In this chapter, we’ll see the basics of multicast. SPOTO is always casting its eye into the Multicast. Recently, SPOTO has gained huge achievement in passing the Certification exams, such as CCIE wireless lab, Collaboration lab, CISSP, CCIE RS, CCNA, CCNP, AWS and so on. SPOTO will give you some valuable study material, and I hope it is helpful to you.
First, let’s talk about what multicast is well in simple words we can say answer multicast is sending a message from a single source to selected multiple destinations.
We can choose three types of traffic for our network:
1.Unicast
2.Broadcast
3.Multicast
Firstly: Unicast
If we want to send messages from a source to a destination, we use unicast. Broadcast if we want to send a message to everyone from a source, we use a radio. If we want to send messages from a source to a set of receivers, then multicasting? Then we use multicasting.
Why do we want to use multicast instead of unicast or broadcast?
Multimedia using Unicast
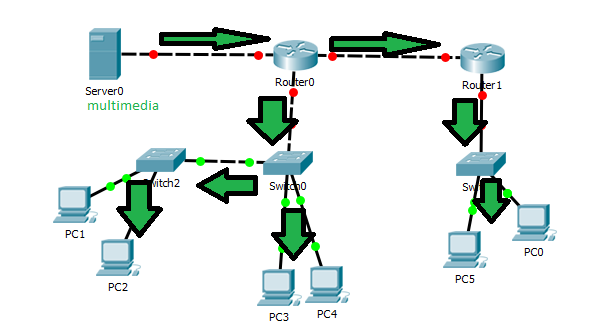
The application sends a copy of each packet to each client. Use only when a few clients need to access the application. If a message must be sent to a large group, the same information must be carried multiple times, even on the same link. The bandwidth usage is proportional to many users. The router makes a separate routing decision based on each source and destination.
Multimedia traffic using broadcast
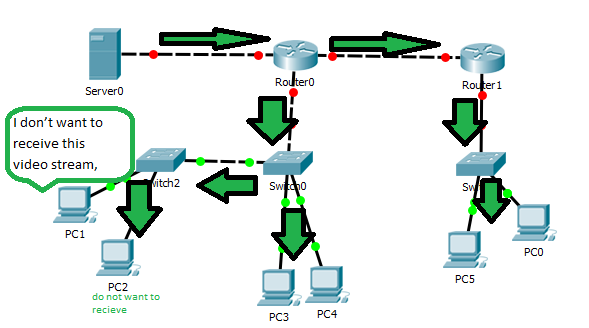
The application uses the broadcast to send a unique copy of each packet. Even if they don't undefined want, all of the terminal hosts need to be processed. An application for transmitting data, voice, or video to a plurality of receivers is not recommended.
Multimedia traffic using multicast
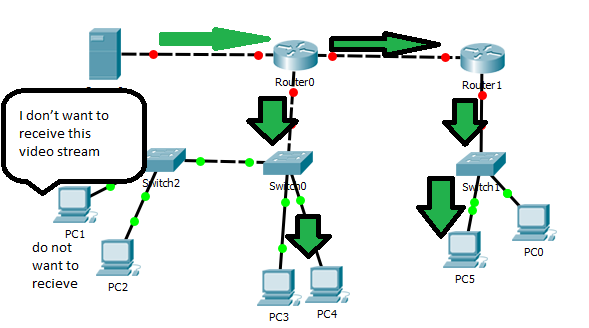
The most effective solution between broadcast and unicast. The server sends a copy of each packet to a special address that represents multiple clients. The server sends a single data stream to a single client.
Advantage of multicast
It saves bandwidth and controls network traffic by forcing the network to copy packets only if necessary. Reduce network bandwidth consumption and host processing. We should Control network traffic and reduce server and CPU load.
Multicast Components
First, we use the specified IP address range for multicast traffic. We use the D range: 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.254. These addresses are used only as destination addresses, but not as source addresses. The source IP address will be the device that sends multicast traffic.
We use IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) to let hosts tell routers the multicast traffic they want to receive.
To help the switch figure out where to forward multicast traffic, we can use IGMP Snooping.
we use a multicast routing protocol: why? we see in this chapter.
DVMRP (Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol)
MOSPF (Multicast Open Shortest Path First)
PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast)
How Multicast Works?
step 1- Multicast server application configured with layer 3 address (class- D)
step 2- Multicast application installed on all the hosts.
step 3- Indicate router that they want to receive multicast traffic for group (IGMP)
step 4- Multicast routing protocol forward multicast server. (PIM)
step 5- Calculate layer 2 multicast MAC address (IGMP Snoping/ CGMP)
This is basic of multicast, Thanks for reading. you can click here to contact us.
Otherwise, we have a piece of good news from SPOTO. There is a Youtube /Facebook live on 3rd, July 2019. The topic of the Live is about MPLS, IP Forwarding Principle and Lable Forwarding Principle. We are waiting for your participation.

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷