1. Why do we need LSA
If we want to know what LSA is, we have to start with Packets. OSPF uses a total of 5 packets to establish a neighbor.
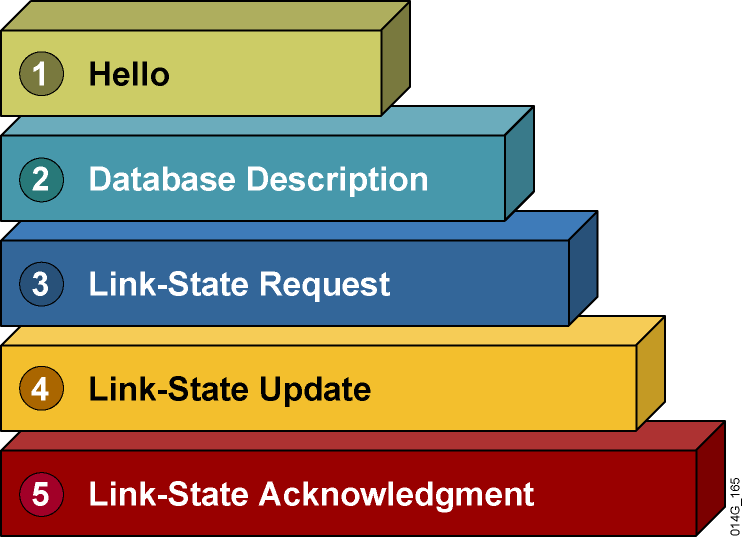
The first Packages are HELLO:
Establish and maintain OSPF neighbor relationships. Hello packets are sent periodically (by default, 10 seconds) to neighboring router interfaces.
If the Hello packet sent by the OSPF router of the other party is not received within a fixed time (default 40 seconds, usually at least 4 times indirect of the Hello packet sending time), the local router will consider the other router invalid.
The second Packets is DBD:
That is, the link-state database description information — The link-state database description information is exchanged between the two routers.
DBD Packets are exchanged for database synchronization when two OSPF routers initiate a connection
| Categories | Exam Code | Pass Exam Dumps |
|---|---|---|
| CCNA | 200-301 | |
| 200-901 DevNet | ||
| 200-201 Cyber Ops |
The third package is LSR
Link state request-request link state information from OSPF neighbors
LSR Packets are used to request part of the data in the link-state database of neighboring routers.
After the two routers have exchanged DBD Packets with each other, they know which LSAs of the peer routers do not have in the LSDB, and which LSAs have expired, then they need to send an LSR Packets to request the required LSA from the other party.
The fourth Packets is LSU
That is, link-state update — update one or more LSAs, eigrp and rip are specific routing entries when updating routes, and two OSPF routers are updating LSAs, LSA is a route that specifically describes link status the way. LSU Packets is used to send the required LSAs to the peer router at the request of LSR Packets. The content is a complete set of multiple LSAs. The content of the LSU Packets includes the total number of LSAs sent and the complete content of each LSA.
The fifth Packets is LSAck
LSAck Packets are the acknowledgment packets sent by the router after receiving the LSU Packets from the peer.
2.LSA Types :
At present, there are 11 types of LSAs in OSPF, but at present, there are only 6 types of lsa that are commonly used or CCIE exams.
In the picture below, you need to know the type of the specific description name of each lsa
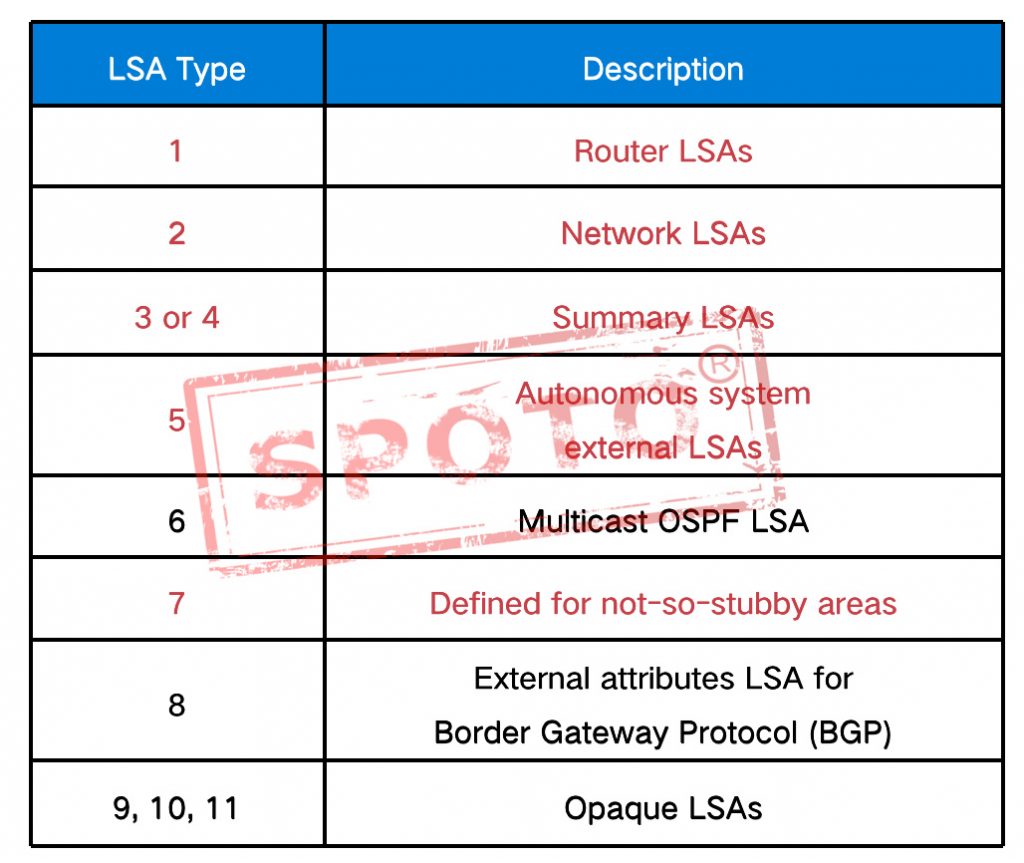
- LSA Detailed:
Type 1–Router LSAs
Each router in the area generates a Router LSA, which includes all direct link information. Each direct link information describing the router contains link information such as link type, IP prefix and mask, and metric. The source router (publishing router) is identified by the Router ID. It only floods in the area and does not cross the ABR.
Producer: All routers
Role: Announce the information of its direct connection port
Scope of announcement: only in this area
Note: In networks that need to elect a DR, the type 1 LSA does not include a mask.
Type2–Network LSAs
Network LSAs have a premise that they must appear under the broadcast multiple access network / broadcast multiple access networks.
The DR routers on this network generate a network LSA, which contains the multi-access link (list of all directly connected routers, the subnet mask of the link), floods only in the area, and does not cross the ABR
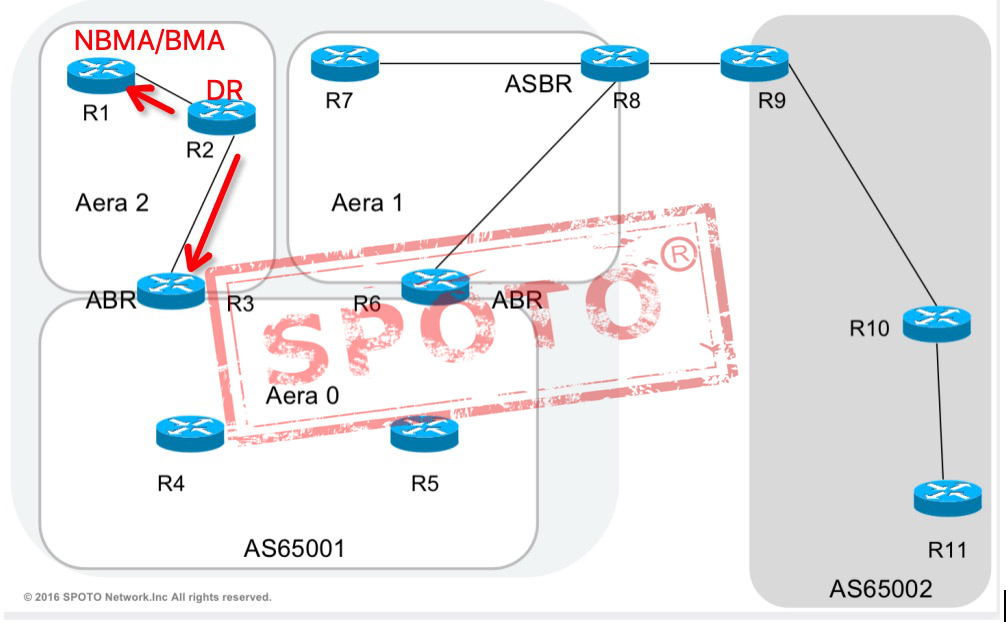
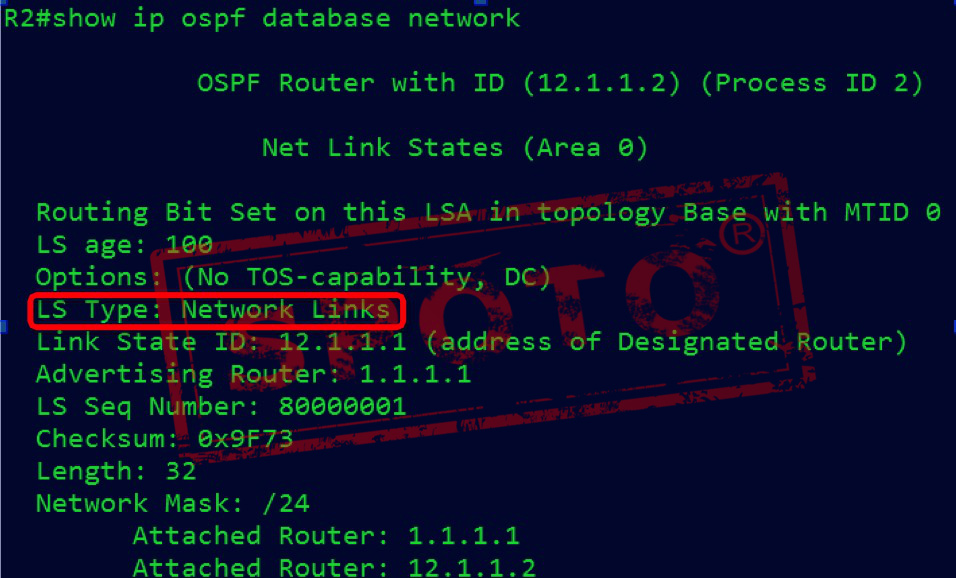
Produced by: DR
Purpose: Notification mask
Scope of announcement: only in this area
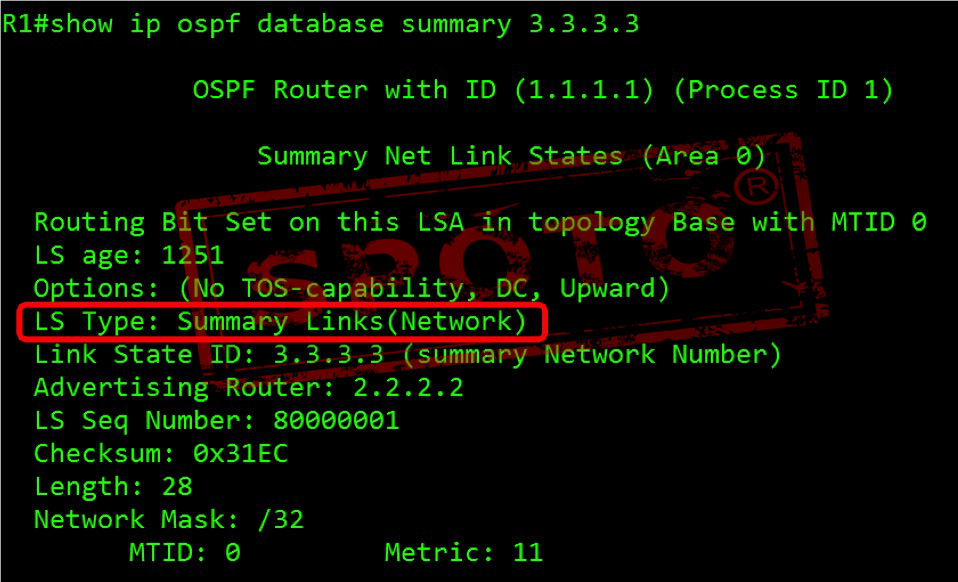
Type-3 Summary LSAs
Type 3 LSAs are generated by ABR area border routers and are used to flood the routing information calculated by the LSAs generated in this area to other areas-describing the network number and mask of the link.
The three types of LSAs carry routing information, and routes are not summarized. Type 3 LSAs will be advertised to each subnet.
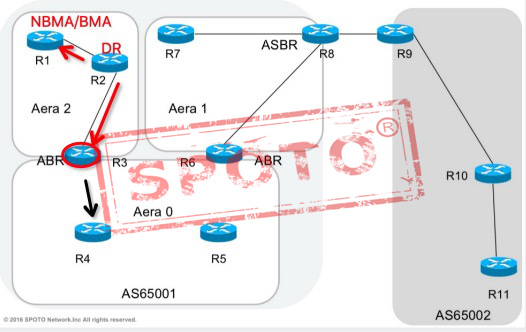
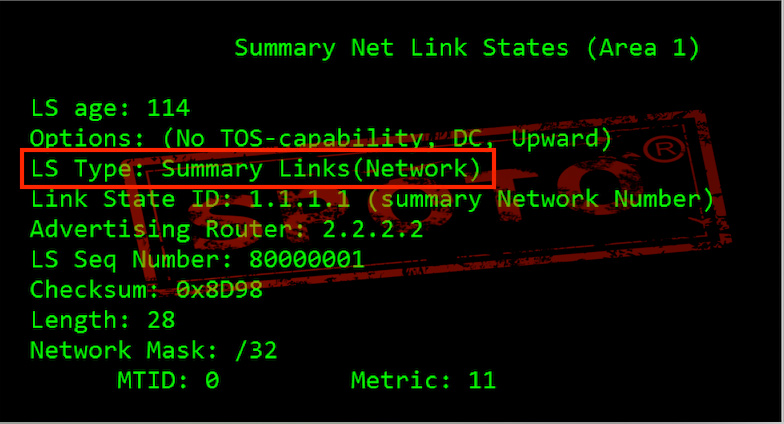
Produced by: ABR
Role: Summarize categories 1 and 2 in this area and notify to other areas
Announcement scope: the entire OSPF network
Note: The essence is routing information, which has the characteristics of distance vectors. Non-zero areas are prohibited from directly transmitting Type 3 LSA
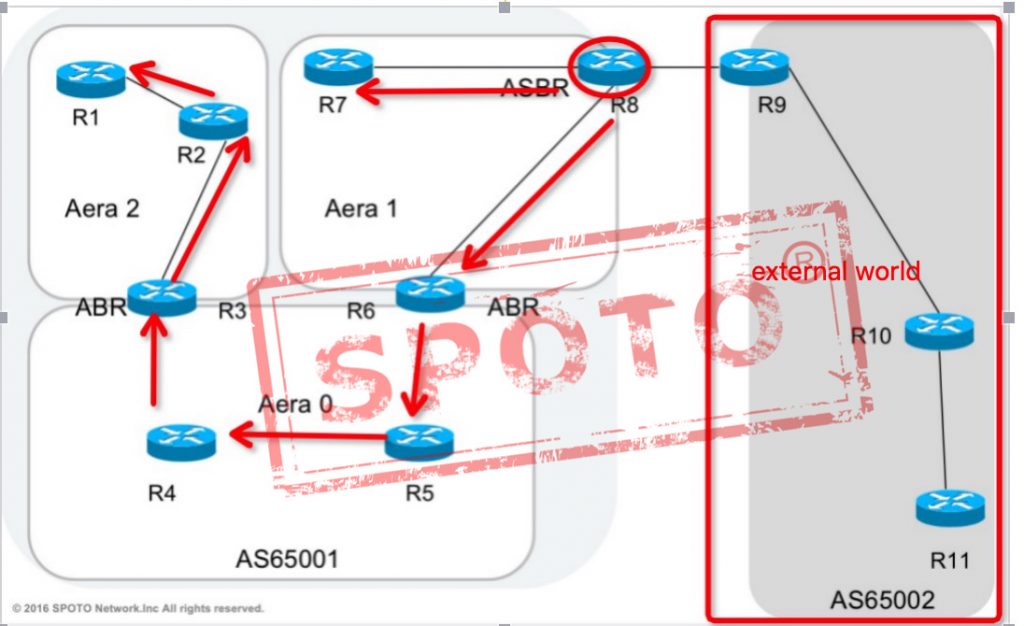
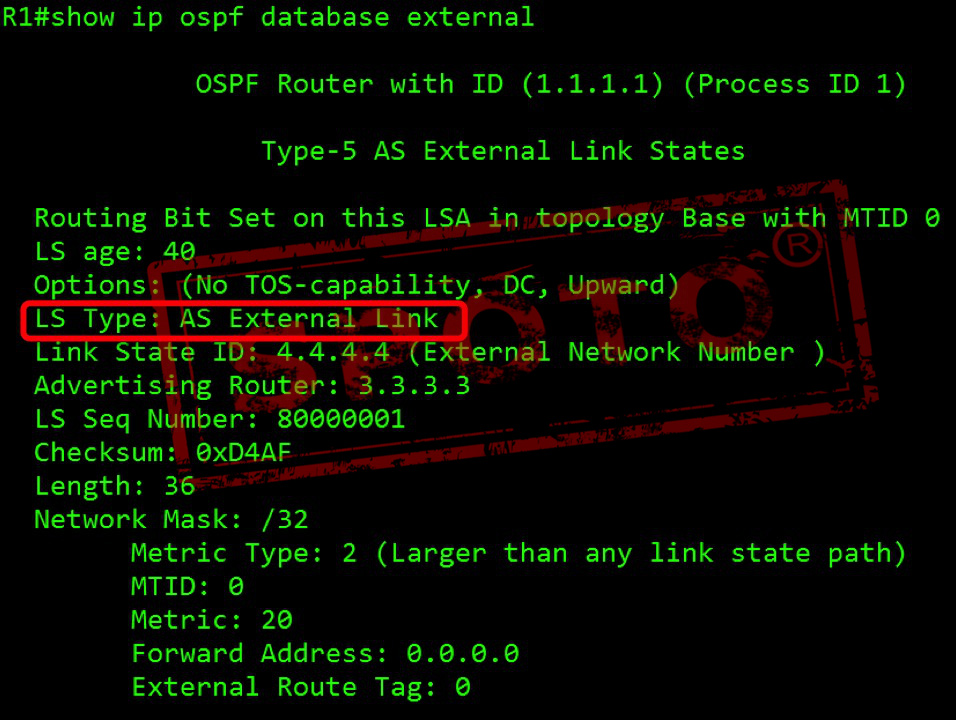
Type-5 Autonomous system external LSA
External (type 5) LSA is used to announce the information from other external networks (outside world AS).
Type 5 LSA originates from ASBR and is advertised by ASBR. Type 5 LSAs transmit routing information.
Type 5 LSAs are flooded throughout the autonomous system. The advertised router ID (ASBR) does not change throughout the autonomous system flood.
Type 4 LSAs are used to find ASBRs. By default, routes are not summarized.
Produced by: ASBR
Role: Advertise external routing information
Announcement scope: the entire OSPF network
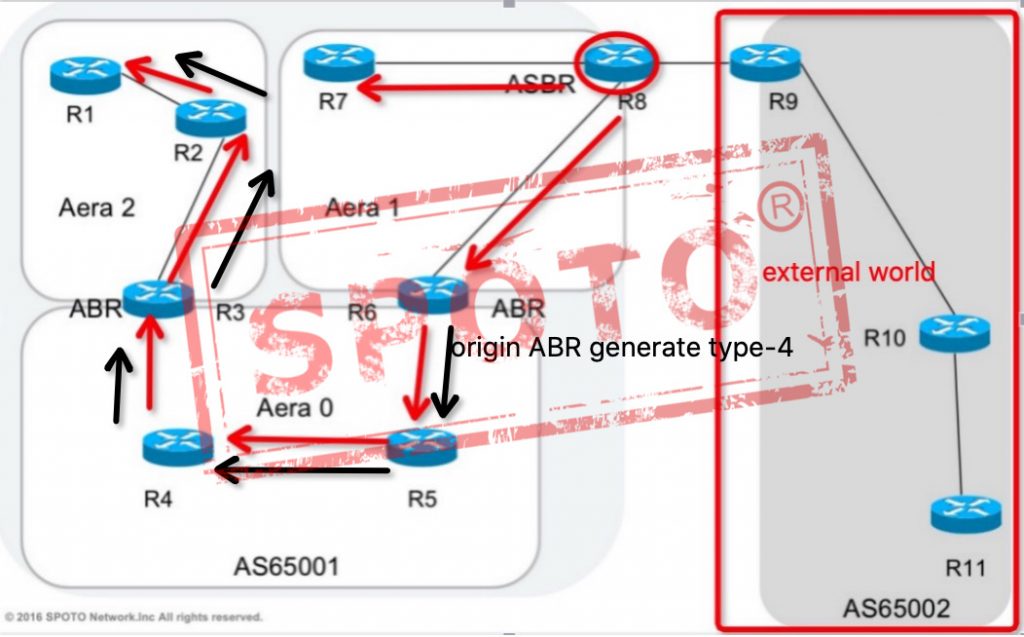
Type-4 Summary LSAs
Category 5 LSAs only advertise the entire as 65001 networks to the outside world routes, but for other areas, such as AREA 0 and AREA 2, only the outside world is known, but the specific exit location of the outside world is not known, so type 4 LSA are used to notify ASBR specific locations to other areas throughout the home-made system,
The Type 4 LSA is generated by the ABR in the starting area. Flooded by other ABRs to the entire autonomous system.
The Type 4 LSA contains the router ID of the ASBR. The Type 4 LSA follows the anti-ring mechanism of the Type 3 LSA.
Produced by: ABR in the ASBR area
Role: Announce ASBR location
Announcement scope: the entire OSPF network
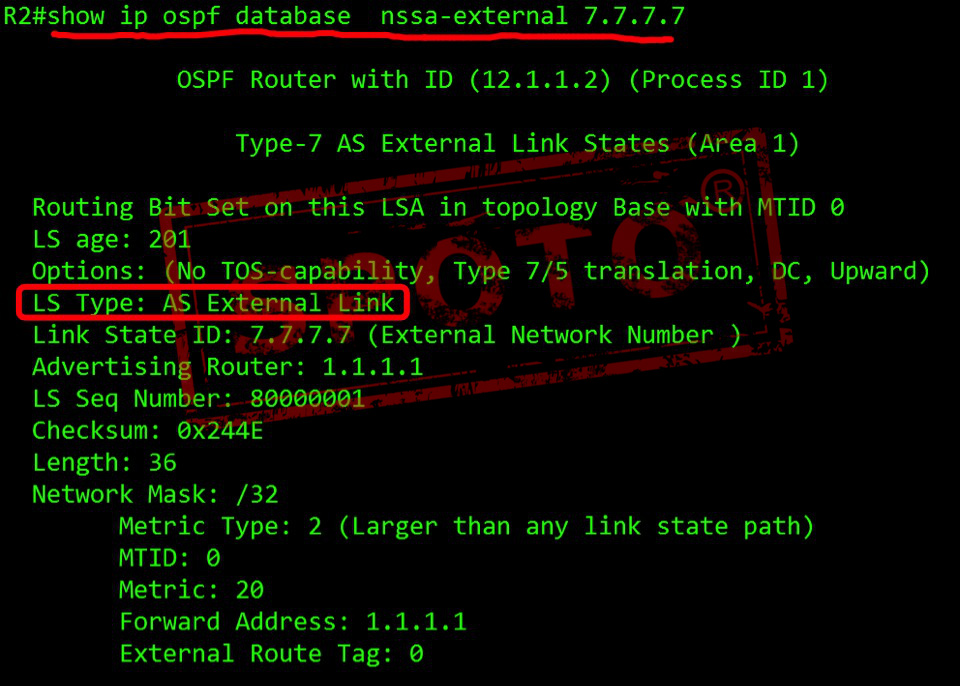
Type-7 Defined for not-so-stubby areas
NSSA External (type 7) LSA is used to advertise information from other external networks in the NSSA area.
Type 7 LSA originates from ASBRs in the NSSA area and is advertised. Type 7 LSAs carry routing information.
Type 7 LSA floods in the NSSA area. When the entire autonomous system is flooded across the NSSA area boundary, it is converted from ABR to type 5 LSA.
The Type 4 LSA does not exist in the NSSA area to find the ASBR, instead of the Forwarding Address.
When the Forwarding Address in other areas is unreachable, the route passed by the seven-to-five LSA will not be written into the routing table.
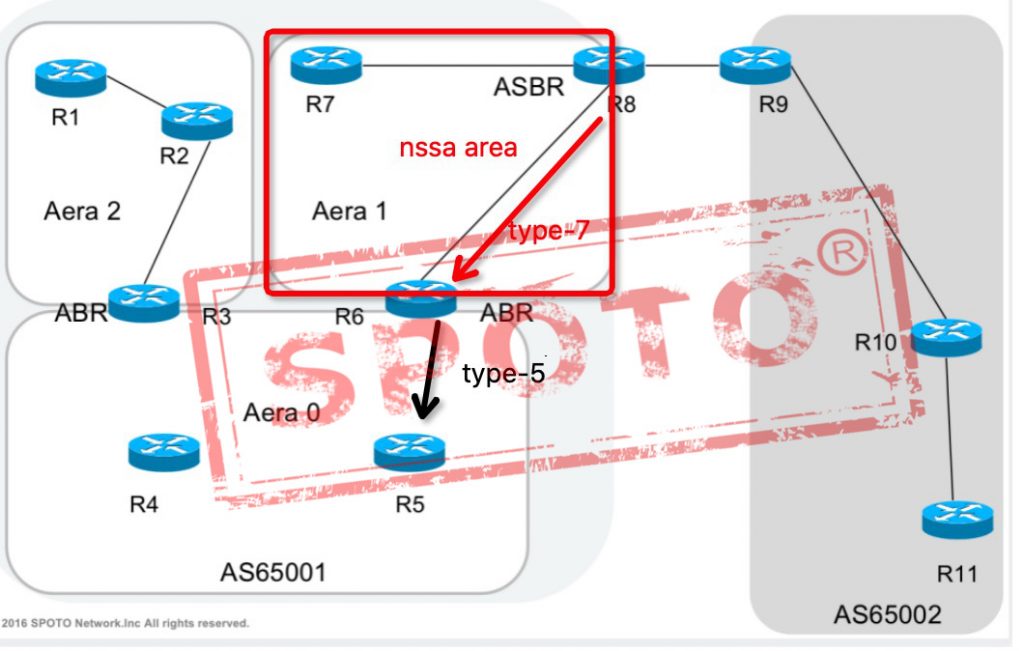
Produced by: ASBR
Role: Advertise external routing information
Announcement scope: NSSA area
We have more theoretical materials and experimental documents here, if you need, please leave your information on the website, we will send the materials to you

Latest passing report-100% pass guarantee
Recommend CCNA exam study materials:
How to Config OSPF Virtual Link\Password Authentication and Totally Stub Area
What Is OSPF LSA?
Black Friday Sale Starts! Get Amazing Offer to Save More on All SPOTO IT Dumps!
Changes to the CCNA Exam 2020: What would be My Employees require to Know?
CCNA 200-301 Exam Official Cert Guide PDF 2020
9 Best Study Techniques to Prepare for Cisco 200-301 Exam Easily
How to prepare CCNA 200-301 at home?












Comments