What Is MPLS?
Multi-Protocol Label Switching is a technology to deliver IP services - MPLS enables network services
such as VPN and traffic engineering
· Forwarding of data packets is via labels
– MPLS enabled routers do not look into IP header to forward packets
·MPLS is known as OSI layer 2.5
– Label info is inserted between Datalink and Network layer and this is sometimes called shim header

MPLS works over most Layer 2 technologies such as ATM, FR, PPP, POS, Ethernet
Why it was developed?
· Network infrastructure convergence
– MPLS enabled network allows to carry different kind of traffic
(IPv4, IPv6, Layer2 frames) across single network infrastructure
· No need to have BGP enabled on all routers
– Very important for scaling lare networks – because MPLS
forwarding is done via labels, we do not need to keep all destination IP addresses in routing tables
Why it was developed?
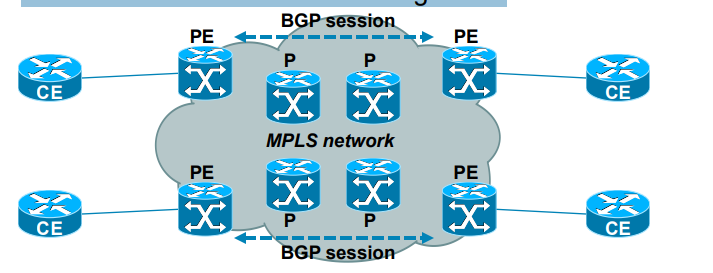
· New approach to VPN technologies
– Allows use of overlapping IPv4 address space
– Allows optimal traffic flow
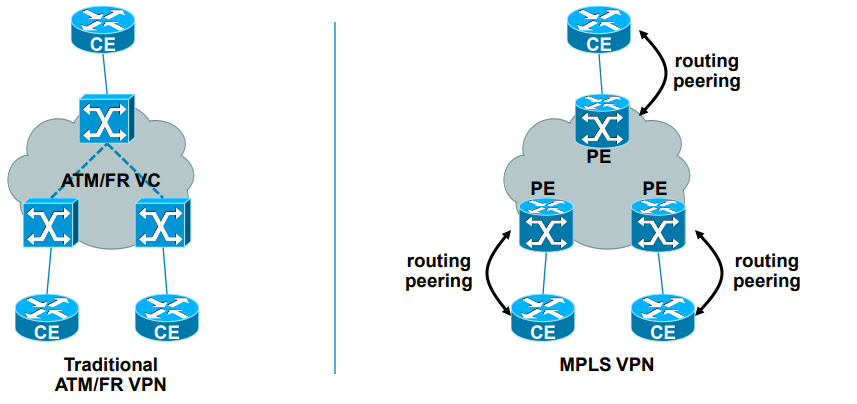
Why it was developed?
· Traffic engineering
– The preffered path is the least-cost path determined by IGP
– Basic idea is to use links in network infrastructure efficiently
– MPLS needs to be able to provide mechanism to divert traffic to other links beside preffered path
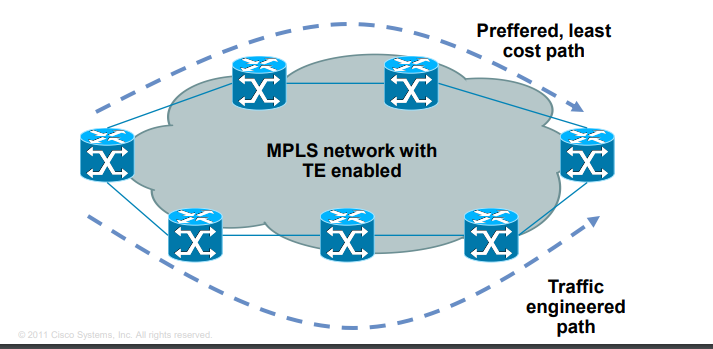
How MPLS works
What are the principles of MPLS?
Main building stones of MPLS:
Label – 32bit value inserted between Layer 2 and Layer 3
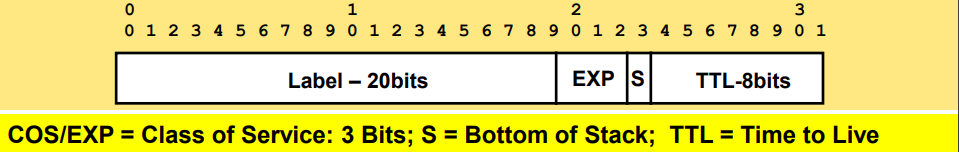
· LSR – Label Switch Router (eg. PE, P)
· LSP – Label Switched Path
· IGP – Interior Gateway Protocol
· LDP – Label Distribution Protocol
· LIB, LFIB – Label Information Base, Label Forwarding Information Base
· MP-BGP, RSVP – Protocols for MPLS VPN and MPLS TE
Join SPOTO to get more latest knowledge of MPLS. And SPOTO offers 100% real and stable Cisco exam dumps to help candidates to pass the exam fast and in the first try.
What are the principles of MPLS?
Life of a packet in MPLS network:
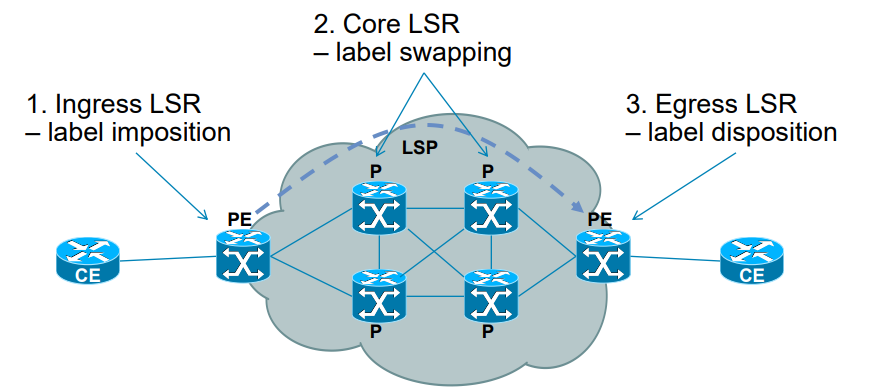
Egress LSR not always performs label disposition
- PHP (Penultimate Hop Popping) signaled via an implicit null label
(LDP advertising MPLS label of value three)
What are the principles of MPLS?
Each LSR needs to run IGP to learn IP prefixes (eg. neighbor
loopbacks, BGP next hops)
· Each LSR then forms LDP neighborship between its directly
connected LSR
· Once LDP neighborship is formed, each LSR uses LDP to assign
labels to IP prefixes it knows about – each LSR does this
independently and advertises its labels to its LDP neighbors
· LDP is standards-based – RFC 3035 and RFC 3036
· LDP uses UDP for session discovery (port 646 and destination IP
224.0.0.2)
· LDP uses TCP (port 646 and destination IP of its LDP peer) for rest of the messages (label advertisement, label withdrawal, session maintenance, session teardown)
Assigning and distributing MPLS labels
© 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 12
What are principles of MPLS?
Forwarding MPLS packets – which label to use?
· RIB stores IP prefixes, LIB stores MPLS labels
· LFIB is created from both RIB and LIB and used to forward MPLS tagged packets
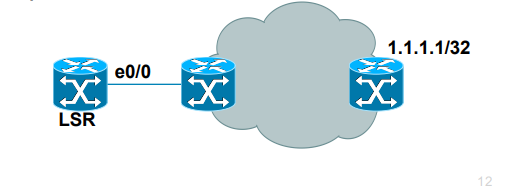
Example for LSR in bottom picture:
- RIB has 1.1.1.1/32 learned via IGP over e0/0 interface
- LIB has label “L” for prefix 1.1.1.1/32 learned from its LDP peer
- LFIB has: “to forward packet to 1.1.1.1/32, use label L and send
packet using peer LDP nexthop over e0/0 interface”
What are the uses of MPLS?
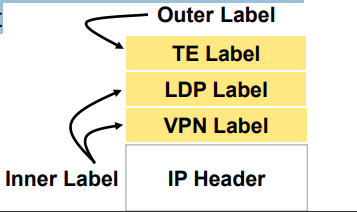
Label stacking
Labeling does not make forwarding of packets faster
· Label stacking is the primary use of MPLS that enables use of
MPLS L2 and L3 VPNs, traffic engineering and other services
· Most used examples of label stacking:
- 2 labels for MPLS VPN – the bottom label indicates which VPN this
packet belongs to, outer is used by core LSRs for packet
forwarding
- 3 labels for MPLS TE – the most upper label is used to indicate
which TE tunnel to forward this packet
What are uses of MPLS?
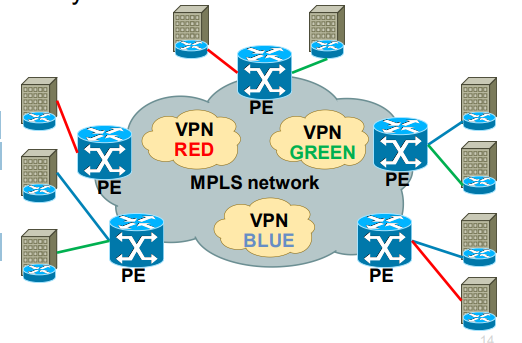
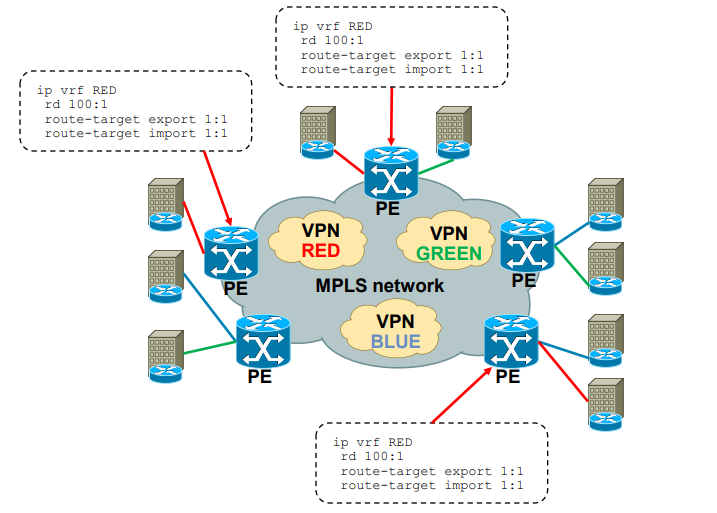
Use of MPLS to build Layer 3 VPN
MPLS VPN is set of sites that communicate with each other – these
sites can be connected to MPLS infrastructure at various PE routers
· PE LSR acts as aggregation router in MPLS VPN – each site is
identified by its own VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) instance,
which is logically separated and by default communication between
VRF is not allowed
Each PE router assigns distinct MPLS label for each VRF it communicates
with other PE routers – this label is not assigned by LDP, but by MP-BGP, and is used to know which VRF site remote PE needs to send packet to
What are the uses of MPLS?
Use of MPLS to build Layer 3 VPN
RD (Route Distinguisher) is attached to each IP prefix exchanged in
VPN to make them unique – RD + prefix = VPN prefix
· RD allows using overlapping IP addresses among VPNs
· RD length is 64 bits and is informant X: Y, where X is usually
Autonomous System Number or IP address – usually one RD is
assigned per one customer
d RT (Route Target) governs which VPN prefixes are allowed to be
imported or exported out of particular VPN
· Using RT you create intranet or extranet
- Intranet – different sites of “same” VPN can communicate
- Extranet – different sites of “different” VPNs can communicate
· In order to bring L3 VPN into life, you need to exchange both RD
and RT – this is done by MP-BGP
What are uses of MPLS?
MPLS Layer 3 VPN Intranet for customer in VPN RED
What are uses of MPLS?
MPLS Layer 3 VPN Intranet for customer in VPN GREEN
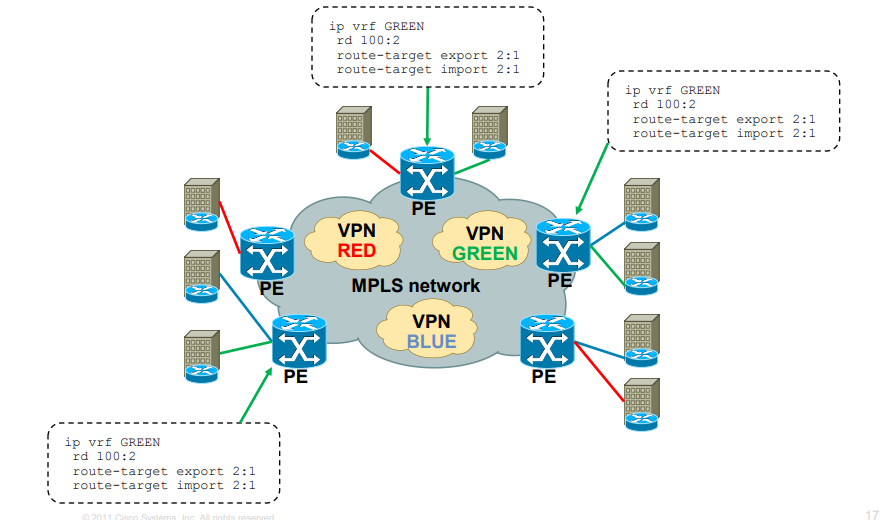
What are uses of MPLS?
MPLS Layer 3 VPN Intranet for customer in VPN BLUE
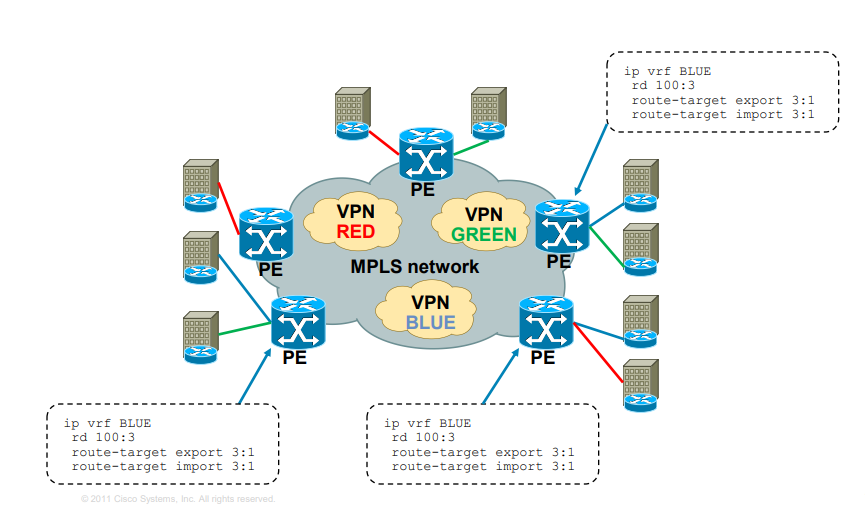
What are uses of MPLS?
MPLS Layer 3 VPN Extranet between customer VPN RED and VPN BLUE
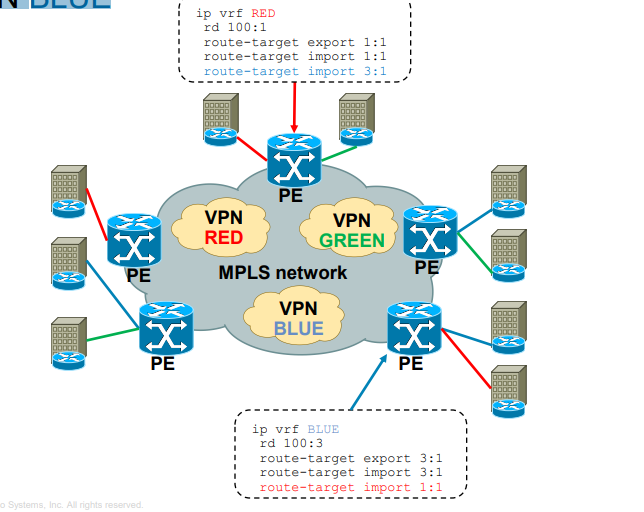
What are uses of MPLS?
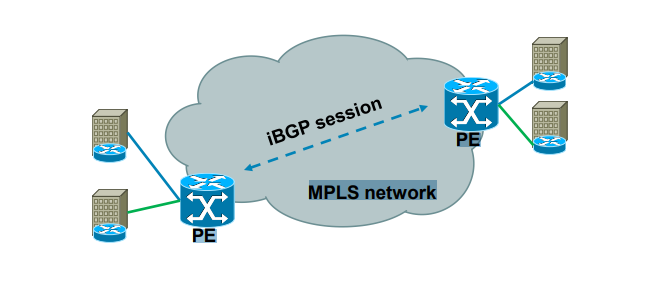
Exchanging RD, RT and VPN label over MPLS network
MPLS network
PE
· Each PE router forms iBGP session with other PE router
· Over this iBGP sessions, PE routers exchange VPN prefixes
· Each VPN prefix is exchanged with its associated RT and VPN
label – RT is for importing routes into VRF RIB, VPN label is for
actual packet forwarding
What are the uses of MPLS?
Packet forwarding with MPLS Layer 3 VPN
· IGP label is assigned by LDP
· VPN label is assigned by MP-BGP
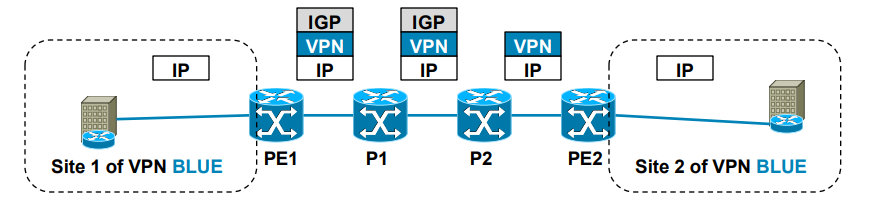
1.) PE1 receives IP packet on VRF interface assigned to site 1 of VPN BLUE.
2.) PE1 looks up VPN and IGP label, imposes this label stack to IP packet and forwards it to MPLS network. IGP
label is known based on iBGP next hop, which is IP address of PE2.
3.) P1 router swaps IGP label based on its LFIB table.
4.) P2 removes IGP label due to PHP, but does not touch VPN label.
5.) PE2 router receives IP packet with VPN label, which it uses to select correct outgoing VPN site
6.) PE2 then strips off VPN label, makes lookup in its VRF RIB for particular VPN site to get the outgoing interface to
Join SPOTO to get more latest knowledge of MPLS. And SPOTO offers 100% real and stable Cisco exam dumps to help candidates to pass the exam fast and in the first try.

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷














