Today, Cisco is introducing a new agile process they call minor revisions to keep up with the rapid evolution of products and technologies. it will allow the Cisco certification exams faster with the industry changes.
Minor revisions provide Cisco the agility and speed they need to adapt their programs to industry changes and technological evolution. This will update the track details (exam blueprint, equipment list and software) more often while keeping changes (less than 20%) to a minimum. It allows to keep the Cisco certification exam content current and minimize learning curves between revisions.
These minor revisions have the following primary objectives:
- Exam Objectives are more clear: Cisco has refined the exam blueprint so that the objectives can be easily understood.
- Exam Tasks Relevant to Industry Requirements: Cisco has introduced new tasks into the blueprint in order to ensure that exams are relevant to industry requirements.
- Remove Outdated Solutions: Cisco is phasing out older technology and products that are no longer relevant.
- Updates to Equipment and Software: Cisco updates its recommended equipment and software in order to reflect the most recent advancements and technology.
Today, Cisco is revising the CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure lab exam to enhance its effectiveness and relevance in light of these goals.
Table of Contents
CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure Lab Exam, minor revision 1.1: Ensuring Exam Relevancy
The new CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure lab exam is coming. It will be updated with a minor revision, which is small and incremental. The exam blueprint is similar in its overall structure, but this revision adds and removes technology solutions to ensure exam relevance. The exam reflects the most recent industry standards and addresses the ever-changing landscape of security technology.
Please, refer to www.cisco.com/go/CertRoadmap for the list of exam topics covered in the updated CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure exam and for more information about the CCIE certification program.
Comprehensive Summary of CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure v1.1 Lab Exam Blueprint
| V1.0 | V1.1 |
| 2. Software Defined Infrastructure | 2. Software Defined Infrastructure |
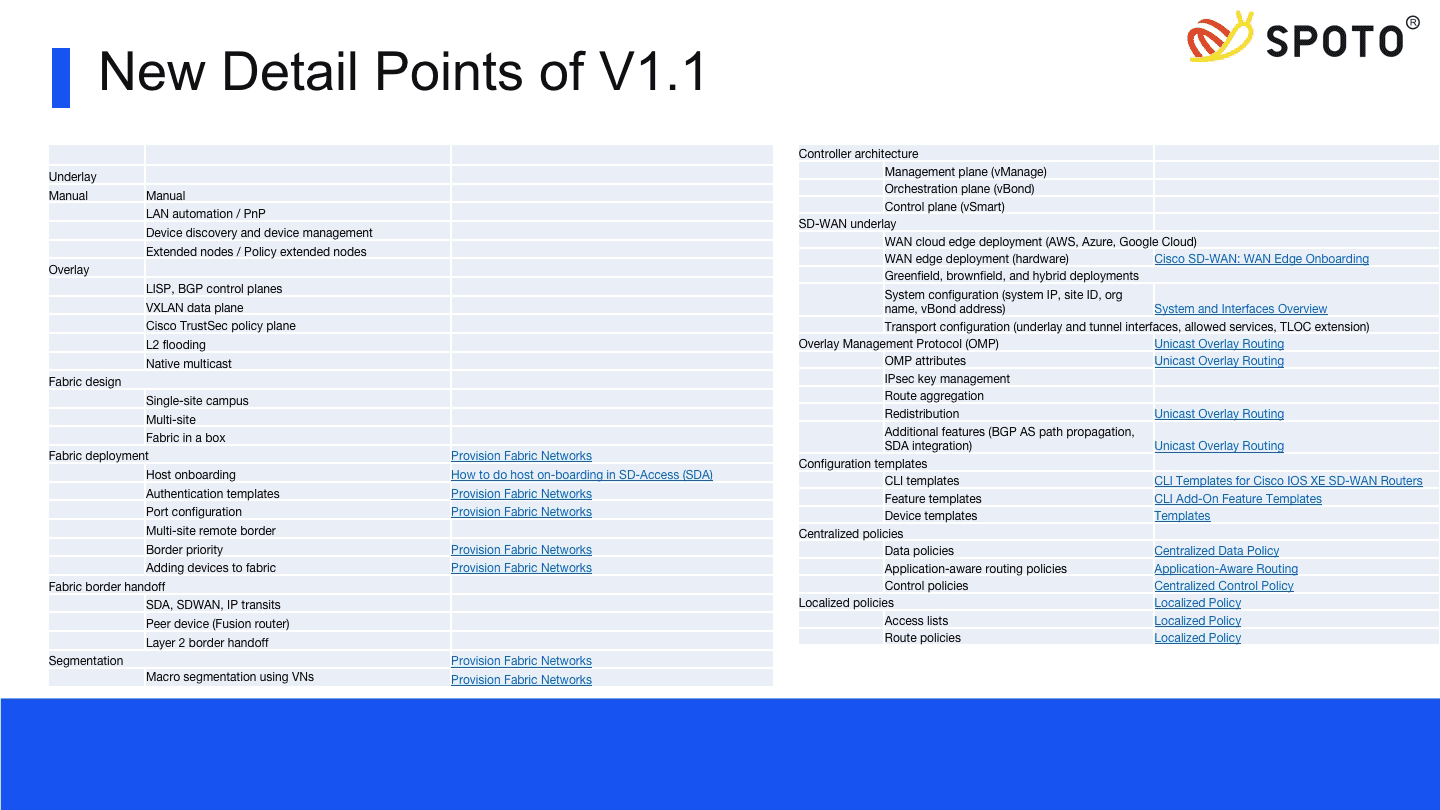
| 2.1 Cisco SD Access 2.1.a Design a Cisco SD Access solution 2.1.a i Underlay network (IS-IS, manual/PnP) 2.1.a ii Overlay fabric design (LISP, VXLAN, Cisco TrustSec) 2.1.a iii Fabric domains (single-site and multi-site using SD-WAN transit) 2.1.b Cisco SD Access deployment 2.1.b i Cisco DNA Center device discovery and device management 2.1.b ii Add fabric node devices to an existing fabric 2.1.b iii Host onboarding (wired endpoints only) 2.1.b iv Fabric border handoff 2.1.c Segmentation 2.1.c i Macro-level segmentation using VNs 2.1.c ii Micro-level segmentation using SGTs (using Cisco ISE) 2.1.d Assurance 2.1.d i Network and client health (360) 2.1.d ii Monitoring and troubleshooting 2.2 Cisco SD-WAN 2.2.a Design a Cisco SD-WAN solution 2.2.a i Orchestration plane (vBond, NAT) 2.2.a ii Management plane (vManage) 2.2.a iii Control plane (vSmart, OMP) 2.2.a iv Data plane (vEdge, cEdge) 2.2.b WAN edge deployment 2.2.b i Onboarding new edge routers 2.2.b ii Orchestration with zero-touch provisioning/Plug-And-Play 2.2.b iii OMP 2.2.b iv TLOC 2.2.c Configuration templates 2.2.d Localized policies 2.2.e Centralized policies | 2.1 Cisco SD-Access 2.1.a Underlay 2.1.a i Manual 2.1.a ii LAN automation/PnP 2.1.a iii Device discovery and device management 2.1.a iv Extended nodes / policy extended nodes 2.1.b Overlay 2.1.b i LISP, BGP control planes 2.1.b ii VXLAN data plane 2.1.b iii Cisco TrustSec policy plane 2.1.b iv L2 flooding 2.1.b v Native multicast 2.1.c Fabric design 2.1.c i Single-site campus 2.1.c ii Multisite 2.1.c iii Fabric in a box 2.1.d Fabric deployment 2.1.d i Host onboarding 2.1.d ii Authentication templates 2.1.d iii Port configuration 2.1.d iv Multisite remote border 2.1.d v Border priority 2.1.d vi Adding devices to fabric 2.1.e Fabric border handoff 2.1.e i SDA, SDWAN, IP transits 2.1.e ii Peer device (Fusion router) 2.1.e iii Layer 2 border handoff 2.1.f Segmentation 2.1.f i Macro segmentation using virtual networks 2.1.f ii Micro-level segmentation using SGTs and SGACLs 2.2 Cisco SD-WAN 2.2.a Controller architecture 2.2.a i Management plane (vManage) 2.2.a ii Orchestration plane (vBond) 2.2.a iii Control plane (vSmart) 2.2.b SD-WAN underlay 2.2.b i WAN Cloud Edge Deployment (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) 2.2.b ii WAN Edge Deployment (hardware) 2.2.b iii Greenfield, Brownfield, and Hybrid deployments 2.2.b iv System Configuration (system IP, site ID, org name, vBond address) 2.2.b v Transport configuration (underlay and tunnel interfaces, allowed services, TLOC extension) 2.2.c Overlay Management Protocol (OMP) 2.2.c i OMP attributes 2.2.c ii IPsec key management 2.2.c iii Route aggregation 2.2.c iv Redistribution 2.2.c v Additional features (BGP AS path propagation, SDA integration) 2.2.d Configuration templates 2.2.d i CLI templates 2.2.d ii Feature templates 2.2.d iii Device templates 2.2.e Centralized policies 2.2.e i Data policies 2.2.e ii Application-aware routing policies 2.2.e iii Control policies 2.2.f Localized policies 2.2.f i Access lists 2.2.f ii Route policies |
| 3. Transport Technologies and Solutions | 3. Transport Technologies and Solutions |
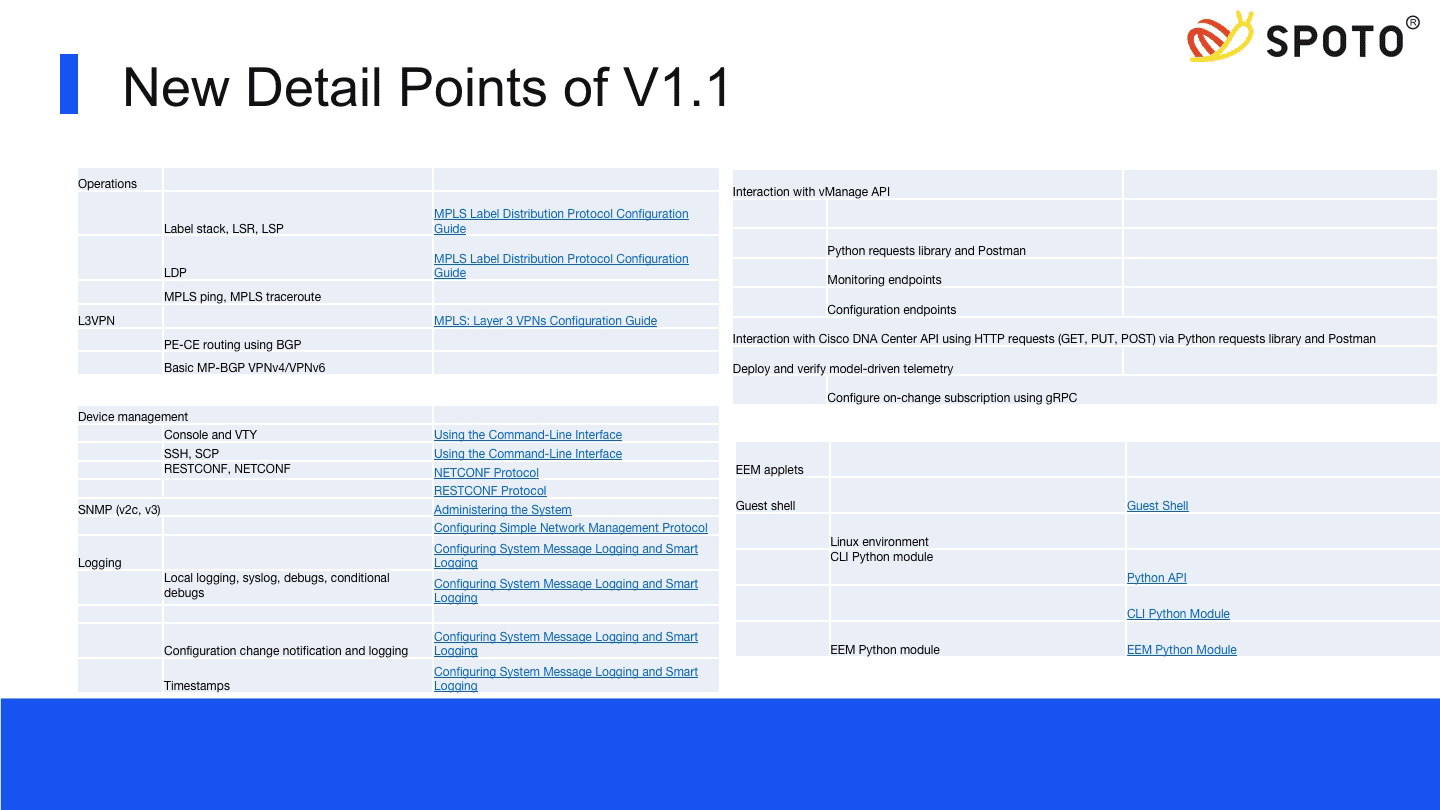
| 3.1 MPLS 3.1.a Operations 3.1.a i Label stack, LSR, LSP 3.1.a ii LDP 3.1.a iii MPLS ping, MPLS traceroute 3.1.b L3VPN 3.1.b i PE-CE routing 3.1.b ii MP-BGP VPNv4/VPNv6 3.1.b iii Extranet (route leaking) 3.2 DMVPN 3.2.a Troubleshoot DMVPN Phase 3 with dualhub 3.2.a i NHRP 3.2.a ii IPsec/IKEv2 using pre-shared key 3.2.a iii Per-Tunnel QoS 3.2.b Identify use-cases for FlexVPN 3.2.b i Site-to-site, Server, Client, Spoke-to-Spoke 3.2.b ii IPsec/IKEv2 using pre-shared key 3.2.b iii MPLS over FlexVPN | 3.1 Static point-to-point GRE tunnels 3.2 MPLS 3.2.a Operations 3.2.a i Label stack, LSR, LSP 3.2.a ii LDP 3.2.a iii MPLS ping, MPLS traceroute 3.2.b L3VPN 3.2.b i PE-CE routing using BGP 3.2.b ii Basic MP-BGP VPNv4/VPNv6 3.3 DMVPN 3.3.a Troubleshoot DMVPN Phase 3 with dual hub 3.3.a i NHRP 3.3.a ii IPsec/IKEv2 using preshared key |
| 5. Infrastructure Automation & Programmability | 5. Infrastructure Automation & Programmability |
| 5.1 Data encoding formats 5.1.a JSON 5.1.b XML 5.2 Automation and scripting 5.2.a EEM applets 5.2.b Guest shell 5.2.b i Linux environment 5.2.b ii CLI Python module 5.2.b iii EEMP Python module 5.3 Programmability 5.3.a Interaction with vManage API 5.3.a i Python requests library and Postman 5.3.a ii Monitoring endpoints 5.3.a iii Configuration endpoints 5.3.b Interaction with Cisco DNA Center API 5.3.b i HTTP request (GET, PUT, POST) via Python requests library and Postman 5.3.c Interaction with Cisco IOS XE API | 5.1 Data encoding formats 5.1.a JSON 5.1.b XML 5.1.c YAML 5.1.d Jinja 5.2 Automation and scripting 5.2.a EEM applets 5.2.b Guest shell 5.2.b i Linux environment 5.2.b ii CLI Python module 5.2.b iii EEMP Python module 5.3 Programmability 5.3.a Interaction with vManage API 5.3.a i Python requests library and Postman 5.3.a ii Monitoring endpoints 5.3.a iii Configuration endpoints 5.3.b Interaction with Cisco DNA Center API using HTTP requests (GET, PUT, POST) via Python requests library and Postman 5.3.c Deploy and verify model-driven telemetry |
New Detail Points of V1.1
Hardware and Software Equipment
The lab environment has been updated to support the new CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure v1.1. Candidates who preparing for the exam should now use the following latest Cisco software and equipment releases.
Virtual Machines
- Cisco Catalyst 8000V Routers with Cisco IOS XE Software Release 17.9
- Cisco IOSv with Cisco IOS Software Release 15.8
- Cisco IOSv-L2 with Cisco IOS Software Release 15.2
- Cisco SD-WAN (vManage, vBond, vSmart, cEdge) Software Release 20.9
- Cisco DNA Center, Release 2.3
Physical Equipment
- Cisco Catalyst 9300 Switches with Cisco IOS XE Software Release 17.9
Other (supporting virtual machines)
- Cisco Identity Services Engine 3.1
- Linux Desktop
Exam format
No changes have been made to the lab exam format for this minor revision.
SPOTO offers the latest & comprehensive CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure v1.1 lab exam dumps. We are designed to provide you with the latest updates and techniques needed to pass the CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure Lab exam. Our expert guidance and resources will ensure that you are ready and successful in achieving the CCIE Enterprise Infrastructure certificate.











Comments