The following sections describe how to configure and verify EIGRP for IPv6 EIGRP is an enhanced version of IGRP. It is an enhanced distance vector protocol, which relies on diffusion update algorithm to determine the shortest path to the destination in the network. The EIGRP of IP version 6 will work in the same way as EIGRP IP version 4 and can be configured and managed separately. The IPv6 is an important part of the Cisco certification exam, which will improve your ability to pass the exam.
From IPv4 to IPv6, the mechanism and configuration technology will be slightly different. Engineers or professionals using IPv4 will be able to gain access to IPv6 concepts very easily. Inappropriate cases, EIGRP maintenance protocol function parity. Because of this difference, the operation and configuration will be slightly different.
There are few key differences between version 4 and version 6 are such as:
The EIGRP for IPv6 routing process will use the shutdown feature
With the EIGRP for IPv6, the router ID is needed on each router or a routing process will not start.
The EIGRP for the IPv6 is configured directly on a router interface.
To solve some of the problems in IGRP, Cisco has created an enhanced version of EIGRP, which is significantly more functional than IGRP. In order to advertise routing information when necessary and change without periodic notification of routers, layer 3 independent transparent protocols can carry out reliable multicast and unicast transmission. In order to keep the loop-free operation at each time, EIGRP uses feasibility conditions to identify neighbors and provide a guaranteed loop-free path for a given destination. It will allow EIGRP routers to avoid forwarding packets from routing loops to neighbors.
In order to deal with multiple topological changes in single diffusion calculation, EIGRP implements the finite state machine as a diffusion update algorithm to control diffusion calculation, inserts the collected information, and processes the response into the routing table, or only connects the additional diffusion calculation.
Internet protocol version 6 packets are disabled by default. To enable IPv6 packet forwarding, you must use the ipv6 unicast-routing command in the global configuration before enabling EIGRP. The router ID is a forced router ID. for IPv6 EIGRP to function properly Assuming 1 is not manually configured, one will be generated with the help of a physical interface or loopback. Unlike IPv4undefineds EIGRP, IPv6 may not need to use a command network to advertise the network. This command must be configured on all router interfaces participating in EIGRP. If configuring this command on the interface fails, the network cannot advertise, so neighbors cannot learn. Although EIGRP for IPv6, is configured throughout the interface, log messages will notify that an adjoining has been formed.
You can use passive-interface commands to control routing information notifications. When exchanging updates through other interfaces is allowed, this command allows route updates to be suppressed through some interfaces. When it is used with EIGRP, it suppresses hello packet exchange between routers, which will result in loss of neighbor relationships. Therefore, it is only used in interfaces with no router connected to it. It not only stops routing updates in ads but also suppresses incoming route updates.
To configure EIGRP, for IPv6, you must have knowledge of EIGRP IPv6 and IPv6 addressing. There are also some limitations to configuring EIGRO for IPv6. You can use EIGRP for IPv6 to configure the interface directly without using a global IPv6 address. There is no network declaration in IPv6undefineds EIGRP. IPv6undefineds EIGRP has a shutdown function that ensures that the routing process is in mode-you can start running the protocol without shutting it off. Before running, you need to configure the router ID. for the EIGRP IPv6 protocol instance
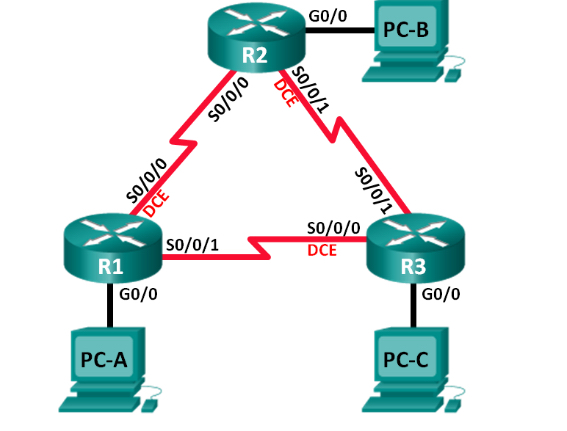
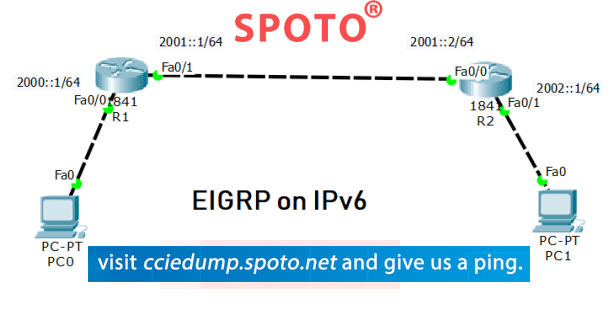
Build a network and check the connectivity:
Set up the network topology, just configure basic settings, such as device access, password, and interface IP address.
as shown in the network topology above, the connection network
Configure the PC host to initialize and reload the router configuration settings for each router as needed to disable DNS Lookup to configure the router IP address as indicated in the address table. In this case,
configure the FE80: x link-local address and the unicast address for each router interface.
The device name given in the configuration topology allocates Cisco to vty and console passwords. Specify the class as a privileged
EXEC password to configure logging synchronous to prevent vty and console messages from interrupting command entries.
Configure a one-day messageCopy a running configuration to startup the configuration.
Verify the connectivity
Routers must be able to ping each other, and each PC must be able to ping its default gateway. PC cannot ping other PC. until EIGRP routing is configured Then verify and troubleshoot as needed.
Configure the EIGRP for the IPv6 routing:
1.Enable the IPv6 routing on a router
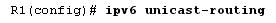
2.Assign the router ID of each router
To start an EIGRP for IPv6 routing configuration process, provide command as ipv6 router eigrp 1, where AS number is denoted as 1.
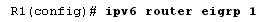
The EIGRP for the IPv6 needs the 32-bit address for a router ID. Then use the command router-id to configure a router ID in a router configuration mode.

3.Enable the EIGRP for IPv6 routing on every router
An IPv6 routing process is shut down as default. Then provide command of no shutdown to enable the EIGRP for IP version 6 routing on the entire router.

4. Configure the EIGRP for IPv6 by using the AS 1 on a gigabit Ethernet and serial interfaces on a router.
Provide the ipv6 eigrp 1 command on the interface that participates in the EIGRP routing process. Assign AS number 1.R in step 2! The configuration is as follows:

Assign the EIGRP participation interface on R3 and R2. When the interface is added to the routing process of the EIGRP, you can find the neighbor adjacent message. The following is the R1 message.

Verify the end to end connectivity
Verify the EIGRP for IPv6 routing:
1. Determine a neighbor adjacency
2. On R1, provide the command show ipv6 eigrp neighbors to verify that the neighbor router has completed the adjoining. The link-local address of the neighbor router displayed in the neighbor table is as follows
3.Examine an EIGRP IPv6 routing table
4. Use the command show ipv6 route eigrp to demonstrate some IPv6 EIGRP routes on the entire router.
5.Examine an EIGRP topology
The example as shown below:
R1# show ipv6 eigrp topology
and if you want to further study the knowledge, and you can contact us by clicking here:
Verify current state and parameters of an active IPv6 process of routing protocol
Provides the command show ipv6 protocols to verify the parameters of the configuration. In the output, EIGRP is the configured IPv6 routing protocol and 1.1.1.1 as R! Router ID. Routing protocols are also associated with autonomous systems 1 with three active interfaces, such as S0 / 0 / 1, S0 / 0 / 0 and G0 / 0.

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷