HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
HTTP is a client-server protocol that allows clients to request web pages from Web servers. It is an application-level protocol widely used on the Internet. The client is usually a Web browser. When a user wants to access a web page, the browser sends an HTTP request message to the Web server. The server responds with the requested web page. By default, the Web server uses TCP port 80.
The client and the Web server communicate with each other using the request-response method, the client sends the HTTP request, and the server uses the HTTP response to respond. Clients typically send their requests using the get or post methods, such as get/homepage.html. The Web server responds with a status message (returns 200 if the request succeeds) and sends the requested resource.
An example will clarify this process:
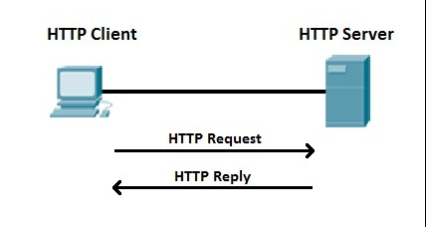
The client accesses the http://google.com and points its browser to the URL http://google.com(, which is an example of an HTTP request message). The network server hosting http://google.com receives the request and responds with web content (HTTP response message).
A web server typically uses a well-known TCP port 80. If the port is not specified in the URL, the browser will use this port when sending an HTTP request. For example, when you request http://google.com and http://google.com:80, you will get the same results.
NOTE
The most commonly used version of HTTP today is HTTP / 1.1. Most browsers provide and support newer versions of HTTP / 2.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
Hypertext transfer protocol security is a secure version of HTTP. The protocol uses encryption to achieve secure communication between clients (for example, Web browsers) and servers (for example, Web servers). HTTPS uses transport layer security (TLS) protocol or its predecessor secure socket layer (SSL) to encrypt.
HTTPS is usually used over some insecure networks (for example, the Internet). Much of the traffic on the Internet is unencrypted and vulnerable to sniffing attacks. HTTPS encrypts sensitive information to make the connection secure.
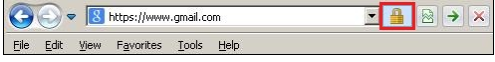
The HTTPS URL starts with https instead of HTTP. In Internet Explorer, you can immediately identify that a Web site is using HTTPS because a lock appears on the right side of the address bar:
NOTE
HTTPS uses a well-known TCP port 443. If the port is not specified in the URL, the browser will use this port when sending HTTPS requests. For example, when you request https://gmail.com and https://gmail.com:443, you will get the same results.
Note
if you are interested in the articles, and you can follow SPOTO. SPOTO is committed to various certification exam answers and questions.
More Recommended Articles
3. 19 Best Study Tips for Cisco Exams

 Join Telegram Study Group ▷
Join Telegram Study Group ▷