The IP header is the prefix of the IP packet that contains information about the IP version, the packet length, the source IP address, and the destination IP address. It consists of the following fields:
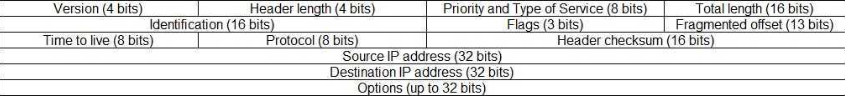
Here is a description of each field:
Version – The version of the IP protocol. For IPv4, the value for this field is 4.
Header length –The length of the header (in 32-bit words). The minimum value is 20 bytes and the maximum value is 60 bytes.
Priority and Type of Service – Specifies how the datagrams should be processed. The first 3 bits are priority bits.
Total length – The length of the entire packet (header data). The minimum length is 20 bytes and the maximum length is 65535 bytes.
Identification – For distinguishing segmented data packets from different datagrams.
Flags – used to control or identify fragments.
Fragmented offset – If the packet is too large to fit into the framework, it is used for segmentation and reorganization.
Time to live – Limit the lifetime of the datagram. If the packet does not reach the destination before the TTL expires, it is discarded.
Protocol – Define the protocol used in the data section of the IP Datagram. For example, TCP is represented by the number 6, and UDP by the number 17.
Header Checksum – Error check for the header. If the packet reaches the router and the router calculates a checksum that is different from the checksum specified in this field, the packet is discarded.
Source IP address – the IP address of the host that sent the packet.
Destination IP address – the IP address of the host that should receive the packet.
Options – Used for network testing, debugging, security, etc. This field is usually empty.
Consider the following IP header, captured with Wireshark:
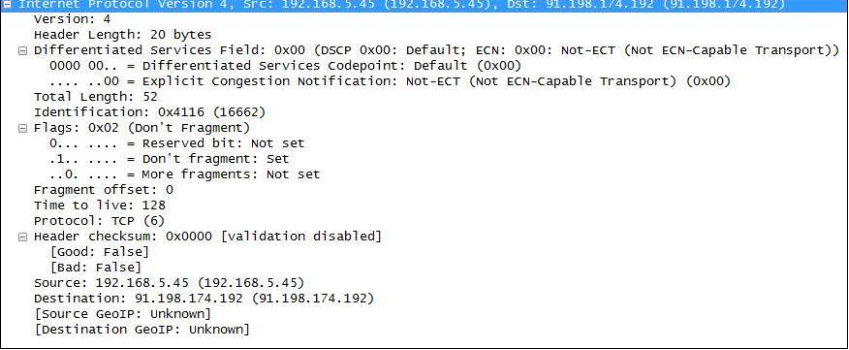
Note the fields in the header: the IP version is the IPv4, header length of 20 bytes, the upper layer protocol set the TCP, TTL value to tu 128, lists the source IP address and the destination IP address, and so on.
SPOTO is committed to training in various Cisco certification exams, and we timely update the latest exam information that many candidates are interested in. We also update related technical topics, and you can follow SPOTO where you will get more useful articles.
The latest news:
CCIE Routing and Switching exam seats can be book now:
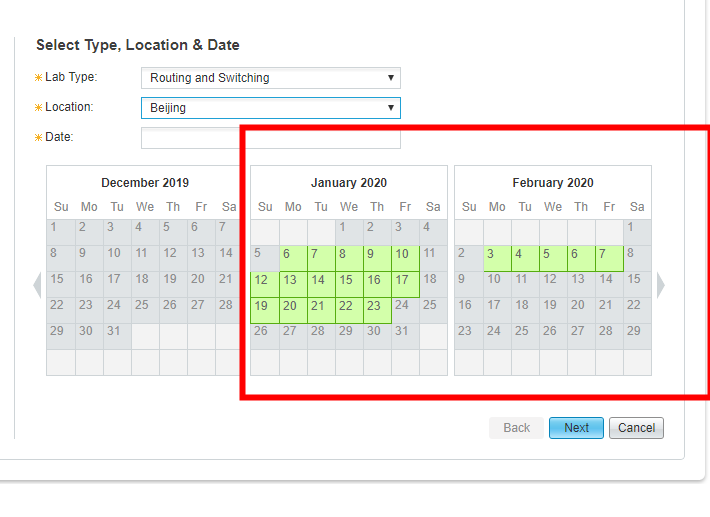
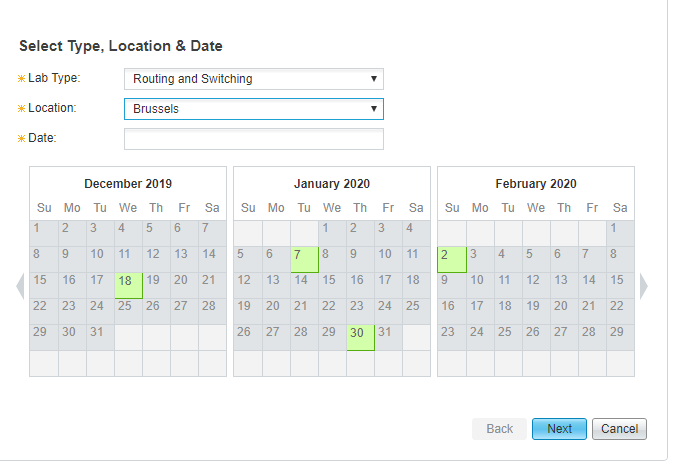
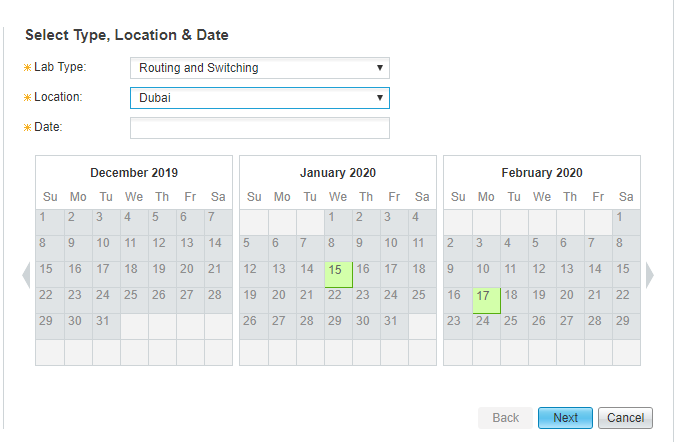
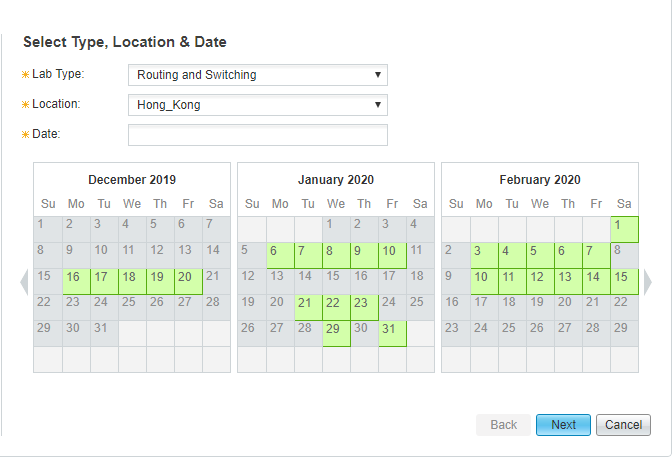
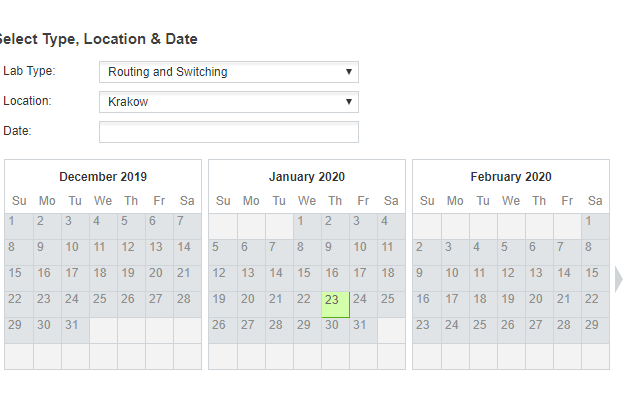
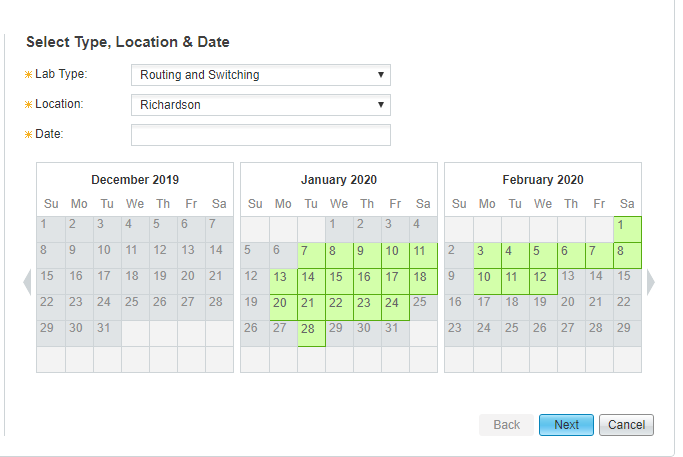
Note: if you want to get more exam seat information, and you can join SPOTO WhatsApp study group: https://chat.whatsapp.com/FwQuSIDASCd7DHTDdIIcSa
More Recommended Articles
1. 6 Hot IT Skills You Should Gain to Discover the Internet of Things
2. New CCNP: How to Prepare in 2020?
3. Looking Ahead: The Future of CCIE Lab in 2020

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷














