1, MPLS multi-protocol label switching
Today, SPOTO will review the MPLS VPN and some basic knowledge of MPLS. It will be helpful for you to prepare CCIE certification exam. SPOTO offers 100% real and valid Cisco exam questions and answers to help you pass the exam fast.
(1) Comparison of IP and MPLS
IP forwarding principle:
The routing table (static\RIP\OSPF, etc.) is used to generate the routing table and forward it according to the destination IP address. During the forwarding of IP packets, the destination IP address remains unchanged. Two tables are used:
RIB (Routing Table): A routing information base that obtains routing information through various routing protocols.
FIB (CEF table): Forward the information base generated based on the RIB to guide the forwarding of the IP message.
The router receives the data packet, looks at the destination IP address (IP header) of the data packet, looks up the CEF table, and forwards the data according to the CEF table.
Note: If you have any questions or are looking for more information regarding the MPLS and Cisco practice tests, click here and contact us now.

And You can watch SPOTO online training videos to know the basic introduction of MPLS.
MPLS forwarding principle:
An Mpls header may be inserted between the second layer header and the third layer header to insert a plurality of Mpls headers. The router receives the data packet, looks at the label of the data packet (MPLS header), looks up the label forwarding table, and forwards the data according to the label forwarding table. The label forwarding table is generated by the LDP protocol.
The length of the IP header is 20 bytes, and the length of the MPLS message header is 4 bytes. The efficiency based on Mpls forwarding is higher than the efficiency based on IP forwarding.
The IP network forwards data hop by hop, receives the data packet, and finds the routing table and sends it to the next hop. It does not care who the next hop router will send the packet to. In an MPLS network, labels are pre-assigned and LSPs are generated.
IP hop-by-hop forwarding. At each hop that passes, the longest matching lookup of the routing table must be performed (possibly multiple times), and the speed is slow. MPLS tag forwarding establishes a label forwarding channel (LSP). For the packet through pre-assigned tags Only one label exchange (fast search) is required for each device passing through the channel.
(2) MPLS terminology
Label: Similar to the role of the destination IP address, the router forwards the data based on the label. Is a relatively short, fixed-length, usually only local-meaning identity, these tags are usually located between the data link layer encapsulation header and the three-layer data packet of the data link layer, and the label is mapped to the FEC through the binding process.
Note: If you have any questions or are looking for more information regarding the MPLS and Cisco practice tests, click here and contact us now.

LIB: A tag information base that obtains tag values through a tag protocol.
LFIB: Label forwarding information base is generated based on LIB to guide MPLS message forwarding.
FEC: Forwarding Equivalence Class, a group of data packets that are processed in an equivalent manner during the forwarding process. A routing entry is an FEC. The MPLS router generates a label for each FEC (Route Entries). The FEC can be created by using an address, a tunnel, a COS, etc., and only one route in the MPLS currently seen corresponds to one FEC. Usually one label is assigned the same label on one device.
LSP: Label switching channel. The path taken by the data stream is related to the MPLS VPN. An FEC data stream is assigned a deterministic label at a different node, and data forwarding is performed according to these labels.
LSR: Label Switching Router. The LSR is the core switch of the MPLS network. It provides label switching and label distribution.
LER: Label Switching Edge Router. At the edge of the MPLS network, traffic entering the MPLS network is divided into different FECs by the LER, and corresponding labels are requested for these FECs. It provides traffic classification and labels mapping, label removal.
The LDP neighbor does not send the label learned from the neighbor to the neighbor. It is valid locally and is passed to the neighbor to generate the label.
(3) Working principle of MPLS forwarding
In local label: The Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) assigns a unique label value to each local FEC.
Out remote label: LDP obtains the label assigned by the neighbor to the FEC, and selects the optimal placement into the FIB.
Four actions of MPLS forwarding:
The data packet enters the MPLS domain from the IP domain, and the LER pushes the label (PUSH) according to the label forwarding table.
When the MPLS domain forwards a packet, the LSR replaces the label (SWAP) according to the label forwarding table.
When a packet leaves the MPLS domain, the LER is a pop-up tag (POP). PHP: The penultimate jump pops up.
Remove all tags (Untag) at the last hop.
How does the LSR determine that the received packet is an MPLS label message?
Determine whether the bearer is an MPLS packet according to the Layer 2 protocol field: Ethernet: 0x8847 (unicast) and 0x8848 (multicast); PPP: 0x8281 MPLSCP, a new NCP protocol.
(4) MPLS packet header structure:
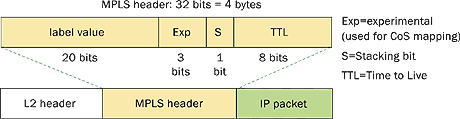
(5) Advantages and disadvantages of FEC
The subtleties of FEC:
IP packets of different destination addresses (which belong to the same network segment) are classified into the same FEC in the ingress and have the same label. In the LSR, only the labels can be quickly exchanged. For traditional IP routing, there is actually a process of re-dividing FEC at each hop. If a router uses the cache function for IP routing and label switching since only the host route can be recorded in the cache for the route, the entry will be very limited, and the label corresponds to the FEC, which may be the network segment. Very few entries match a large number of messages.
Fatal flaws in FEC:
For an FEC, all devices along the way must have the same route (the prefix and mask must be identical) to build an LSP. In other words, on all the devices along the way that use MPLS forwarding, the route aggregation operation cannot be performed for the route to be forwarded by the label.
SPOTO has committed to the MPLS in CCIE, and we have a LIVE focusing on the introduction to MPLS. you can click the bottom to follow us:
Note: If you have any questions or are looking for more information regarding the MPLS and Cisco practice tests, click here and contact us now.
About SPOTO:
SPOTO focus on online IT Certification training for 16 years. SPOTO offers 100% real and valid Cisco CCNA, CCNP, CCIE, ISC, Amazon AWS, Microsoft, and other IT exam practice tests. If you’re still worrying about to prepare and pass the Cisco exam, try SPOTO now. SPOTO tutors will help you get the CCIE number at the first try.
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEjAjr00o5VmNn5r9dIOY5g

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷