Table of Contents
Overview:
SDN is a software-defined network. It is a new type of network innovation architecture proposed by the CLean State research group at Stanford University in the United States. It is also a way to implement network virtualization. Its core technology, OpenFlow, achieves flexible control of network traffic by separating the control and data planes of network devices, making the network as a pipeline more intelligent, and providing a good platform for core network and application innovation.
It tries to get rid of the limitations of the hardware on the network architecture so that the network can be modified like upgrading and installing software so that more APPs (applications) can be quickly deployed on the network.
If the existing network is regarded as a mobile phone, the goal of SDN is to make an Android system in the network world, which can be installed and upgraded on the mobile phone and can also install more and more powerful mobile APPs.
Over the past 30 years, IP networks have been fully distributed, with outstanding achievements, and solved various customer needs. Today, SDN is for better and faster realization of user needs in the future. It is not that there is no demand that cannot be achieved by traditional methods, but that SDN is faster, better and simpler.
The essence of SDN is to network software and improve network programmability. It is a reconstruction of network architecture, not a new feature or function. SDN will implement various functional features better, faster and easier than the original network architecture.
If you want to learn more info about SDN, contact SPOTO to get the latest technological theory!

Features of SDN:
Separation of transfer control: The control plane of the network element is on the controller, which is responsible for protocol calculation and generating a flow table; the forwarding plane is only on the network device.
Centralized control: The device network element centrally manages and delivers the flow table through the controller, so that there is no need to operate the devices one by one, only the configuration of the controller.
Open interface: Third-party applications only need to define a new network function through the open interface provided by the controller, and then run it on the controller.
Traditional network architecture
The traditional network is a distributed control architecture. Each device contains an independent control plane and data plane.
Distributed control:
In a traditional IP network, the control plane used for protocol calculation and the data plane for packet forwarding are located on the same device.
After the route calculation and topology change, each device has to perform the route calculation process again, which is called the distributed control process.
In a traditional IP network, each device independently collects network information, calculates independently, and only cares about its own routing.
The disadvantage of this model is that all devices lack uniformity when calculating paths.
Limitation
Traditional networks usually deploy a network management system as the management plane, while the control plane and data plane are distributed and run on each device.
The adjustment of the traffic path needs to be achieved by configuring the traffic strategy on the network element, but the adjustment of the traffic of the large network is not only cumbersome but also prone to failure; of course, the TE tunnel can also be deployed to achieve the traffic adjustment, but due to the TE tunnel The complexity is very high for the maintenance personnel’s skills.
Traditional network protocols are more complex, including IGP, BGP, MPLS, and multicast protocols, and they are still increasing.
In addition to standard protocols, equipment manufacturers have some private protocol extensions. Not only are there many equipment operation commands, but also the equipment operation interfaces of different manufacturers are quite different, and the operation and maintenance are complicated.
In the traditional network, because the control plane of the device is closed, and the implementation mechanism of devices of different manufacturers may also be different, the deployment of a new function may cause a longer period; and if you need to upgrade the device software, you also need to Operate on each device greatly reduces work efficiency.
SDN network architecture
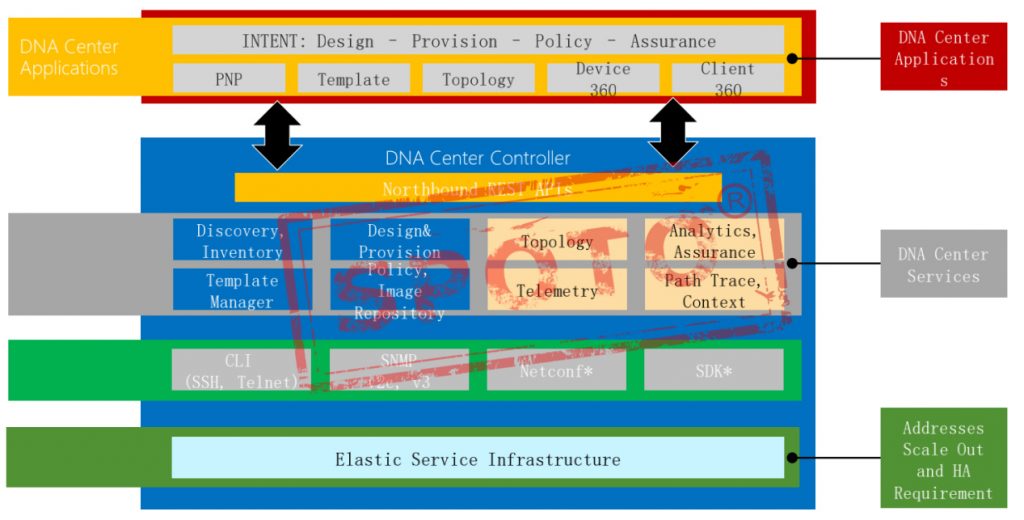
Application layer:
This layer is mainly a variety of upper-layer applications that reflect the user’s intentions. Such applications are called collaboration layer applications. Typical applications include OSS (Operation support system), Openstack, and so on. The traditional IP network also has a forwarding plane, a control plane, and a management plane. The SDN network architecture also includes these three planes. However, the traditional IP network is distributed and the SDN network architecture is centralized.
Control layer:
The control layer is the control center of the system, responsible for the generation of internal switching paths and border service routes of the network, and is responsible for handling network state change events.
Forwarding layer:
The forwarding layer is mainly composed of the lines of the repeater and the connector. This layer is responsible for the forwarding of user data. The forwarding entries required in the forwarding process are generated by the control layer.
Northbound interface:
the interface for communication between the application layer and the control layer. The application layer controls the device forwarding function through the open API control
Southbound interface:
The interface between the control layer and the data layer. The controller sends the flow table through OpenFlow or other protocols.
Advantages of SDN
The rapid innovation of network services:
The programmability and openness of SDN allow us to quickly develop new network services and accelerate business innovation. If you want to deploy new services on the network, you can implement rapid network programming by modifying the SDN software, and the services are quickly launched.
The key point of the SDN network is that an SDN controller is added to the network architecture, and the originally distributed control plane is centralized on an SDN controller, and the centralized controller realizes the centralized control of the network. The SDN network architecture has three basic characteristics: transfer control separation, centralized control, and open interface.
SDN can simplify the network and rapidly innovate services by adding a centralized SDN controller to the network. But its essential technical principle is to improve the network programmability through the network software process of the SDN controller. The communication plane still contains the management plane, the control plane, and the data plane. The SDN network architecture simply redistributes the functions of the three planes of the system. The traditional network control plane is distributed and distributed on each forwarding device, while the SDN network The architecture is to centralize the
distributed control plane into an SDN controller to achieve centralized control, while the management plane and data plane have not changed much.
Simplify the network:
The SDN network architecture simplifies the network and eliminates many IETF protocols. The removal of the agreement means that the cost of learning is reduced, the cost of operation and maintenance is reduced, and the business deployment is rapidly improved. This value is mainly due to the separation of network centralized control and transfer control under the SDN network architecture.
Because of the centralized control of the network under the SDN network architecture, many protocols within the network controlled by the SDN controller are basically unnecessary, such as the RSVP protocol, LDP protocol, MBGP protocol, and PIM multicast protocol. The reason is that the path calculation and establishment inside the network are all completed by the controller. The controller calculates the flow table and sends it directly to the repeater. No protocol is required. A large number of traditional east-west protocols will disappear in the future, while north-south control protocols such as the Openflow protocol will continue to evolve to meet SDN network architecture requirements.
NOTE: want to learn more new knowledge, and you can join our WhatsApp group:
https://chat.whatsapp.com/KaTtyc4LGJQCkV3aGQEctl

Read more:












Comments