The software-defined network is the physical separation between the network control plane and the forwarding plane, and the control plane controls multiple devices. Software-defined networking (SDN) makes the network flexible and flexible. It provides better network control, thus enabling cloud computing service providers to respond to changing business needs quickly.
As we all know, SDN is a new technical point in the Cisco CCIE Lab exam after Cisco’s reform in 2020. This blog will introduce the SDN overview, structure, and working mechanism in detail to help you further understand SDN. If you want to learn more about SDN, please contact us to register for the SPOTO CCIE training course! SDN needs some equipment involving emulators and Real Rack. SPOTO will provide you with physical equipment and real racks. Click here for more.
All You Need to Know–Key Points of Cisco Live 3rd Webinar on CCIE EI Lab Exam
Table of Contents
What is software-defined networking (SDN)?
Software-defined networking (SDN) is a networking method that uses a software-based controller or application programming interface (API) to communicate with the underlying hardware infrastructure and direct traffic on the network.
This model is different from traditional networks, which use dedicated hardware devices (i.e., routers and switches) to control network traffic. SDN can create and control virtual networks (or control traditional hardware) through software.
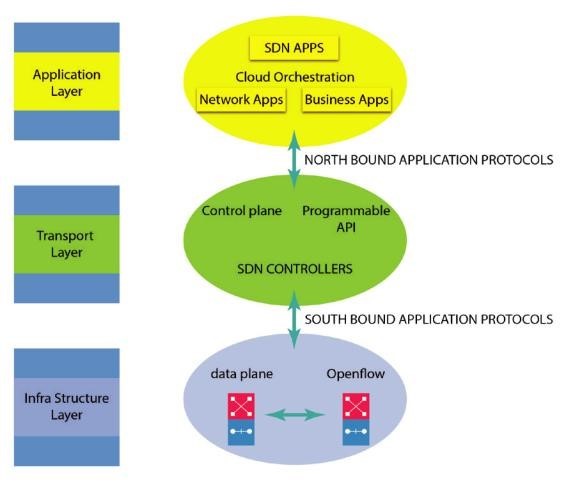
SDN architecture
The SDN architecture comprises three layers: application layer, control layer, and infrastructure layer.
There is no doubt that the SDN application layer contains typical network applications or functions, such as intrusion detection systems, load balancing, or firewalls. Traditional networks use dedicated devices, such as firewalls or load balancers, while software-defined networks replace appliances with applications that use controllers to manage data plane behavior.
The SDN architecture divides the network into three different layers; applications use northbound APIs to communicate with the control layer. The control layer uses southbound APIs to communicate with the data plane. The control layer is considered to be the brain of SDN. The intelligence of this layer is provided by centralized SDN controller software. The controller resides on the server and manages policies and traffic throughout the network. The physical switches within the network constitute the infrastructure layer.
How SDN works
SDN is an orchestration of multiple technologies internally. The use of well-defined APIs for network virtualization and automation is a crucial factor. Functional separation increases value by reducing dependencies.
A knowledge packet arrives at a network switch in a classic SDN scenario, and rules built into the switch’s proprietary firmware tell the switch where to forward the info packet. These packet processing rules are sent from the central controller to the switch.
The switch (also called the info plane device) queries the controller for guidance as required and provides the controller with information about the traffic it handles. All data packets of hosts with the same destination are processed similarly and forwarded by the switch along the same path.
The virtualization aspect of SDN works through the virtual overlay, which is a logically independent network on the physical network. To segment network traffic, end-to-end coverage can be achieved. Therefore, users can also abstract the underlying network. This micro-segmentation is particularly useful for service providers and operators with multi-tenant cloud environments and cloud services. They can provide each tenant with a separate virtual network with specific policies.
In conclusion
SDN represents the path to more general network hardware and more open software. SDN with NFV is the future of the network and is increasingly becoming the core of the modern data center!
If you do CCIE EI now and when there will be engineers required to implement the SDN technology, you will be the first choice to implement, because you have already understood the underlying technology which is needed to understand and implement SDN.
Also read: Guide to CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure Certification
At SPOTO, we track the development of SDN and we are excited about the potential of SDN. SPOTO CCIE Training course covers the latest SDN technology to make you follow the latest technical trend!
Latest passing report-100% pass guarantee
Recommend SDN study materials:













Comments