Now, SPOTO introduces the IPV6 and you can have a better mastery of the details. SPOTO specialized in IT training over the past 16 years.
The emergence of IPv6 is to fundamentally solve the problem of exhaustion of IPv4 addresses (IPv4 addresses were officially exhausted as early as 2011). The IP address of the IPv4 version is only 4 bytes in size, that is, a 32-bit length IP address. The IPv6 version of the IP address has a size of 16 bytes, which is 128 bits in length.
Migrating from IPv4 to IPv6 is a very difficult task. Because this requires all the host and router IP addresses to be reset. Of course, the emergence of IPv6 also wants to solve most of the flaws in the IPv4 version.
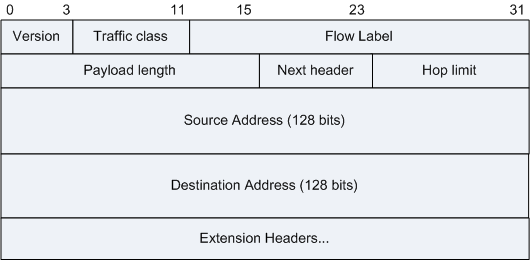
IPv6 Datagram Format
IPv6 Features
The emergence of IPv6 will inevitably lead to an increase in IP addresses and an increase in routing control tables.
The packet header length is fixed at 40 bytes (the IPv4 packet header is typically 20 bytes, but not fixed), and the header check code is no longer used. Simplify the structure of the header, the router no longer does fragmentation processing, reducing the burden on the router.
1. Support plug and play, automatically assign an IP address
2. Authentication and encryption are used.
3. Multicast, mobile IP, etc. may also be supported.
IPv6 Address
IPv6 will usually represent the IP address in hexadecimal notation. Each 16-bit group is separated by a colon. If consecutive 0s are present, these consecutive 0s can be omitted, and two colons are used to indicate the omission. However, an IP address is only allowed to appear once omitted.
In the IPv6 version, the global unicast address is unique worldwide. In IPv6, the first 64 bits of the IP address is the network identifier, and the last 64 bits are the host identifier. Specifically, it can be divided into the following functions:
1. Global route prefix (48 bits)
2. Subnet ID (16 bit)
3. Interface ID (64-bit)
The interface ID is the host identification part, which usually holds the 64-bit version of the MAC address. Sometimes you don't want the other party to know your MAC address, you can use a "temporary address." Such addresses are generally randomly generated and updated regularly.
The form of the link-local unicast address of IPv6: 1111111010+54 0+64 interface IDs. The interface ID here is generally a 64-bit MAC address. This address is used to communicate within the same data link without going through a router.
In order to improve security, some companies use a unique local address that is used when Internet communication is not used (used only within the company). Its form is as follows:
1.1111110+L+Global ID (40 bits) + Subnet ID (16 bits) + Interface ID
2.L is usually set to 1 and the global ID is random.
3. When an intranet communicates with the Internet, it usually uses NAT or a gateway.
IPv6 Fragmentation
IPv6 fragmentation is not performed on the router. This fragmentation will be done once on the sending host, which will increase the network speed. Therefore, in IPv6, "path MTU discovery" is indispensable. However, IPv6 also limits the minimum MTU to 1280 bytes.
IPv4 to IPv6 Transition
The IPv6 datagram is encapsulated into an IPv4 datagram and then transmitted over the IPv4 network. Call it a "tunnel." This requires the router to support both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols.
Finally, SPOTO announces a piece of breaking news. We will have Live on SPOTO Youtube and SPOTO CLUB Facebook. our professionals will further introduce the IPV6. if you are wan to get further study, and you can watch the Live. Don’t miss our Live.

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷














