Table of Contents
In the realm of communications engineering and Cisco networking, the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a fundamental technology that ensures a loop-free topology for any bridged Ethernet local area network. Chapter 3 of the "CCIE Routing and Switching v5.0 Official Cert Guide, Volume 1" delves deep into the intricacies of STP, its various enhancements, and how they contribute to network stability and efficiency. This blog post will explore key aspects of STP, including IEEE 802.1D, Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP), and essential STP optimizations and security features.
IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol
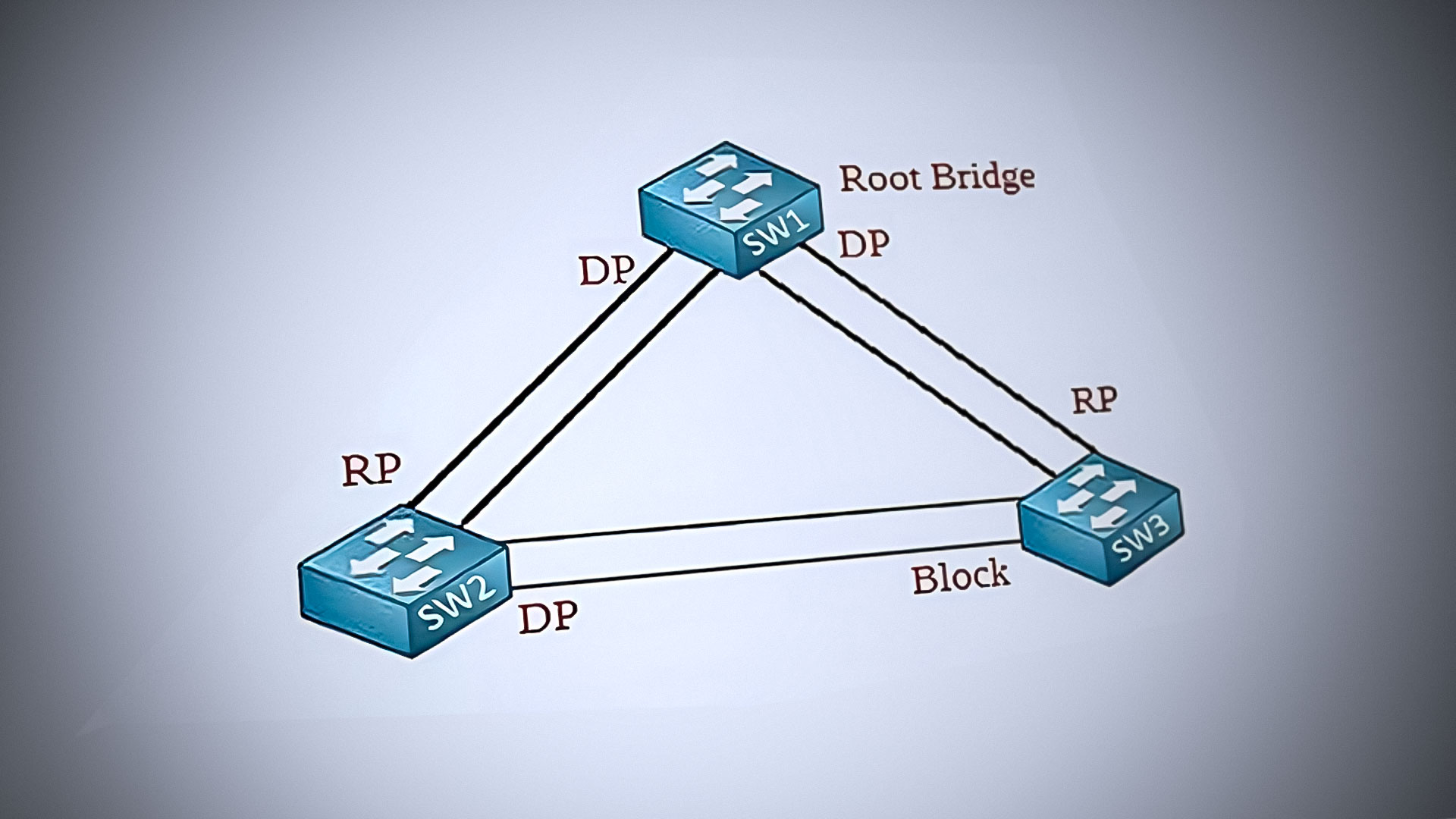
The IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol is the original version of STP, designed to prevent loops in network topologies by creating a spanning tree that logically blocks redundant paths. This protocol stabilizes the network by causing some interfaces to enter a blocking state, ensuring that no loops can form, while others remain in a forwarding state to maintain connectivity.
Key Elements of IEEE 802.1D STP:
· Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDU): These are the messages exchanged between switches to maintain the spanning tree. Each switch uses BPDUs to share information about its own identity and the state of its interfaces.
· Timers: There are three primary timers in STP:
o Hello Timer: The interval at which the root bridge sends configuration BPDUs, typically set to 2 seconds.
o Forward Delay Timer: The time a switch port spends in the listening and learning states before transitioning to the forwarding state, usually set to 15 seconds.
o Max Age Timer: The maximum time a switch port can wait without receiving a BPDU before it begins to reconfigure the spanning tree, typically set to 20 seconds .
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) - IEEE 802.1w
RSTP, standardized as IEEE 802.1w, is an evolution of the original STP that provides faster convergence. This protocol is backward-compatible with 802.1D but introduces significant improvements in terms of convergence speed and efficiency.
Key Features of RSTP:
· Port Roles and States: RSTP defines new port roles (e.g., Alternate and Backup) and states (e.g., Discarding, Learning, Forwarding) to streamline the process of topology change.
· Rapid Convergence: By using mechanisms such as proposal/agreement handshakes and immediate transition to forwarding state for edge ports (equivalent to PortFast in Cisco terminology), RSTP achieves much faster convergence than its predecessor .
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) - IEEE 802.1s
MSTP, standardized as IEEE 802.1s and incorporated into IEEE 802.1Q, allows multiple VLANs to be mapped to a single spanning tree instance, reducing the number of spanning tree instances required in a network with many VLANs.
Key Characteristics of MSTP:
· Region Concept: MSTP introduces the concept of regions, where switches within the same region share the same MST configuration and VLAN-to-instance mappings.
· Instance Mapping: By mapping multiple VLANs to a single spanning tree instance, MSTP optimizes the utilization of network resources and reduces the processing load on switches .
Optimizations and Enhancements
Cisco has developed several enhancements to the basic STP to improve network stability, convergence times, and security.
PortFast: PortFast is an enhancement that allows a port to skip the usual listening and learning states and immediately transition to the forwarding state. This is particularly useful for ports connected to end devices, such as computers, to minimize startup delay.
BPDU Guard: BPDU Guard is a security feature that disables a port if it receives a BPDU, effectively protecting the network from potential topology loops caused by accidental or malicious BPDU transmissions.
Root Guard: Root Guard ensures that a designated port does not become the root port, thus maintaining the current root bridge's stability and preventing unwanted topology changes.
Loop Guard: Loop Guard prevents alternative or root ports from becoming designated ports due to the absence of BPDUs, thereby avoiding potential loops in the network.
Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD): UDLD is a Cisco proprietary protocol that monitors the physical configuration of fiber-optic and twisted-pair links to prevent unidirectional links that can cause network issues .
Command Reference for STP
Understanding and configuring STP involves several Cisco IOS commands. Key commands include:
· spanning-tree mode {mst | pvst | rapid-pvst}: Sets the STP mode.
· spanning-tree vlan vlan-id {forward-time seconds | hello-time seconds | max-age seconds | priority priority | root {primary | secondary}}: Configures various STP parameters for a VLAN.
· spanning-tree portfast [trunk]: Enables PortFast on an interface.
· spanning-tree bpduguard {enable | disable}: Enables or disables BPDU Guard on an interface .
Conclusion
The Spanning Tree Protocol and its enhancements are critical for maintaining robust, loop-free network topologies in Ethernet networks. Understanding the intricacies of IEEE 802.1D, RSTP, MSTP, and various Cisco-specific optimizations and security features is essential for network engineers aiming to design and manage efficient and secure network infrastructures. As networking technologies continue to evolve, mastering these protocols and their applications will remain a cornerstone of advanced network engineering.










