Today this article will describe the entire system of MPLS in a series of forms. The first one is to tell you the defects of the traditional network and why we need the technical integration form of MPLS + BGP.
Existing VPN technology basically meets the requirements of customer private network interconnection through public infrastructure, but it also has some inherent defects. Typically, the coverage model and the peer model are not compatible. But customers often require their VPN networks to have the advantages of both.
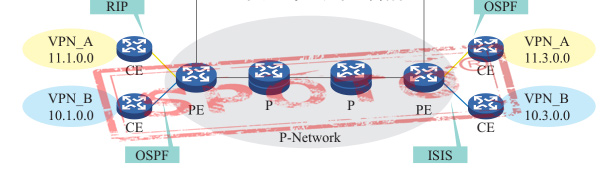
Requirements as shown in the figure: VPN clients on both the yellow site and the green site require the use of private addresses (the private addresses of different VPNs can be duplicated), and tunnels can be dynamically established like peer-to-peer VPNs. The current VPN technology (overlay type, peer-to-peer type) cannot meet this demand, so new technology is urgently needed to integrate the advantages of these two VPN models to meet customer needs. MPLS VPN technology perfectly integrates multiple VPN models and promotes the continued development of VPN.
Background
The emergence of MPLS VPN is mainly to solve some inherent defects of traditional VPN technology, which has many technical problems to be solved, the most important one is the problem of address overlap. There must be a technology to ensure that different users VPN can use the same private address space, and can exchange data without affecting each other on the public backbone network.
To solve the problem of overlapping address spaces, there are the following problems:
■ The problem of local route conflict, that is: how to distinguish the same route of different VPNs on the same PE;
■ The problem of route propagation in the network, two identical routes are propagated in the network, how to distinguish the receiver;
■ The problem of packet forwarding, even if the routing table conflict is successfully resolved, but when the PE receives an IP packet, how can it know which VPN to send to? Because the only information available in the IP header is the destination address. This address may exist in many VPNs.
Technology fusion
From the technical difficulties mentioned above, the main problems exist in the characteristics related to routing, so to solve these problems must be considered from the routing protocol. However, none of the existing routing protocols have the conditions to solve these problems, so they must be implemented by transforming the existing routing protocols. Choosing a suitable routing protocol to achieve transformation becomes the first solution to Resolved issues.
As a candidate routing protocol, it must be able to adapt to a huge number of VPN routes, and the protocol must have good scalability. Qualified agreements must be based on TLV elements (easy to expand). Analysis of existing routing protocols, OSPF is the most widely used routing protocol, but the scalability of this protocol is relatively poor, and it is a link-like The dynamic routing protocol requires a lot of calculations on the received LSA, and it is difficult to adapt to the huge number of VPN routes on the public network. From the perspective of expansion, RIP is based on TLV architecture.
The scalability should be okay, but the operation mechanism of RIP is not suitable for large networks. Other routing protocols also have corresponding unsuitable places, and ultimately this heavy responsibility falls to the existing BGP, the backbone routing protocol used by the Internet. BGP has many characteristics that make it very suitable for transformation to meet the problem of overlapping addresses on the VPN network. Its characteristics are as follows:
■ The number of VPN routes in the public network is very large, BGP is currently the only routing protocol that supports a large number of routes;
■ BGP is also designed to exchange information between routers that are not directly connected, which eliminates the need for P routers to include VPN routing information;
■ BGP can carry any information appended to the route. As optional BGP attributes, any BGP router that does not understand these attributes will forward them transparently (of course these attributes are all transferable), which makes the Propagation routing is very simple. The main consideration here is that you can identify the same in different VPNs by extending attributes Route.
Because BGP has the above advantages, the task of solving the technical difficulties mentioned above falls on it. Through the transformation of the existing BGP protocol, the aforementioned problems that need to be solved can basically be solved, the solution is as follows:
■ The problem of local routing conflict can be solved by creating different routing tables on the same router, and different interfaces can belong to different routing tables, which is equivalent to simulating a shared PE into multiple dedicated PEs;
■ You can add another logo to this route during the route transfer to distinguish different VPNs;
■ Since the format of the IP packet cannot be changed, but some information can be added to the IP header, and the originating VPN will mark it, so that the PE can forward the packet according to this mark when receiving the packet.
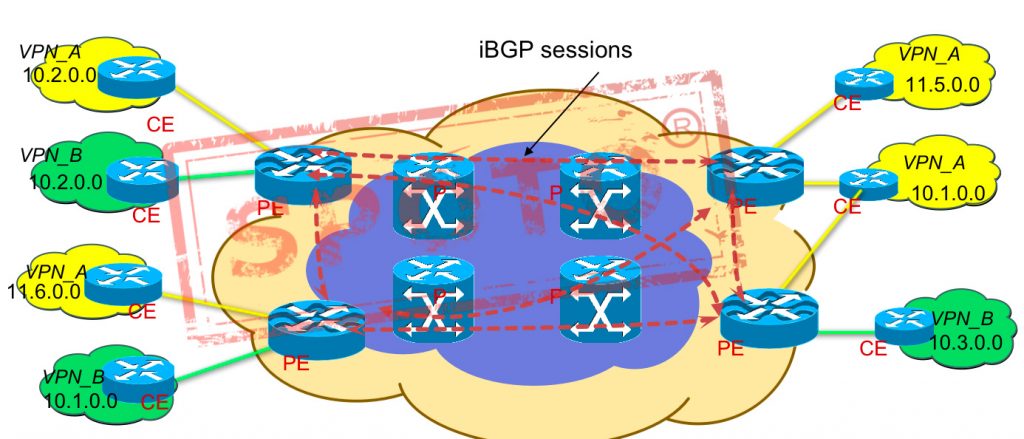
In the article 《mpls VPN architecture-2》, I will introduce the specific solution to the first problem
The problem of local routing conflict, that is, how to distinguish the same route of different VPNs on the same PE;
The solution is You can create different VRF routing tables on the same router, and different interfaces can belong to different VRF routing tables. This is equivalent to simulating a shared PE into multiple dedicated PEs; while combining BGP groups The attribute is used to mark the route for distinction. If you want to know more information, you can check the Mpls VPN architecture-2 document.
By the way, our SPOTO offers 100% latest and real Cisco Certification Practice Exams to all candidates. Simulated exam experiences to help you prepare for the real exam easily. If you are interested, you can enter our group chat by leaving your email information











Comments