Table of Contents
The Project Management Professional (PMP) certification is a globally recognized credential that signifies a high level of expertise in project management. Many aspiring project managers often wonder about the difficulty of the PMP exam. While it is undoubtedly a rigorous assessment, with the right preparation and mindset, it is an achievable goal.
The PMP Exam: A Closer Look at Its Difficulty
The PMP exam is designed to test a candidate's comprehensive understanding of project management principles and their ability to apply these concepts in real-world scenarios. Its reputation for difficulty stems from several factors, including its broad syllabus, the application-based nature of its questions, and the stringent eligibility criteria set by the Project Management Institute (PMI).
Exam Structure: Questions and Time Limit
The PMP exam consists of 180 questions, and candidates are allotted 230 minutes (3 hours and 50 minutes) to complete it. The questions are a mix of various formats, including multiple-choice, multiple-response, matching, hotspot, and limited fill-in-the-blank. The exam includes two optional 10-minute breaks. Successfully navigating this structure requires not only knowledge but also strong time management skills, as the timer runs continuously for the entire exam duration.
Average PMP Exam Score and Performance Domains
PMI does not publish a fixed passing percentage for the PMP exam. Instead, it utilizes a sophisticated psychometric analysis to determine whether a candidate has passed. Results are reported in terms of proficiency levels across three performance domains: People (approximately 42% of the exam), Process (around 50%), and Business Environment (about 8%). Candidates receive a performance rating of "Above Target," "Target," "Below Target," or "Needs Improvement" for each domain. To pass, candidates generally need to demonstrate overall proficiency, typically achieving "Target" or "Above Target" in most domains. This scoring method emphasizes competency over simply memorizing facts.
PMP Exam Pass Rate by Region and Country
While PMI does not publicly disclose official global PMP exam pass rates, industry estimates from various training providers suggest that the first-time pass rate for well-prepared candidates typically falls within the 60-70% range. Some estimates indicate a failure rate for first-time test-takers between 40-50%. These figures underscore the exam's challenge, yet also highlight that success is within reach for dedicated individuals. Regional and country-specific pass rates can vary, often influenced by the quality and accessibility of training resources and the maturity of project management practices in those areas. For example, regions with a high concentration of PMI Authorized Training Partners may see higher success rates due to structured preparation.
Understanding PMP Certification Requirements
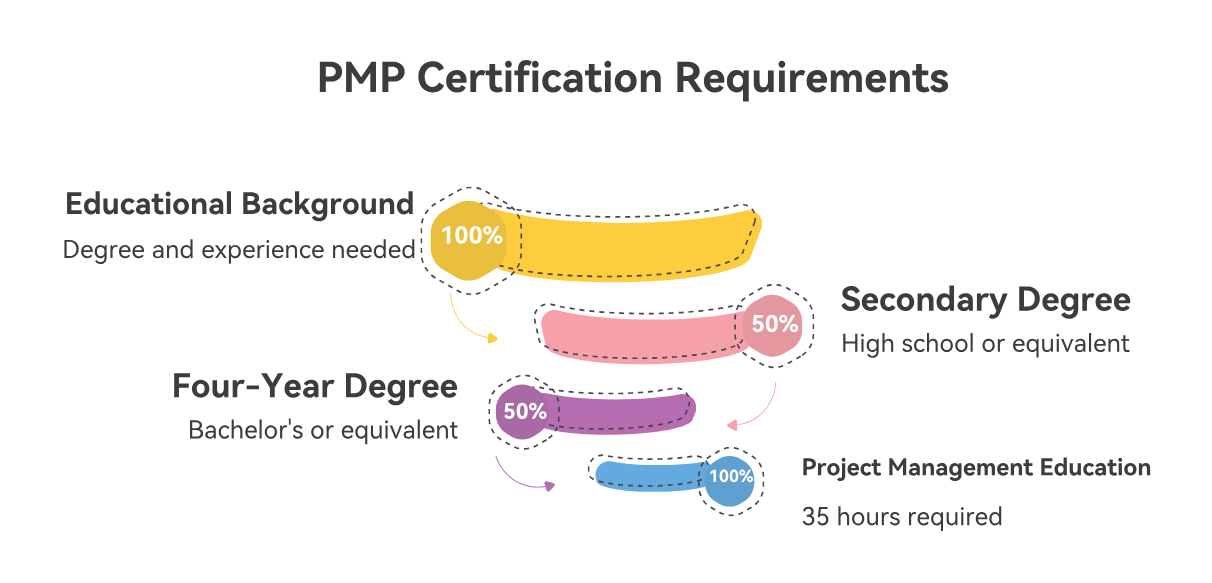
The PMP certification has strict eligibility criteria, which in themselves contribute to the perceived difficulty of obtaining the credential.
-
Educational Background: Candidates must possess either a secondary degree (high school diploma, associate's degree, or global equivalent) with 60 months (five years) of non-overlapping professional project management experience, or a four-year degree (bachelor's degree or global equivalent) with 36 months (three years) of non-overlapping professional project management experience.
-
Project Management Education: All candidates are required to complete 35 hours of project management education, which can be obtained through various training programs. This foundational requirement ensures that candidates have a structured understanding of project management principles before attempting the exam.
Does PMP Exam Difficulty Vary by Industry?
The PMP exam is designed to be industry-agnostic, meaning its difficulty does not inherently vary based on the candidate's industry background. The questions are scenario-based and focus on universal project management principles applicable across diverse sectors like IT, construction, healthcare, and finance. However, a candidate's practical experience in their specific industry can influence how easily they relate to and understand the situational questions. The quality of available training and the emphasis on formal project management within an industry can indirectly affect preparation levels and, consequently, individual success rates.
PMP vs. Other Project Management Certifications
Comparing the PMP to other project management certifications helps contextualize its difficulty and value.
PMP Exam Difficulty vs. CAPM Exam
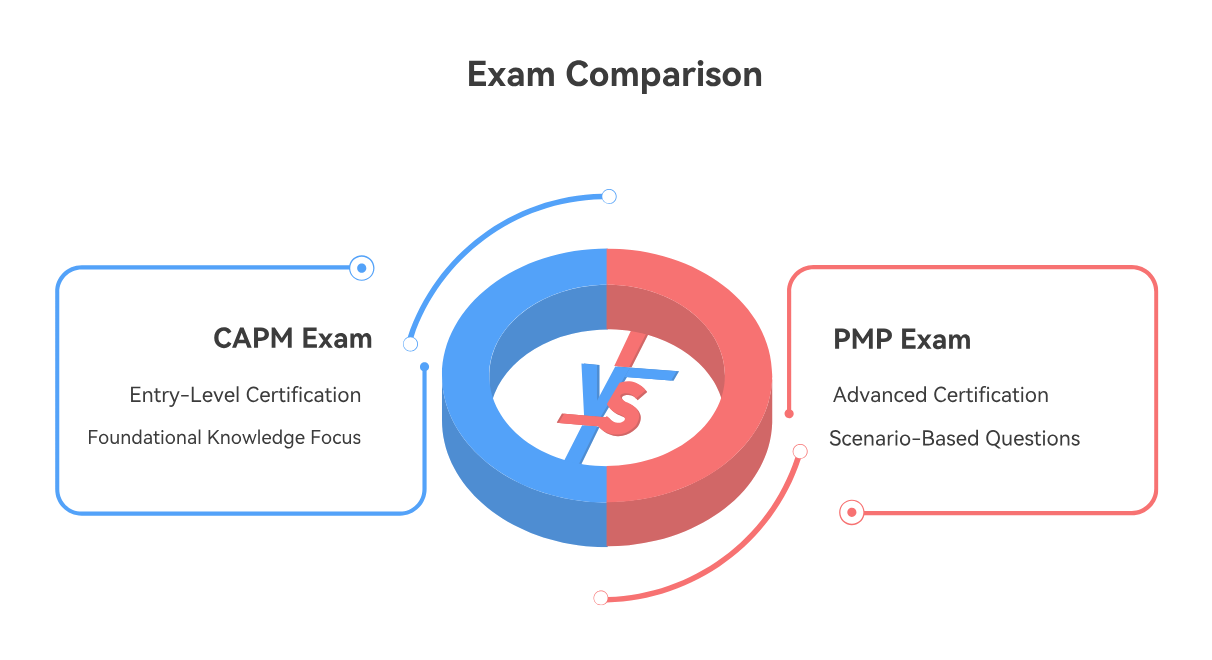
The Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) is another certification offered by PMI, often considered an entry-level credential.
-
Experience Level: The CAPM is geared towards individuals with less or no project management experience, while the PMP requires significant practical experience.
-
Exam Content: The CAPM exam primarily focuses on foundational project management knowledge and memorization of terms from the PMBOK Guide. In contrast, the PMP exam is more comprehensive, featuring a higher proportion of scenario-based and application-oriented questions that require critical thinking and real-world judgment.
-
Rigor: Consequently, the PMP exam is widely considered to be significantly more rigorous and challenging than the CAPM exam. While both require dedicated study, the PMP demands a deeper understanding and the ability to apply complex concepts.
Identifying Difficult Topics
While individual challenges may vary, many candidates find the application-based and situational questions to be the most difficult aspects of the PMP exam. These questions require more than rote memorization; they demand that candidates analyze a given scenario and apply the most appropriate project management principle or tool. The agile and hybrid methodologies, which constitute a significant portion (approximately 50%) of the exam content, can also be challenging for those with limited practical exposure to these approaches. Questions related to predictive, agile, and hybrid approaches often test a candidate's ability to choose the best method for a given project context.
Strategies to Conquer PMP Exam Difficulty
The PMP exam's difficulty can be overcome with a structured and dedicated approach to preparation.
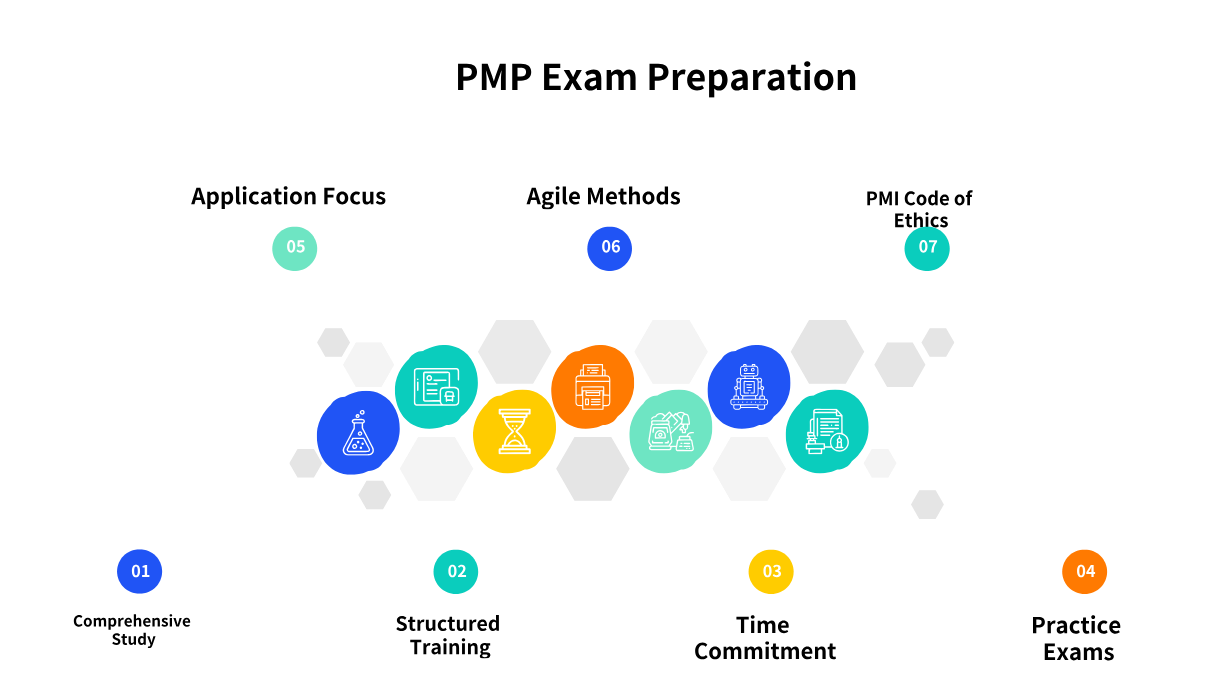
PMP Exam Study Tips for Beginners
For those new to the PMP certification journey, a strategic approach is key to success.
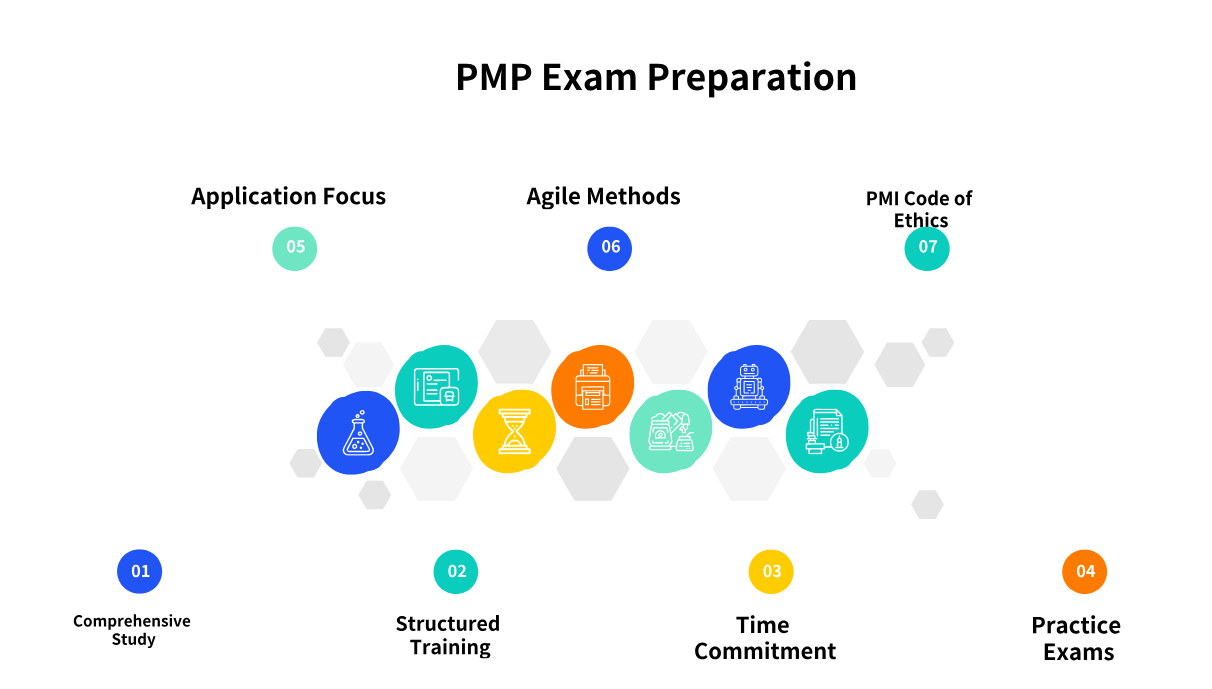
-
Comprehensive Study: Begin by understanding the PMP Exam Content Outline, which details the tasks, enablers, and knowledge areas covered. Utilize official PMI resources and high-quality study materials from PMI Authorized Training Partners.
-
Structured Training: Enroll in a PMP exam prep course (which fulfills the 35-hour education requirement). These courses provide structured learning, often incorporating practice questions and real-world examples.
-
Time Commitment: Allocate a substantial amount of time for preparation. Most successful candidates report dedicating between 150 to 300 hours of study over a period ranging from 2 to 6 months. Consistency in daily or weekly study sessions is more effective than sporadic cramming.
-
Practice Exams: Regularly take full-length practice exams to familiarize yourself with the exam format, question types, and time constraints. Analyze your performance to identify weak areas and refine your strategy. Aim for consistent scores of 70-80% on practice tests before scheduling your exam.
-
Focus on Application: Shift your mindset from memorization to understanding how to apply project management principles in various scenarios. The PMP exam heavily emphasizes situational judgment, requiring you to select the best course of action.
-
Agile and Hybrid Focus: Given the current exam's emphasis, dedicate significant study time to agile and hybrid project management methodologies. Understand their principles, practices, and how they integrate with traditional project management.
-
Review the PMI Code of Ethics: Familiarize yourself with the PMI Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct, as ethical considerations are often woven into exam questions.
Required Preparation Time for the PMP Exam
The time needed to prepare for the PMP exam varies significantly among individuals, largely depending on their prior project management experience, study habits, and the resources they utilize.
-
Average Time: While some highly experienced individuals may prepare in a shorter timeframe, the consensus among successful candidates suggests an average preparation period of 2 to 6 months. This allows ample time to cover the extensive material, practice questions, and consolidate understanding.
-
Hours of Study: Within this timeframe, the total study hours typically range from 150 to 300. This includes time spent on coursework, reading the PMBOK Guide and Agile Practice Guide, reviewing notes, and taking numerous practice exams.
-
Consistency is Key: Consistent, focused study sessions, even for shorter durations daily, are often more effective than infrequent, long sessions. This approach helps in better retention and understanding of complex concepts.










