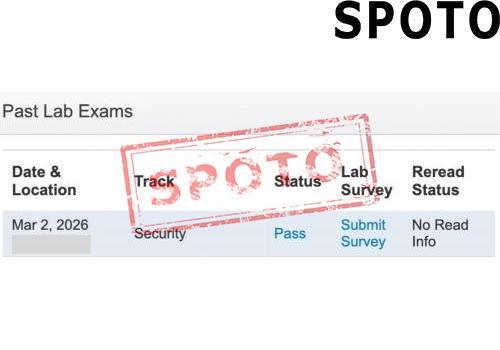
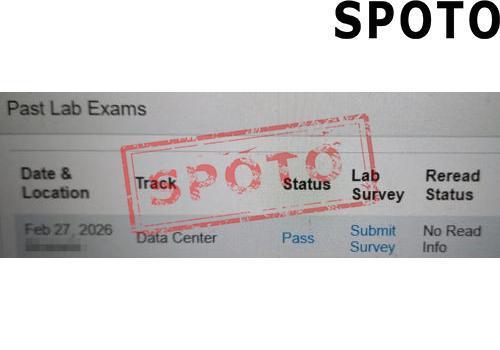
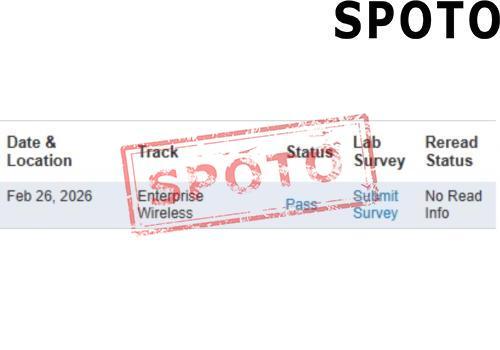
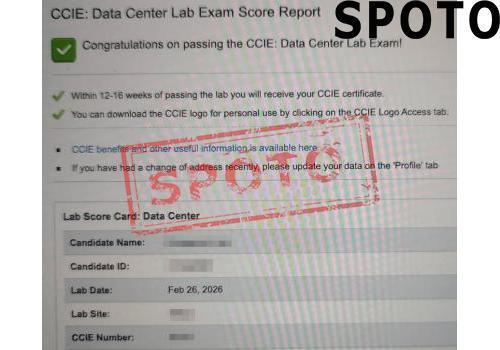
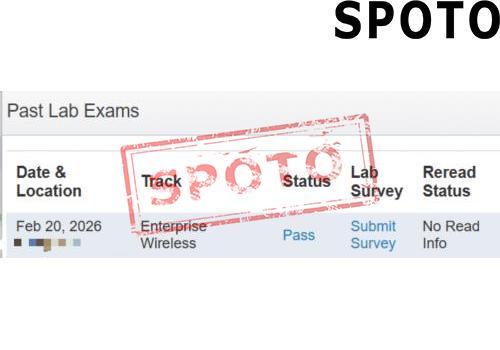
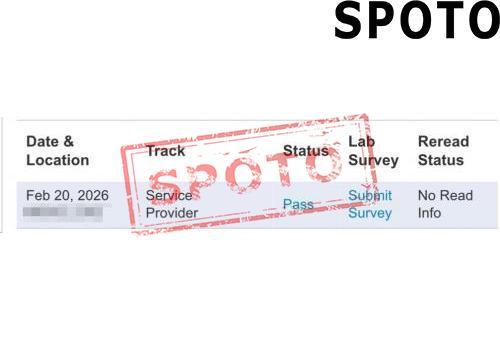
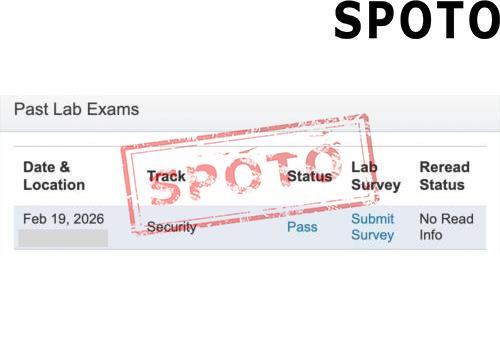
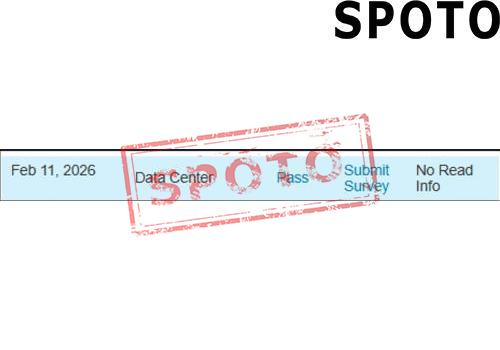
When pursuing a Cisco certification, particularly at the CCIE level, candidates often face a crucial decision: should they specialize in Enterprise Infrastructure (EI) or Wireless? Both tracks offer lucrative career opportunities and demand deep expertise, but their focus areas, skill requirements, and industry roles differ significantly. To make an informed choice, let's explore the key factors that set these two specializations apart.
1. Scope and Focus Areas
Enterprise Infrastructure (EI)
EI focuses on designing, implementing, and troubleshooting enterprise-level networks. Its primary components include:
- Routing and Switching: Core networking protocols like BGP, OSPF, and EIGRP.
- SD-WAN: Modern networking solutions for optimized wide-area network management.
- Network Automation: Tools like Python, Ansible, and Cisco DNA Center.
- Security Integration: Implementing secure connectivity across enterprise networks.
EI is ideal for professionals who enjoy working on complex, multi-layered network infrastructures.
Wireless
Wireless specialization delves into building and managing secure, high-performance wireless networks. Key focus areas include:
- RF Fundamentals: Understanding radio frequency behavior and spectrum management.
- Wireless LAN (WLAN) Design: Creating robust wireless networks for diverse environments.
- Wi-Fi 6 and Beyond: Leveraging the latest wireless technologies for optimized performance.
- Security in Wireless: Mitigating vulnerabilities unique to wireless networks.
Wireless appeals to professionals passionate about mobility, connectivity, and cutting-edge wireless technologies.
2. Career Opportunities
Enterprise Infrastructure Roles
- Network Engineer: Managing and troubleshooting enterprise networks.
- Solutions Architect: Designing scalable network solutions.
- SD-WAN Specialist: Implementing and optimizing SD-WAN systems.
- Automation Engineer: Streamlining operations with network automation tools.
Wireless Roles
- Wireless Network Engineer: Ensuring the smooth operation of wireless infrastructures.
- RF Specialist: Designing and maintaining radio frequency systems.
- WLAN Consultant: Advising on advanced wireless solutions for businesses.
- Wireless Security Analyst: Protecting wireless networks from cyber threats.
While EI offers broader roles, Wireless professionals often specialize in environments like corporate campuses, healthcare facilities, and smart cities.
3. Industry Demand
Enterprise Infrastructure
The demand for EI professionals remains high due to the growing need for robust, automated networks in industries like finance, healthcare, and manufacturing. Skills in SD-WAN and network automation are especially sought after in hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Wireless
As organizations embrace mobility and IoT, the need for wireless specialists has surged. Businesses require experts to design high-capacity, low-latency networks capable of handling massive device connectivity.
4. Skills Required
Enterprise Infrastructure
- Strong knowledge of routing and switching protocols.
- Familiarity with SD-WAN, MPLS, and hybrid cloud networks.
- Proficiency in Python and Ansible for automation.
- Understanding of cybersecurity principles and practices.
Wireless
- Deep understanding of RF behavior and wireless standards (e.g., 802.11 protocols).
- Experience with Cisco wireless controllers and access points.
- Skills in site surveys and WLAN design tools like Ekahau.
- Knowledge of wireless security measures, including WPA3.
5. Certification Challenges
Enterprise Infrastructure
The EI track requires extensive knowledge of various technologies, often making it one of the most challenging CCIE certifications. Candidates must master routing, switching, automation, and SD-WAN while managing time-intensive lab scenarios.
Wireless
Wireless certification is equally demanding due to its heavy focus on real-world RF troubleshooting and design. Candidates must be proficient in configuring wireless controllers, designing WLANs, and addressing wireless security challenges.
6. Choosing the Right Track
When deciding between EI and Wireless, consider:
- Your Interests: Are you passionate about core networking or mobility solutions?
- Career Goals: Do you see yourself managing large enterprise networks or leading wireless innovations?
- Industry Trends: Which specialization aligns better with your region's job market?
- Existing Knowledge: Do you already have a strong foundation in either domain?
7. Key Advantages of Each Track
Enterprise Infrastructure
- Broader career opportunities across various industries.
- Strong focus on automation and emerging technologies like SD-WAN.
- High demand for professionals with multi-layered network expertise.
Wireless
- Thriving opportunities in mobility-driven industries like IoT and healthcare.
- Focus on cutting-edge technologies like Wi-Fi 6 and IoT integrations.
- Niche specialization with fewer professionals increases job competitiveness.
Conclusion
Choosing between CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure and CCIE Wireless ultimately depends on your career aspirations, interests, and the opportunities you wish to pursue. Both tracks offer rewarding paths, but EI provides a broader scope for network engineers, while Wireless offers a unique specialization in the rapidly growing mobility sector. Evaluate your goals, consider your strengths, and align your certification journey with the future you envision.