ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is a network protocol used to find the hardware (MAC) address of a device from an IP address. this feature will be used when the device is to communicate with certain other devices on the local network (e.g., on the ethernet network that needs to know the physical address before sending the packet). The sending device uses ARP to convert IP addresses to MAC addresses. The device sends an ARP request message containing the IP address of the receiving device. All devices on a local network segment can see the message, but only a device with that IP address can respond with an ARP reply message containing its MAC address. Now the sending device has enough information to send packets to the receiving device.
ARP request packet is sent to broadcast address (for Ethernet broadcast, is FF: FF: FF: FF: FF: FF: FF: for IP broadcast is 255.255.255.255).
Here is the explanation of the ARP process:
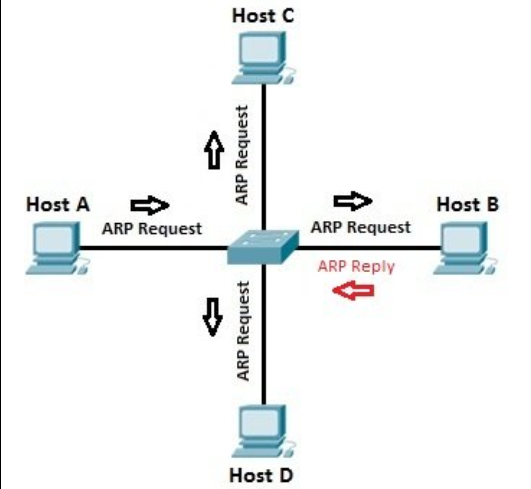
Suppose host A to communicate with host B. Host A knows the IP address of host B, but does not know the MAC address of host B. To find the MAC address of host B, host A sends ARP request, lists the IP address of host B as the destination IP address, and lists the MAC address of FF: FF: FF: FF: FF (Ethernet broadcast). Switching opportunities forward frames to all interfaces (except incoming interfaces). Each device on a network segment receives the packet, but since the destination IP address is the IP address of host B, only host B will respond using the ARP reply packet and list its MAC address. Host A now has enough information to send traffic to Host B.
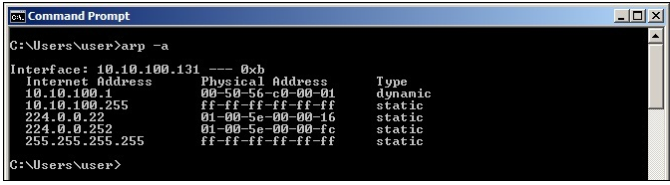
All operating systems maintain ARP caches that were checked before sending ARP request messages. Each time a host needs to send a packet to another host on the LAN, it first checks its ARP cache for the correct IP address and the matching MAC address. The address will be kept in the cache for a few minutes. You can use the arp-a command to display ARP entries in Windows:
Notice that SPOTO will update more CCNA technical articles. if you are interested in this, and you can follow SPOTO. you can get some free study materials. besides, SPOTO is a leader for training in the various certification exams, and we have real exam answers and questions. we can guarantee you can pass the exam in the first try.
More Recommended Articles
1. The CCNA Basic: Pipe character in IOS
2. How much is it going to cost for taking the CISSP exam?
3. Top 10 Certifications You Can Do In 2020
4. Will a CCNA security certification help in cybersecurity jobs (freshers)?

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷














