The article is mainly about MPLS Configuration Gns3 LAB.
MPLS is an important part of SPOTO CCIE RS 400-101 laboratory examination. However, some candidates find it difficult to master these parts of the CCIE RS Lab exam easily for MPLS, SPOTO candidates. More information can be found in the SPOTO Cisco WhatsApp team.
MPLS configuration Gns3 lab
This article is about MPLS (Multiprotocol label switching, a telecom operator (ISP). That is commonly used in remote connection solutions Before discussing the technology, the first thing to note is that the enterprise environment or technology configuration in the enterprise is completely different from the MPLS cloud service provider (ISP).
Why use MPLS
MPLS is a fast packet-based switching based on the label. The routing device switching process is usually used, where whenever a data packet is received, it checks its IP address and forwards the IT after matching the routing table. This process can involve "transmitting the MAC address of the ARP request". Imagine that when high traffic like VOIP, the process becomes a little slow. For example, an IP phone call packet can use 100 / S, and then each router 100 can execute on the packet processor. Other layers 2 technologies (i.e. HDLC, ATM, and Frame Relay) and traditional technologies for different remote applications use MPLS label base layer technology, also known as routing label base. The solution is that each packet router in MPLS allocates tags for fast switching.
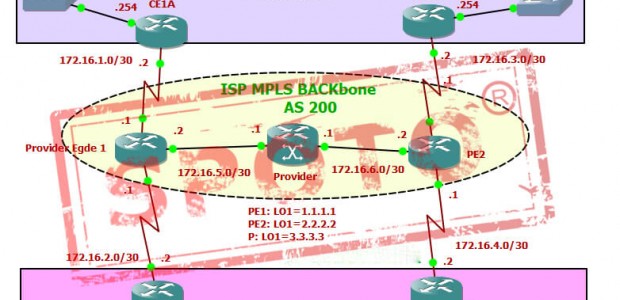
Here is our lab MPLS cloud, which is created in GNS3. You can see that we have a network service provider marked as an "ISP MPLS Backbone" and have two customer benefits.
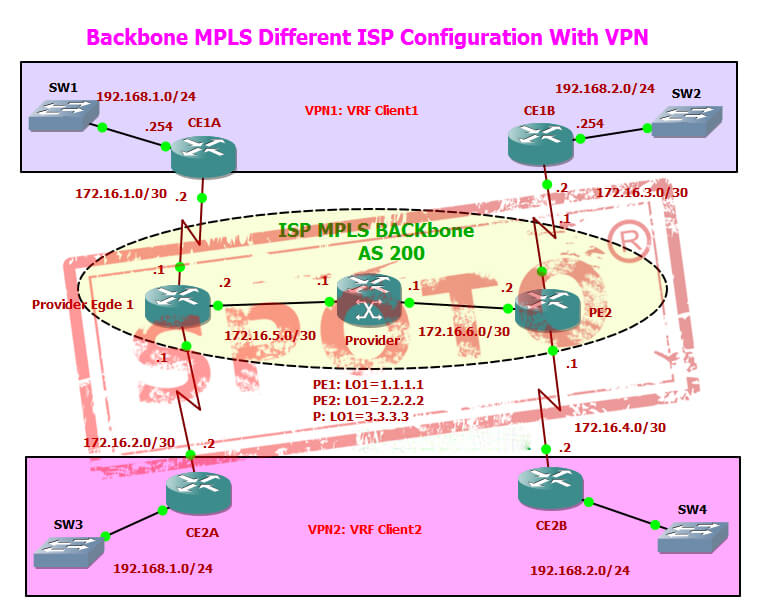
Before entering the configuration, the reader must bear in mind some basic concepts to understand the elements involved in the scene role
Customer Edge (CE)
The customer edge (CE) device is installed in the remote unit company and will receive the connection provider solution.
Provider Edge (PE)
Provider Edge (PE) connects to one (or more) client router carrier routers, PE and P routers. P (provider) represents the network infrastructure of operators distributed by other routers MPLS cloud.
Virtual Routing and Forwarding
Another key concept is the technology VRF (Virtual routing and forwarding), which brings two other equally important elements: RD (routing differentiation) and RT (routing target). With VRF, you can create multiple instances of the routing table that exist in the router at work. This partition is increased by allowing network paths without using multiple devices. In all customer operator subnetworks, a single table does not have separate VRF routing traffic, which would not be good from a security point of view. Another common benefit is that it enables customers to use the same network address.
However, at some point, the route between the router and the corporate (CE) and the operator router (PE) must be reassigned to the BGP process of the PE.
Here there is a problem: Obviously, VRF may have duplicate addresses, because they represent different routing tables. This can only be a unique so-called the RD (routing identifier) identifying pain by adding a route.
Follow Cisco MPLS configuration step by step and more articles, and you can contact SPOTO blog. we will timely the latest news that you can know something happening.
About SPOTO
SPOTO focus on online IT Certification training for 16 years. SPOTO offers 100% real and valid Cisco CCNA, CCNP, CCIE, ISC, Amazon AWS, Microsoft, and other IT exam practice tests. And we have many free online training courses of Cisco exam on YouTube. You can find many useful and helpful tips and suggestions. If you’re still worried about to prepare and pass the Cisco exam, try SPOTO now. SPOTO tutors will help you get the CCIE number at the first try.

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷