In this blog, SPOTO will introduce some basic knowledge IPsec VPN, and you can improve your knowledge. The following is the details:
IPSec VPN or VPN
IPSec VPN provides secure IP communication over an insecure network. IPSec VPN has the following features:
Confidentiality
Integrity
Data Origin Authentication
Anti-Replay
Recommended Read:
Introduction to VPN-Virtual Private Network
You would be interested in watching these videos on the Cisco VPN
To Download Self-Study Guide to Cisco VPN IOS
Confidentiality
Confidentiality means using encryption algorithms to keep data secret.
Encryption Algorithm
The encryption algorithm is a mathematical algorithm, which applies data to data, making it impossible for anyone but those with the decryption key to read the data. There are two types of encryption algorithms:-
Symmetric Encryption
Asymmetric Encryption
Symmetric Encryption
The symmetric encryption algorithm is also referred to as secret key encryption. As the name implies, there is a secret key for encrypting and decrypting data. Common symmetric encryption algorithms include:
DES (data encryption Standard) it has a 56-bit key and can be completed in less than 24 hours using a modern computer.
It is no longer in use. 3DES (Triple data encryption Standard) three different 56-bit keys (DES encryption, DES decryption, DES encryption) are used to create ciphertext.
It has not yet been broken, but it has theoretical knowledge.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) 128bit to 256bit keys are used for encryption.
It is a widely used symmetric encryption standard. asymmetric encryption The asymmetric encryption algorithm uses two keys for encryption and decryption. These keys are referred to as public and private keys. No matter what is encrypted by the public key, it can only be decrypted by the private key and vice versa. A common asymmetric algorithm is a digital certificate and an RSA signature.
Integrity
In IPSec VPN, Integrity ensures that your data is not changed during transmission. Before transmitting data from the source, algorithms such as MD5 and SHA are used to calculate mathematical hash values. After the destination receives the data, the hash value is calculated again, and even if a bit is modified during transmission, the hash value does not match. If the hash value does not match, the packet is changed during transmission and will, therefore, be discarded.
Data Origin Authentication
This means that the two devices authenticate to each other before using a pre-shared key or certificate (public key infrastructure) for actual data transfer. It ensures that you send and receive data with the real party.
Pre-sharing-in this method, a single key is applied to two peers. This key is shared before use, so the name is Pre-Shared. Public key Infrastructure-it provides a framework for managing security properties between peers who communicate securely over insecure networks. PKI consists of many elements and network entities.
Some of them are described as follows: digital certificates-contain information that uniquely identifies peers. A signed copy of the public encryption key is used for secure communication, certificate validity, and signature of the certificate-issuing CA.
X.509v3 is the version of the digital certificate currently in use. Distribution mechanism-A method of distributing certificate cancellation list (CRL) over the network. Some common examples can be LDAP and HTTP.
Peers-these devices or people communicate securely over insecure networks (also known as end hosts). Certificate Authority (CA)-Grant and maintain digital certificates. It can be a public CA, Entrust such as VeriSign or an organization can create its own private CA. on Cisco IOS, Microsoft and Linux server operating systems PKI message flow
The host generates the RSA signature and requests the public key of the CA
CA sends it public keys.
The host generates a certificate request and sends to CA.
The CA will use its private key to sign the certificate request and send the certificate to the host.
The host will save it.
The certificate will be used for secure communication.
Anti-Replay
This means that transmission has time or volume effectiveness. If data arrives late it will be considered as altered and will be dropped. Anti-Replay can be defined in kilobytes or seconds.
IPSec Protocols
IPSec uses the following protocols:
Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
Authentication Header (AH)
Internet Key Exchange
IKE is a protocol used to establish security associations between IPSec peers. It provides a framework for exchanging security parameters and policies between them. These security policies must be manually defined by peers. It has the following patterns:
Main Mode
Aggressive Mode
Quick Mode
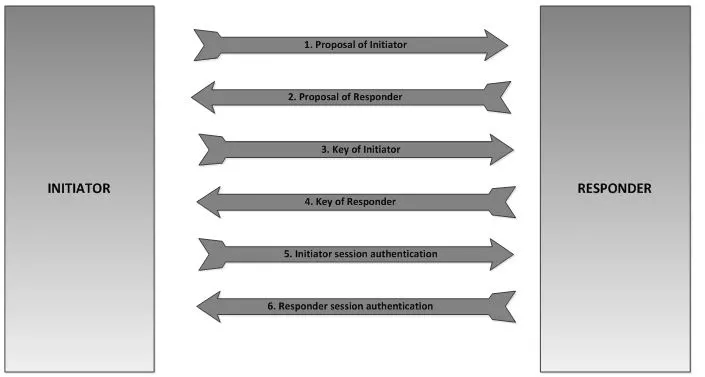
1.The main mode exchanges these six messages in three steps as follows:
step 1-proposal exchange
message 1-the initiator will send his own proposal message to the responder 2-the responder will send his own proposal to the initiator
step 2-key exchange
message 3-the initiator sends his own key to the responder
message 4-the responder sends his own key to the initiator
Step 3-session Authentication
message 5-the initiator will validate session
message 6-the responder will verify a better understanding of the session.
Please refer to the figure below. The positive pattern is converted to three of these six messages. The message sent is as follows: the initiator sends his proposal and key to the responder.
The responder will verify the sponsor undefined proposal. It also sends its own proposal and key to the initiator. The initiator validates the session. For a better understanding, see the following figure for one of the two IKE patterns, which can only be used at a time. The fast mode in fast mode, they will use SPI (security parameter index) to re-check its properties. Each packet sends SPI.
The peer The IKE phase IKE has the following stages:
phase 15 (optional)
phase 2 IKE
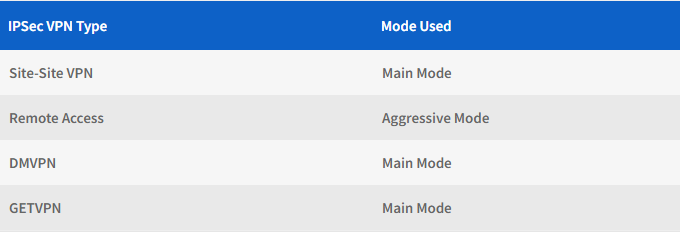
phase 1 in Phase1, which creates an IKE two-way tunnel. A single key is used to verify the session. The pattern used depends on the IPSec VPN.
Table 1 / 3 mentioned below can be used as a reference.
IKE phase 1.5 this is an optional IKE phase. Phase 1.5 provides an additional authentication layer called Xauth (extended Authentication).
Xauth forces users to authenticate before using IPSec connections.
Phase 2 of IKE

when phase 1 is successfully completed, start phase 2. If phase 1 is not completed, phase 2 will never start. In phase 2, they create multiple IPSec one-way tunnels. Each protocol ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) or AH (Authentication Header) creates two tunnels.
Internet security association key management protocol (ISAKMP) IKE is a management protocol which uses ISAKMP for key and attributes exchange. ISAKMP uses UDP port 500.
The IKE version compares the differences between the two IKE versions, The following table shows the steps for IKE version 2 IKE message exchange:
IKE_SA_INIT_ (two messages)
IKE_AUTH CREATE_CHID_SA (two messages)
IKE_ CREATE_SECOND_CHID_SA (optional) / (two messages)
IKE_SA_INIT:
message 1 initiator simultaneously proposes that the basic SA attribute authentication material is equivalent to message 1 and 3
IKE_SA_INIT: message 2 responders in IKEv1 Back to a set of acceptable properties under SA, And the authentication material is equivalent to the message 2 and 4
IKE_AUTH: message 3 authentication material in IKEv1 and the CHILD_SA information has sent the equivalent of message 5-master mode and is part of the fast mode in IKEv1
IKE_AUTH: message 4 authentication material and CHILD_SA information has sent the equivalent of message 6-master mode and is part of the fast mode in IKEv1. VTI, GRE and IPSec complete.
Optional
CREATE_CHILD_SA: message 1 initiator sends its authentication material and ID additional sub-exchange-equivalent to fast mode
CREATE_CHILD_SA: message 2 responder in IKEv1 sends its authentication material and ID additional sub-exchange-equivalent to fast mode in IKEv1

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷