Background:
With the commercialization of the Internet, the internal network of a large number of enterprises (such as banks, railways, companies, etc.) is interconnected with the Internet, which has caused a fundamental change in the concept of a modern corporate network.

In the past, the traditional way of interconnection between government departments and intra-regional intra-enterprise networks was through leased private lines. If people on business trips need to access the company’s internal network, in the past they had to use long-distance dialing to connect to the internal network of the company’s location. These interconnection methods are very expensive, and generally, only large enterprises can afford them. At the same time, it caused repeated construction and investment of the network. The development of the Internet has promoted the development of a virtual private network based on the public network so that it is possible to realize the interconnection between different departments of enterprises across regions or between different departments of the government through public networks, which can save enterprises a lot The communication costs and funds can also prevent government departments from building networks repeatedly. These new business needs to provide huge business opportunities for operators of public networks. However, how to ensure the security and confidentiality of the internal data transmission of the enterprise through the public network, and how to manage the different nodes of the enterprise network on the public network have become the issues of great concern to enterprises.
The virtual private network technology uses a dedicated network encryption and communication protocol, which enables enterprises to establish virtual encrypted channels on the public network and build their own secure virtual private network. Cross-regional departments or business personnel of an enterprise can remotely pass through the public network and connect to the internal network of the enterprise through a virtual encrypted channel, while users on the public network cannot access the internal network of the enterprise through the virtual channel.
VPN classification commonly used two classifications: customer access and routing information exchange.
Customer Access:

Site to Site
Site-to-site connection technology is a major VPN connection method, mainly used for connection between important sites. The two sites are virtually connected using VPN technology, and they communicate as if the network cables were directly connected together. Users do not feel the existence of VPN technology but feel that the sites they visit are on the same intranet.
Typical technologies:
GRE: The general routing encapsulation protocol can encapsulate data packets of various network-layer protocols (such as IP and IPX), and the encapsulated data packets can be transmitted in the IP network.
MPLS VPN: refers to the use of MPLS technology to build an enterprise IP private network on a broadband IP backbone network.
Remote Access
Site-to-site VPN connection technology can only meet the connection between company sites, which means that customers must use this technology to connect to other sites within the company. If the customer is on a business trip, you need to use it to access the company’s intranet anytime, anywhere Remote access VPN connection technology.
Generally, a VPN client needs to be installed on the client computer in advance (the client varies depending on the specific implementation technology used), and dials to the company VPN gateway through this client. If the dialing is successful, the customer is connected to the company VPN gateway virtually through a network cable, and then obtains an address of the company’s internal network, and uses this address to access the company’s internal server
Typical technology:
VPDN:
The virtual private dial-up network is a specific technology of VPN services including PPTP, L2TP, and PPPoE, etc. It is a virtual private dial-up network service based on dial-up users. Remote access and mobile office for enterprises and government management departments.
SSL VPN:
This refers to the VPN technology that establishes a remote secure access channel based on the SSL protocol of the secure socket layer. It is a VPN technology that has emerged in recent years, and its application has developed rapidly with the popularity of the Web and the rise of e-commerce and remote office. Due to attractive prices and reduced security risks, most users will switch to SSL VPN when building an extranet.
IPSec VPN is a comprehensive technology, which is not only applicable to site-to-site VPN but also can deploy remote access VPN. Data privacy is to encrypt data. It cannot be restored to plaintext after being stolen. It is an industry-standard network security protocol that can provide transparent security services for IP network communications and ensure that data is not tampered with by third parties during transmission. Source authentication is to authenticate the source that sent the data packet to ensure that it is a legitimate source that sent the data packet.
Routing Information Exchange
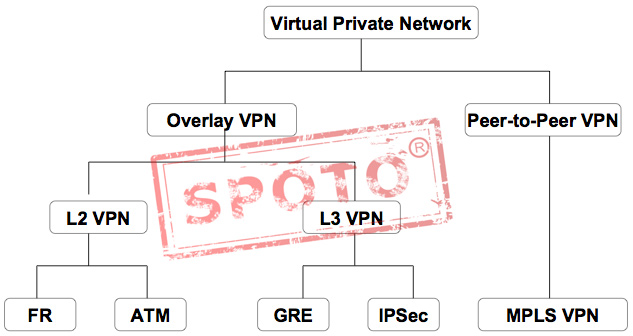
Overlay network
This refers to the virtual network built on the existing network, which is composed of logical nodes and logical links with independent control and forwarding planes. For the terminal system connected outside the overlay edge device, the physical network is transparent and is a physical network The in-depth extension to cloud and virtualization enables cloud resource pooling capabilities to get rid of physical network constraints, which is the key to achieving cloud-network integration.
Typical technologies: Layer 2 tunneling technologies such as X.25, Frame Relay, and ATM; layer 3 tunneling technologies such as IP-over-IP tunneling technology. Among them, the IP-over-IP tunnel technology covers the VPN network through the dedicated IP backbone or the Internet. The most commonly used technologies are GRE and IPsec.
Main defects: When the connectivity is more complicated, the management overhead is very large; to correctly provide the capacity of VC, it is necessary to understand the traffic situation between the sites, which is difficult to count. The essence of Overlay VPN is a kind of “static” VPN, which is like static routing, so it has all the defects similar to static routing: all configuration and deployment need to be done manually if a customer adds a new node in the VPN Point, you need to complete the following work
Create tunnels and related routes with all existing N nodes on this newly added node. For the existing N nodes, it is necessary to establish a tunnel and related routes between the newly added nodes on each node. Since it is a “static” VPN, it cannot reflect real-time changes in the network.
Peer-to-Peer
Like static routing, everything with a “static” nature is not well-suited for large-scale applications and deployments, making it difficult to shoulder heavy responsibilities. Therefore, the first problem to be solved is to make the deployment and routing of VPNs dynamic. Peer-to-Peer VPN is derived from this idea.
Peer-to-Peer here refers to CE-to-PE, that is to exchange private network routing information between CE and PE, and then PE will propagate these private network routes in P-Network (affirmed on P-Network It is running a dynamic routing protocol) so that these private network routes will be automatically propagated to other PEs.
Because this kind of VPN will leak private network routes to the public network, it must be strictly controlled by routing, that is, to ensure that only the routes of this VPN can be on the CE router of the same VPN. Therefore, the routing protocol running between CE and PE is usually different from the routing protocol running on P-Network. Even if they are the same, there must be a good route filtering and selection mechanism.
The PE equipment of the service provider directly participates in the routing exchange of the CE equipment. If the route to a specific network is not installed in the router’s forwarding table, the network is unreachable on that router. The premise of implementing Peer-to-Peer VPN is that all CE addresses are globally unique!












Comments