BGP Confederations
We’ll exchange the BGP Confederation with you in this section. You might know, IBGP requires a comprehensive mesh peering which can become administrative overhead. If you don’t know why we need a comprehensive mesh, I advise consulting BGP peers first. Over the past 16 years, SPOTO is a leader in the IT training, and you can get various exam materials to help you clear all certification exam. Let’s look at the following contents now.
IBGP full mesh issues
·As for iBGP, every router in the BGP autonomous system must fully mesh.
·Large number of TCP sessions
·Unnecessary duplicate of routing traffic
·Manual configuration
Solution
1.Route reflector
2.BGP confederations
A BGP confederation consists of AS and sub-ASes to reduce the number of required IBGP peerings. In brief, BGP Confederations Feature is used to divide an autonomous system into smaller autonomous systems.
Confederations are usable only for huge autonomous systems where you can afford to divide them into several sub-ASes. Each sub-as in a confederation is required to have its internal iBGP peers either fully meshed or use route reflector internally. The confederations are not much of an advantage for small ASes having a few BGP routers.
let's see the configuration for better understanding.
Topology:
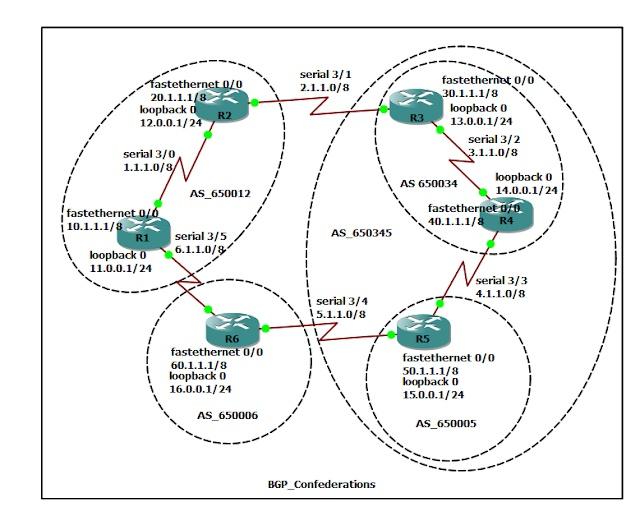
Goal:
·configure the topology as per the diagram and assign the IP addresses.
·configure iBGP and EBGP configuration.
·configure BGP peerings using BGP Confederations.
R1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 10.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Serial3/0 1.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Serial3/5 6.1.1.2 YES manual up up
Loopback0 11.0.0.1 YES manual up up
R2#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 20.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Serial3/0 1.1.1.2 YES manual up up
Serial3/1 2.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Loopback0 12.0.0.1 YES manual up up
R3#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 30.1.1.1 YES manual up down
Serial3/1 2.1.1.2 YES manual up up
Serial3/2 3.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Loopback0 13.0.0.1 YES manual up up
R4#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 40.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Serial3/2 3.1.1.2 YES manual up up
Serial3/3 4.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Loopback0 14.0.0.1 YES manual up up
R5#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 50.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Serial3/3 4.1.1.2 YES manual up up
Serial3/4 5.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Loopback0 15.0.0.1 YES manual up up
R6#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 30.1.1.2 YES manual up up
Serial3/4 5.1.1.2 YES manual up up
Serial3/5 6.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Loopback0 16.0.0.1 YES manual up up
R1(config)#router bgp 650012
R1(config-router)#neighbor 6.1.1.1 remote-as 650006
R1(config-router)#neighbor 1.1.1.2 remote-as 650012
R1(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0
R1(config-router)#network 1.0.0.0
R1(config-router)#network 6.0.0.0
R1(config-router)#network 11.0.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#no auto-summary
R1(config-router)#no synchronization
R1(config-router)#exit
R2(config)#router bgp 650012
R2(config-router)#neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 650012
R2(config-router)#neighbor 2.1.1.2 remote-as 650345
R2(config-router)#network 1.0.0.0
R2(config-router)#network 2.0.0.0
R2(config-router)#network 20.0.0.0
R2(config-router)#network 12.0.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#no auto-summary
R2(config-router)#no synchronization
R2(config-router)#exit
R3(config)#router bgp 650034
R3(config-router)#bgp confederation identifier 650345
R3(config-router)#neighbor 2.1.1.1 remote-as 650012
R3(config-router)#neighbor 3.1.1.2 remote-as 650034
R3(config-router)#network 30.0.0.0
R3(config-router)#network 3.0.0.0
R3(config-router)#network 2.0.0.0
R3(config-router)#network 13.0.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#no auto-summary
R3(config-router)#no synchronization
R3(config-router)#exit
R4(config)#router bgp 650034
R4(config-router)#bgp confederation identifier 650345
R4(config-router)#bgp confederation peers 650005
R4(config-router)#neighbor 3.1.1.1 remote-as 650034
R4(config-router)#neighbor 4.1.1.2 remote-as 650005
R4(config-router)#network 40.0.0.0
R4(config-router)#network 4.0.0.0
R4(config-router)#network 3.0.0.0
R4(config-router)#network 14.0.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R4(config-router)#no synchronization
R4(config-router)#no auto-summary
R4(config-router)#exit
R5(config-if)#router bgp 650005
R5(config-router)#bgp confederation identifier 650345
R5(config-router)#bgp confederation peers 650034
R5(config-router)#neighbor 4.1.1.1 remote-as 650034
R5(config-router)#neighbor 5.1.1.2 remote-as 650006
R5(config-router)#network 50.0.0.0
R5(config-router)#network 5.0.0.0
R5(config-router)#network 4.0.0.0
R5(config-router)#network 15.0.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R5(config-router)#no auto-summary
R5(config-router)#no synchronization
R5(config-router)#exit
R6(config-if)#router bgp 650006
R6(config-router)#neighbor 5.1.1.1 remote-as 650345
R6(config-router)#neighbor 6.1.1.2 remote-as 650012
R6(config-router)#network 6.0.0.0
R6(config-router)#network 5.0.0.0
R6(config-router)#network 60.0.0.0
R6(config-router)#network 16.0.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R6(config-router)#no synchronization
R6(config-router)#no auto-summary
R6(config-router)#exit
R1#show ip bgp summary
BGP router identifier 11.0.0.1, local AS number 650012
BGP table version is 27, main routing table version 27
16 network entries using 2304 bytes of memory
26 path entries using 2080 bytes of memory
5/4 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 680 bytes of memory
3 BGP AS-PATH entries using 72 bytes of memory
0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
BGP using 5136 total bytes of memory
BGP activity 21/5 prefixes, 31/5 paths, scan interval 60 secs
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
1.1.1.2 4 650012 94 87 27 0 0 01:13:02 12
6.1.1.1 4 650006 31 31 27 0 0 00:21:31 10
R1#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 27, local router ID is 11.0.0.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* i 1.0.0.0 1.1.1.2 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i 2.0.0.0 1.1.1.2 0 100 0 i
* 3.0.0.0 6.1.1.1 0 650006 650345 i
*>i 2.1.1.2 0 100 0 650345 i
* 4.0.0.0 6.1.1.1 0 650006 650345 i
*>i 2.1.1.2 0 100 0 650345 i
* i 5.0.0.0 2.1.1.2 0 100 0 650345 i
*> 6.1.1.1 0 0 650006 i
* 6.0.0.0 6.1.1.1 0 0 650006 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 11.0.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i 12.0.0.0/24 1.1.1.2 0 100 0 i
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 13.0.0.0/24 6.1.1.1 0 650006 650345 i
*>i 2.1.1.2 0 100 0 650345 i
* 14.0.0.0/24 6.1.1.1 0 650006 650345 i
*>i 2.1.1.2 0 100 0 650345 i
* 15.0.0.0/24 6.1.1.1 0 650006 650345 i
*>i 2.1.1.2 0 100 0 650345 i
*> 16.0.0.0/24 6.1.1.1 0 0 650006 i
*>i 20.0.0.0 1.1.1.2 0 100 0 i
* 40.0.0.0 6.1.1.1 0 650006 650345 i
*>i 2.1.1.2 0 100 0 650345 i
* 50.0.0.0 6.1.1.1 0 650006 650345 i
*>i 2.1.1.2 0 100 0 650345 i
R1#show ip route bgp
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷














