Are you trying hard to find info on troubleshooting the MPLS VPNs? Here is all the info you need to collect from this article.
Introduction:
A method of creating a Virtual Private Network (VPN) using Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) is the MPLS VPN. We need to be aware of the equipment involved to understand how MPLS VPN works. In the MPLS network, the equipment required will be:
· Customer Edge (CE) routers. CE routers are used by the enterprise and placed on-site.
· Provider Edge (PE) routers. The MPLS service providers own the PE routers. PE routers receive the data packets from the CE routers.
· Provider (P) routers. P routers are also known as ‘transit routers,’ which are situated in a service provider’s core network. To transmit data packets across the system is the primary function of these routers. Before we discuss the troubleshooting process, you should acquire the study dumps offered at the SPOTO Club to obtain guaranteed success.
Troubleshooting MPLS VPNs
· MPLS VPNs are comparatively complex, but by following an end-to-end, step-by-step approach, troubleshooting can be relatively fast and efficient. Troubleshooting route advertisements between the customer sites and troubleshooting the LSP across the provider backbone are the two essential elements in which the procedure of troubleshooting MPLS VPNs can be broken down.
· Below given flowcharts explain the process used for troubleshooting route advertisements between the customer sites and troubleshooting the LSPs across the provider backbone. These flowcharts can be used to quickly access the section of the chapter relevant to problems experiencing on your network.
· Figure 6-29: Flowchart for Troubleshooting Route Advertisement Between the customer Sites in MPLS VPN.
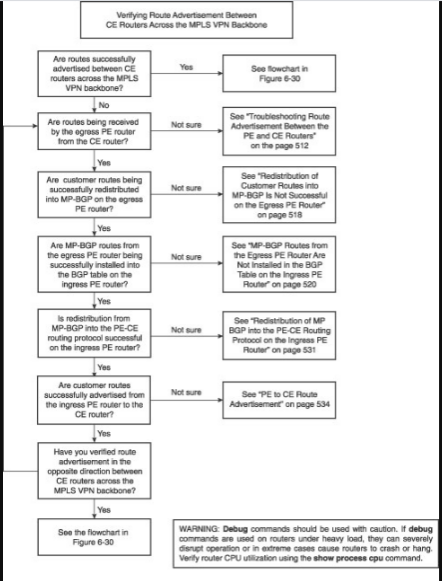
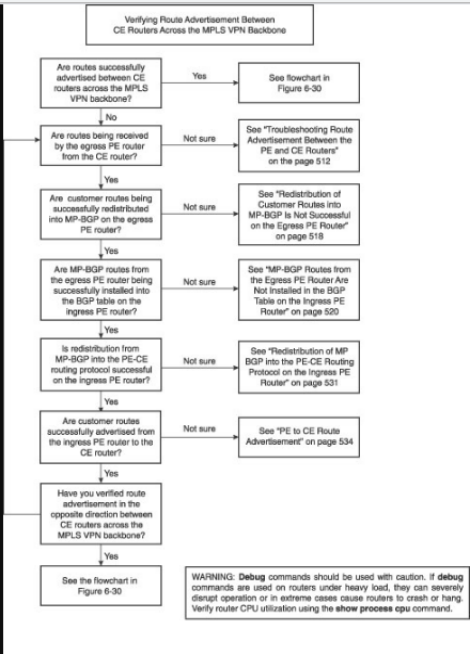
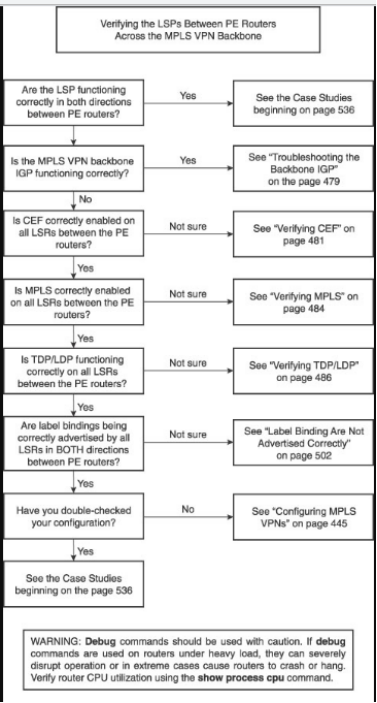
· Figure 6-30: Troubleshooting flowchart the LSPs Across the Provider MPLS Backbone
· Above mentioned MPLS VPN troubleshooting elements are already discussed in the sections. Though, it is a good idea to try to find the issue by using the ping and traceroute commands.
· Topology sample is used as a reference all through this section is illustrated in the below figure.
· Figure 6-31: Sample MPLS VPN Topology
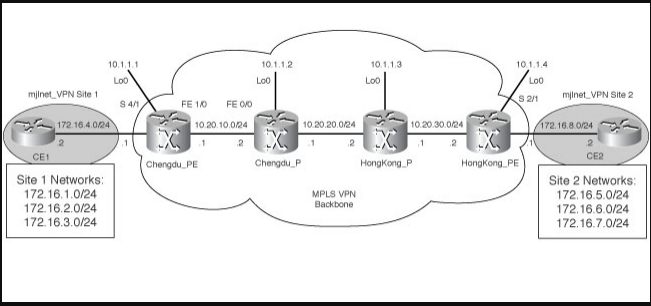
New Cisco IOS software commands are used in the sections that follow. At the end of the chapter shows new powers and their old equivalents. Older authorities use the tag-switching keyword in place of the MPLS keyword, and the TDP keyword instead of the IDP keyword.
Locating the Problem in an MPLS VPN
Ping and traceroute are the two commands that are mainly good for finding problems in the MPLS VPN.
The ping command is generally used to give an idea of the location of the problem. This command is also used to verify the LSP and route advertisement across the MPLS VPN backbone.
On the other hand, the traceroute command can be used for a more comprehensive examination of the LSP.
You need to know that if you are using IOS 12.0(27)S or above, the advantage of the Ping MPLS and trace MPLS can be taken. MPLS Embedded Management feature commands for testing LSP connectivity and trace LSPs. Embedded Management commands use MPLS echo request and reply packets ([labeled] UDP packets on port 3503), that also allows determining a categorize of options that include datagram size, brush off size range, TTL, MPLS echo request timeouts, MPLS echo request intervals, and Experimental bit settings.
Verifying IP Connectivity Across the MPLS VPN
As mentioned earlier, the ping command is useful in locating problems in the MPLS VPN. To ping from the PE router to the connected CE router and from the ingress PE router to the egress PE router are the two tests that can be very useful.
For a more in-depth overview regarding the same, check out the training courses offered at the SPOTO Club to have hands-on knowledge.













Comments