OSPF uses LSDB (link state database) and populates LSA (link state notification) to hold the topology information and LSA saved in LSDB. Instead of using one LSA packet, OSPF has many different LSAs. OSPF LSA is popular with the world in recent years, SPOTO has a 16-year IT training and various certification exams such as CCIE RS, CCNA, CCNP, CISSP, AWS, Huawei and online courses.
Here is the list:
LSA Types | Description |
Type 1 | Router LSAs |
Type 2 | Network LSAs |
Type 3 or 4 | Summary LSAs |
Type 5 | Autonomous system external LSAs |
Type 6 | Multicast OSPF LSAs |
Type 7 | Defined for not-so-stubby areas |
Type 8 | External attribute LSAs for Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) |
Type 9, 10, and 11 | Opaque LSAs |
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Type 9, 10, and 11 Opaque LSAs
LSA Type 1: Router LSA
Type 1 router LSAs are generated by internal routers. It can identify its "O" route in the routing table, only enter type 1 LSA flood in its area; do not cross ABR. In the type 1 LSA, you will find a list of all direct connect links that contain this router.
LSA Type 2: Network LSA
A network LSA or Type 2 is created for each multiple access network. The LSA 2 is only advertised by the traffic network in its area and the DR of the flood, and the LSA network does not cross the ABR. You can identify a "0" route in the routing table. In the Type 2 LSA, you will find all routers, DRs, prefixes, and subnet masks that are connected to multiple access networks.
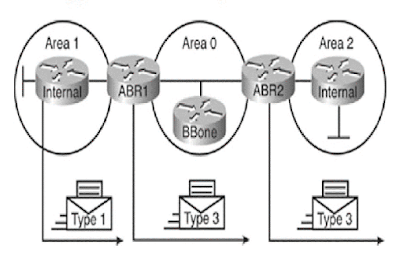
LSA Type 3: summary LSA
The ABR creates a digest LSA to send updates from one zone to another. You can identify the is "OIA" route in the routing table. The LSA is used to flood the original area and cost of the network information subnet but without topology data.
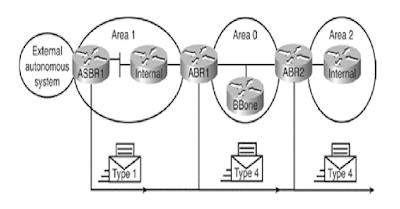
LSA Type 4: ASBR summary LSA
Type 4 LSA is used to advertise as ASBR to all other areas in the autonomous system. ASBR summary LSA includes the router ID of the ASBR in the link-state ID field.
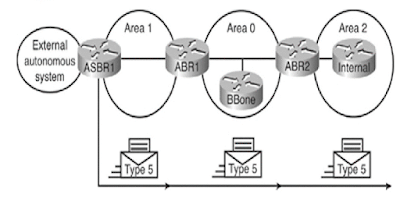
LSA Type 5: External LSA
Type 5 External LSAs, also known as autonomous system external LSA, are external LSAs created by ASBRs for external routes redistributed to OSPF (LSA 5). The external LSAs are advertised and owned by the original ASBR. The external lsa flooded the entire autonomous system, and the IT router ID (ASBR) of the entire autonomous system did not change. To find an ASBR, a Type 4 LSA is required.
LSA-6 Multicast OSPF LSA
Type 6 LSA are used in multicast routing (MOSPF routing protocol) multicast LSA (Cisco routers do not support).
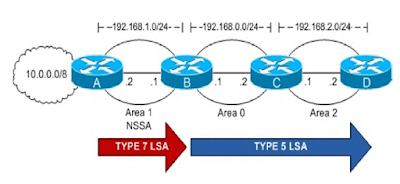
LSA Type 7: NSSA external
Type 7 LSA is created by ASBR inside an NSSA, instead of a type 5 LSA. Type 7 LSA flooded only within its area of origin converted to Type 5 LSA on an ABR toward other areas.
·N1- metric increase as it is passed through the network
·N2- metric doesn’t increase (default)
LSA Type 8: external attribute LSA
External attribute LSA is created by ASBR during BGP to OSPF redistribution to preserve BGP attributes of redistribution network.
LSA Type 9, 10, 11
·Used in OSPF and BGP inter-networking

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷














