OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First.
Definition: OSPF is a routing protocol used to determine the best route to transmit data packets within an IP network. The IETF publishes it as an internal gateway protocol to replace RIP. The OSPF specification is published as “Request for Comments (RFC) 1247”.
Please note that OSPF is a link-state routing protocol, while RIP and IGRP are distance vector routing protocols. The router running the distance-vector algorithm sends all or part of its routing table to its neighbors in routing update messages.
OSPF sends link state advertisements (LSAs) to all other routers in the same area. OSPF LSA contains information about the connected interface, the metrics used, and other variables. OSPF routers use SPF (shortest path first) algorithm to calculate the shortest path to each node. SPF algorithm is also called the Dijkstra algorithm.
If you want to know deeply about OSPF, I would like to suggest you enroll in the SPOTO CCNA training course. Check the IPV6 technology training video below explained by the SPOTO CCIE expert!
Next, we will launch the new CCNA/CCNP video course to help you know better about the technical points! Follow us for more info!
| Dumps | Technical topics |
| CCNA 200-301 | OSPF |
| EIGRP | |
| VLAN | |
| EI 350-401 | OSPF\BGP |
| SD-Access\DNA | |
| Classic topic |
| Categories | Exam Code | Pass Exam Dumps |
|---|---|---|
| CCNA | 200-301 | |
| 200-901 DevNet | ||
| 200-201 Cyber Ops |
Table of Contents
Advantages of OSPF
• OSPF is an open standard and has nothing to do with any particular vendor.
• OSPF may be a hierarchical routing protocol that uses area 0 (autonomous system) at the top of the hierarchy.
• OSPF uses a link-state algorithm, and the OSPF network diameter may be much larger than the diameter of RIP.
• OSPF supports variable-length subnet mask (VLSM), which can effectively utilize network resources.
• OSPF uses multicast within the area.
• After initialization, OSPF only sends updates on the part of the routing table that has been changed, instead of sending the entire routing table, thus saving network bandwidth.
• Use areas to logically segment the OSPF network to improve management and reduce the routing table’s size.
Disadvantages of OSPF:
• Due to the implementation of the SPF algorithm, OSPF takes a lot of processor resources. OSPF maintains multiple copies of routing information, thereby increasing the quantity of memory required.
• Compared with RIP, OSPF is a more complex protocol to implement.
Download Free SPOTO Latest CCNA 200-301 Practice Tests 2020
OSPF network hierarchy:
OSPF is a hierarchical routing protocol. Since the entire network is divided into smaller areas, better management and smaller routing tables can be achieved. OSPF is formed by a backbone (area 0) network that links all other smaller areas in the hierarchy. Some essential components of an OSPF network are as follows:
•Area
•Area border router
• Backbone area
•AS border router
• Stub area
• Not-So-Stubby areas
• Totally Stubby area
•Transit area
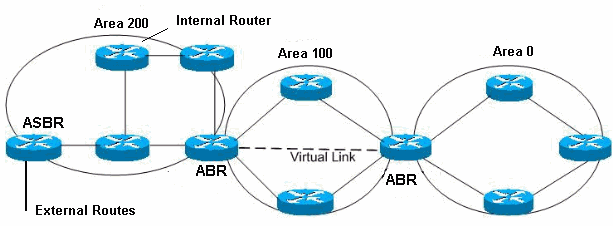
ABR: Area Border Router
ASBR: Autonomous System Border Router
Area: The area composed of routers grouped by management. Generally, an area is a collection of contiguous IP subnet networks. A router entirely in an area is called an internal router. All interfaces on the internal router are directly connected to the network in the area.
In an area, all routers have the same topology database.
Area border router: A router belonging to multiple areas is called an area border router (ABR). ABR maintains a separate topology database for each area to which they are connected.
Backbone area: The OSPF backbone area consists of all routers in area 0 and all area border routers (ABR). The backbone network distributes routing information between different areas.
AS Border Router (ASBR): The router that exchanges routing information with routers in other autonomous systems are called ASBR. They publish externally learned routes throughout the autonomous system.
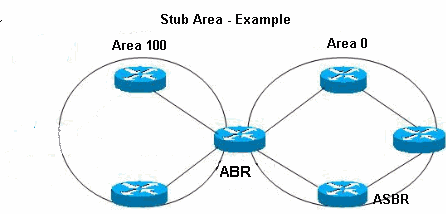
Stub area: The stub area is an area where AS external advertisements are not spread. By not disseminating AS external advertisements, the topology database’s size can be reduced on the internal routers in the stub area. This, in turn, reduces the processing power and memory requirements of the internal routers.
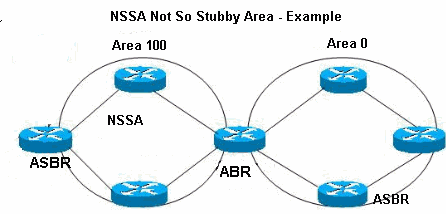
Not-So-Stubby Areas (NSSA): There are no external routes in the OSPF stub area. NSSA allows external routes to flood in the area. These routes then leak to other areas. This feature is useful when you connect a non-OSPF router to the ASBR of NSSA. The route was introduced and flooded the entire area. However, external routes from other areas will still not enter the NSSA.
Totally Stubby Area: Only the default summary route is allowed in the Totally Stubby Area.
Transfer area: The transfer area is used to transfer traffic from adjacent areas to the backbone network. Traffic neither originates from the destination of transportation nor is it the destination of transportation.
Link State Advertisement (LSA):
It is important to understand the different link state advertisements (LSAs) provided by the OSPF protocol.
Type 1: Router link advertisements generated by each router for each area to which it belongs. Type 1 LSA floods only to a single area.
Type 2: A network link announcement generated by a designated router (DR) gives a group of routers connected to a specific network. Type 2 LSA floods to the area containing the network.
Type 3/4: These are summary link advertisements generated by ABR, describing inter-area routes. Type 3 describes the route to the network for summarization.
Type 4 describes the route to the ASBR.
Type 5: Generated by ASBR and provide links to the outside of the autonomous system (AS). Type 5 LSA floods to all areas except the stub area and the full stub area.
Type 6: Group membership link entries generated by the multicast OSPF router.
Type 7: NSSA external route generated by ASBR. Only flooding to NSSA. Before flooding them to the backbone network (area 0), the ABR converts LSA type 7 to LSA type 5.
| Area | Restriction |
| Normal | None |
| Stub | Type 5 AS-external LSA NOT allowed |
| NSSA | Type 5 AS-external LSAs are NOT allowed, but Type 7 LSAs that convert to Type 5 at the NSSA ABR can traverse |
| Totally Stubby | Type 3, 4 or 5 LSAs are NOT allowed except the default summary route |
In conclusion
OSPF is a technical point in the CCNA exam, if you want to learn about OSPF and pass the CCNA exam on the first try, you should opt for SPOTO 100% real CCNA exam dumps & training course for 100% pass! Also, buy CCNA exam dumps now can save more due to the Black Friday Discount! Get now!

Latest passing report-100% pass guarantee
Recommend CCNA exam study materials:












Comments