focus on understanding the "why" and "how" behind the principles.
-
Utilize Diverse Study Resources: Supplement your primary study materials with online forums, study groups, flashcards, and video lectures. Diverse resources can help clarify complex topics and reinforce learning.
-
Practice, Practice, Practice: Take as many practice questions and full-length mock exams as possible. Aim for scores of 70-80% on practice tests before attempting the actual exam. Analyze your incorrect answers to understand the underlying concepts.
-
Focus on Agile and Hybrid Methodologies: A significant portion of the current PMP exam (approximately 50%) covers agile and hybrid approaches. Ensure you have a strong grasp of agile principles, frameworks (Scrum, Kanban), and how they integrate into project management.
-
Develop Strong Time Management Skills: During practice exams, work on your pace to ensure you can complete all 180 questions within the 230-minute time limit. Learn to quickly analyze situational questions and select the best answer.
-
Simulate Exam Conditions: Take your final mock exams in an environment that mimics the actual testing center as closely as possible – quiet, uninterrupted, and timed.
-
Understand PMI's Professional Responsibility: Familiarize yourself with the PMI Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct, as questions related to ethical considerations are often included.










