SPOTO focus on IT certification training for 16 years. We always offer the latest tips and valuable study materials for every engineer. Subscribe us and get more news.
Routing Protocol Authentication (EIGRP )
The router verifies the source of each routing update packet it receives. Many routing protocols support authentication, such as OSPF, EIGRP, ISIS, BGP, and RIPv2.
Cisco routers support methods for receiving different authentication route advertisements from neighboring routers:
1.Plan text authentication
2.Hashing authentication (using MD5)
Simple password authentication:
The router sends the packet and key (if the routing protocol does not support multiple keys, the key number associated with the routing update is 0). If the keys do not match, the routing update is rejected. The only routing protocols for plan text authentication are RIPv2, OSPF, and ISIS.
MD5 authentication
Configure the key (password) and key ID, and the router generates a message digest or hash of the key, key ID, and message. The package key is not sent when the message digest is sent. The neighboring router receives the update and runs the hash algorithm on the route update with the local key. The result is a hash digest. If the hash matches, the router accepts the packet and rejects the update if it does not match. This process is more secure than plain text authentication. IS-IS, OSPF, RIPv2, and EIGRP use MD5.
let see the configuration:-
Topology:
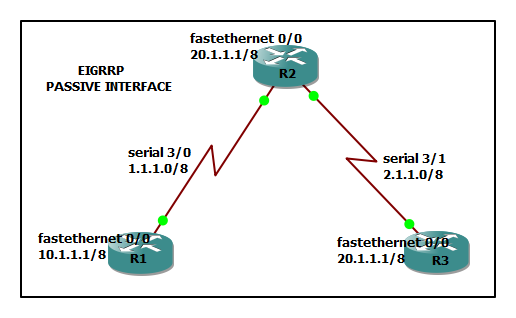
Goal:
·configure the topology as per the diagram
·configure EIGRP 65001 and advertise connected interfaces
·configure router 1 and router 2 to form a neighbor and exchange routing information only after the successful authentication process.
R1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 10.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Serial3/0 1.1.1.1 YES manual up up
R2#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 20.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Serial3/0 1.1.1.2 YES manual up up
R1(config)#router eigrp 65001
R1(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0
R1(config-router)#network 1.0.0.0
R1(config-router)#end
R2(config)#router eigrp 65001
R2(config-router)#network 20.0.0.0
R2(config-router)#network 1.0.0.0
R2(config-router)#end
R1(config)#key chain internetworks
R1(config-keychain)#key 1
R1(config-keychain-key)#key-string ccie
R1(config-keychain-key)#exit
R1(config-keychain)#exit
R1(config)#interface serial 3/0
R1(config-if)#ip authentication mode eigrp 65001 md5
*Mar 18 14:26:40.951: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 65001: Neighbor 1.1.1.2 (Serial3/0) is down: authentication mode changed
R1(config-if)#ip authentication key-chain eigrp 65001 internetworks
R1(config-if)#end
R2#
*Mar 18 14:26:40.903: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 65001: Neighbor 1.1.1.1 (Serial3/0) is down: Interface PEER-TERMINATION received
R2#
*Mar 18 14:26:45.239: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 65001: Neighbor 1.1.1.1 (Serial3/0) is up: new adjacency
R2#
*Mar 18 14:27:26.999: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 65001: Neighbor 1.1.1.1 (Serial3/0) is down: Auth failure
R2(config)#key chain internetworks
R2(config-keychain)#key 1
R2(config-keychain-key)#key-string ccie
R2(config-keychain-key)#exit
R2(config-keychain)#exit
R2(config)#interface serial 3/0
R2(config-if)#ip authentication mode eigrp 65001 md5
R2(config-if)#ip authentication key-chain eigrp 65001 internetworks
*Mar 18 14:30:54.267: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 65001: Neighbor 1.1.1.1 (Serial3/0) is up: new adjacency
R2(config-if)#end
R1#show ip eigrp neighbors
EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(65001)
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 1.1.1.2 Se3/0 14 00:01:59 70 420 0 7
R2#show ip eigrp neighbors
EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(65001)
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 1.1.1.1 Se3/0 10 00:02:27 1296 5000 0 6

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷














