Network troubleshooting commands are a necessity for every network administrator. When getting started in the networking field, it is important to master these skills to troubleshoot a variety of different network conditions.
Today, we sort out top 10 ones based on IT pro generality and command use. It was a great content which deserved serious study.
1.Route
This command is used to display the current status of the routing table on a host. While the use of the route is limited in common situations where the host only has a single IP address with a single gateway, it is vital in other situations where multiple IP address and multiple gateways are available.
You can check the example of the route being used on a Windows machine.
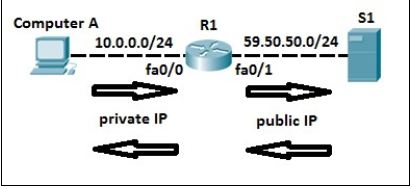
2.Pathping/mtr
In an effort to take advantage of the benefits of both the ping and tracert/traceroute commands, the pathping and mtr were developed. Both of these tools take the functionality and information that can be obtained from these types of tools and provide a more detailed single picture of the path characteristics from a specific host to a specific destination.
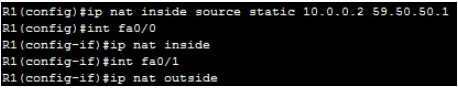
3.Speedtest.net
A very easy test that can be used to both determine the Internet bandwidth available to a specific host and to determine the quality of an Internet connection is the use of the tools available at the speedtest.net website. The speedtest.net site provides the ability to determine the amount of bandwidth that is available to a specific host at a specific point in time; this is often a good tool to use when measuring how long it is going to take to upload or download information from a local to the remote host. This measurement can also be used to determine whether the connection is offering the amount of bandwidth that was purchased from the Internet provider; keep in mind however that some amount of bandwidth difference is expected between the quoted bandwidth purchased and the measured bandwidth.
4.Subnet and IP Calculator
One of the most important tools in the belt of a junior network engineer is an IP network calculator. These can be used to ensure a correct IP address selection and with this a correct IP address configuration. While this type of tool is used by senior-level network engineers, much of the information obtained from the tool becomes simpler to calculate the longer and more experience you have in the field. Two of the more commonly used free IP calculators include Wildpackets (Bitcricket) Network Calculator and Solarwinds Advanced Subnet Calculator which can be found at the links below.
https://www.iptp.net/en_US/iptp-tools/ip-calculator/
http://downloads.solarwinds.com/solarwinds/Release/FreeTool/SolarWinds-Subnet-Calculator.zip
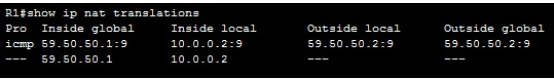
5.PuTTY/Tera Term
When connecting to a variety of different types of equipment, telnet, SSH or serial client is required; when this is required both the puTTY and Tera Term programs are able to provide these functionalities. The selection of one over the other is strictly a personal preference.
6.Netstat
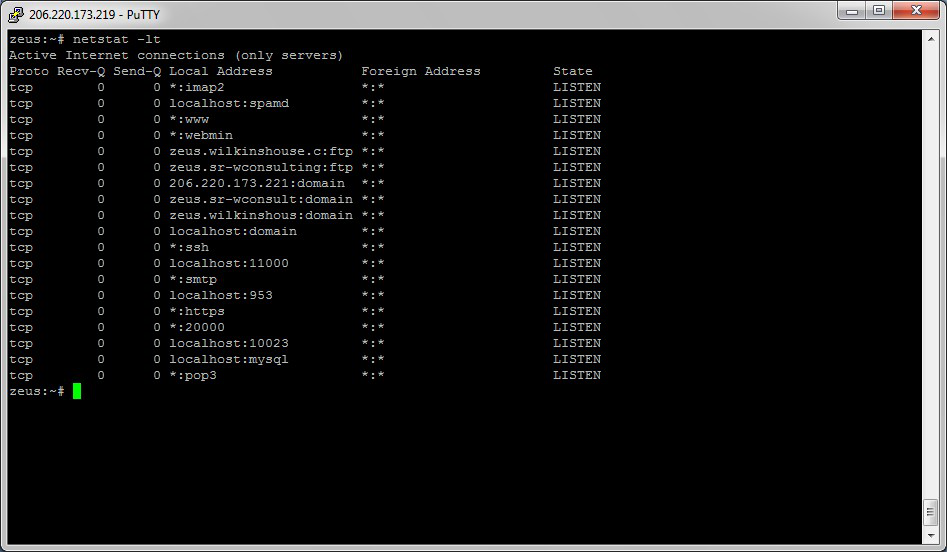
Often, one of the things that are required to be figured out is the current state of the active network connections on a host. This is very important information to find for a variety of reasons. For example, when verifying the status of a listening port on a host or to check and see what remote hosts are connected to a local host on a specific port. It is also possible to use the netstat to determine which services on a host that is associated with specific active ports.
Check this example of the netstat being used to display the currently active ports on a Linux machine.
7.Nslookup
Some of the most common networking issues revolve around issues with Dynamic Name System (DNS) address resolution issues. DNS is used by everyone using the Internet to resolve commonly known domain names (i.e. google.com) to commonly unknown IP addresses (i.e. 74.125.115.147). When this system does not work, most of the functionality that people are used to goes away, as there is no way to resolve this information. The nslookup command can be used to lookup the specific IP address(es) associated with a domain name. If this utility is unable to resolve this information, there is a DNS issue. Along with simple lookup, the nslookup command is able to query specific DNS servers to determine an issue with the default DNS servers configured on a host.
8.Ipconfig/ipconfig
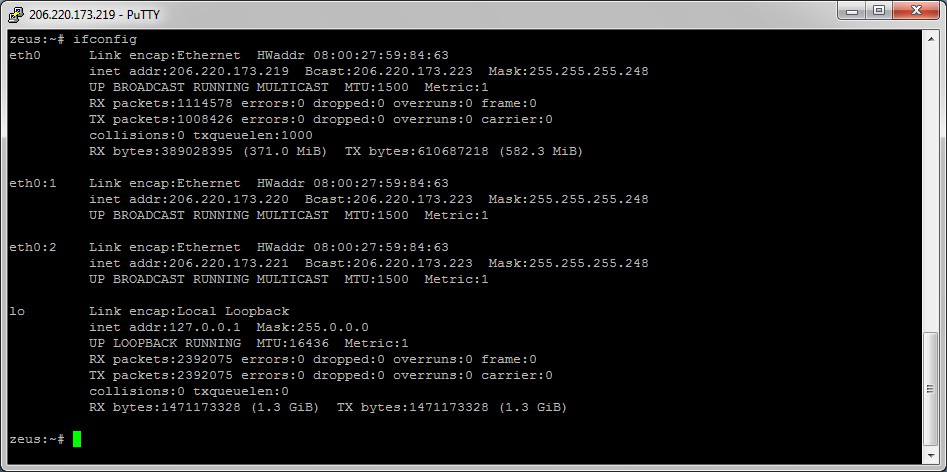
One of the most important things that must be completed when troubleshooting a networking issue is to find out the specific IP configuration of the variously affected hosts. Sometimes this information is already known when addressing is configured statically, but when a dynamic addressing method is used, the IP address of each host can potentially change often. The command that can be used to find out this IP configuration information includes the ipconfig utility on Windows machines and the ifconfig utility on Linux/*nix based machines.
Check this example of the if config utility showing the IP configuration information of a queries host.
9.Tracert/traceroute
Typically, once the ping command has been used to determine basic connectivity, the tracer/traceroute can be used to determine more specific information about the path to the destination host including the route the packet takes and the response time of these intermediate hosts.
10.Ping
The last but the most important one is the Ping. Ping is used to providing a basic connectivity test between the requesting host and a destination host. This is done by using the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) which has the ability to send an echo packet to a destination host and a mechanism to listen for a response from this host. Simply stated, if the requesting host receives a response from the destination host, this host is reachable. This command is commonly used to provide a basic picture of where a specific networking problem may exist. For example, if an Internet connection is down at an office, the ping can be used to figure out whether the problem exists within the office or within the network of the Internet provider.
Check the example of the ping being used to obtain the reachability status of the locally connected router.
If you want to know Mpls configuration in Cisco packet tracer, please read our other blog, you'll get an answer.
Note: if you want to get more commands, and you can contact SPOTO.
More Topic you may be interested:
1. Brief Introduction to Virtual LANs and VLAN Trunking
2. Do Cisco’s New Exam Tracks Deconstruct the Certification Pyramid?
3. Some Valuable and Free Cisco Certification Study Materials to Download

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷