Overview
SD-Access, full name: Software-Defined Access. Like SD-WAN and ACI, SDA defines the enterprise network through software. In an integrated control platform, operation and maintenance and management, unified delivery strategy, network equipment configuration, etc.
SDN is a new type of network innovation architecture, and SDA is just a kind of SDN technology in it. For example, there are SD-WAN and others, DataCenter’s ACI, etc., should belong to SDN.
Cisco DNA Software-Defined Access (SD-Access) combines Campus Fabric and IWAN coverage solutions with Cisco TrustSec to become a general-purpose API-driven GUI ecosystem consisting of DNA centers: APIC-EM, ISE, NDP, etc.
SDA logical architecture
Policy-based automation from the edge to the cloud:
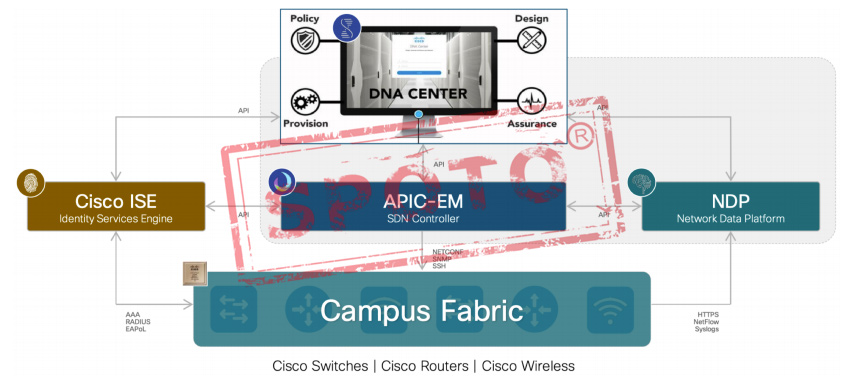
DNA-Center:
Cisco DNA Center
Cisco DNA Center is the network management and command center for Cisco DNA, your intent-based network for the enterprise.
Provision and configure all your network devices in minutes. Use advanced artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to proactively monitor, troubleshoot, and optimize your network. Integrate with third-party systems for improved operational processes.
Four characteristics
Perfect network management system
• Single console for all devices
• Real-time end-to-end health information
• Fine-grained visibility
• Simplified workflow
Analysis guarantee
• Verify the intent of the network settings
• Proactively solve problems
• Reduce troubleshooting time
Automatic configuration
• Zero-touch deployment
• Equipment life cycle management
• Policy Implementation
Extended platform
• Integrate API with third-party solutions
• Immediate integration and customization services
• Evolving operating tools and processes
ISE:
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) is a network administration product that enables the creation and enforcement of security and access policies for endpoint devices connected to the company’s routers and switches. The purpose is to simplify identity management across diverse devices and applications.
Features
Used for group mapping and policy definition of dynamic users or devices.
The basic role of ISE is to provide all identification and policy services for the physical layer and the network layer.
ISE can identify and analyze various forms of the network device and terminal authentication methods, including AAA / RADIUS, 802.1X, MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB), Web Authentication, EasyConnect, etc.
ISE will also collect and use NDP and NCP information.
ISE places the terminal in the correct security group and host pool.
ISE uses this information to provide information to NCP and NDP, so users
can create and manage group-based policies from the management layer.
ISE is also responsible for writing group-based policies on network devices.
APIC-EM:
The Cisco® Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module (APIC-EM) is our Software-Defined Networking (SDN) controller for enterprise networks (in the campus or branch and the WAN). It delivers an elastic platform for policy-based automation that simplifies and abstracts the network. It can enable the transformation of business intent to network control. The platform is built to host multiple, easy-to-use SDN applications that use open, northbound Representational State Transfer (REST) APIs and drive core network automation solutions. The platform also supports a number of southbound protocols that enable it to communicate with the breadth of network devices customers already have in place and extend SDN benefits to both greenfield and brownfield environments, immediately from the start. The goal of the APIC-EM platform is to power next-generation SDN applications that will dramatically lower operational expenditures and increase network agility to align with business needs.
The APIC-EM platform supports both wired and wireless enterprise networks across the WAN, and access and wireless infrastructures. It offers superior investment protection and works with both existing and new infrastructure. The APIC-EM platform delivers many significant benefits. For example, it:
● Creates an intelligent, open, programmable network with open APIs
● Can help customers save time, resources, and costs through advanced automation services
● Can transform business-intent policies into dynamic network configuration
● Provides a single point for network-wide automation and control
NDP :
Cisco NDP, short for Neighbor Discovery Protocol and Neighbor Discovery Packets, is a critical component of Cisco’s auto RF feature, Radio Resource Management (RRM). The purpose of NDP is to provide over the air (OTA) messages between access points (AP). It monitors and manages what each AP sees in the radio frequency (RF). It’s essentially how every AP sees other APs in an RF Group or Neighborhood. The end result is an actual RF path loss between APs.
I see NDP as a way for APs to build a map of their locations in relation to each other based on RF propagation and path losses. Every 180 seconds (3 minutes), an AP will send an over the air (OTA) message to a multicast address, 01:0B:85:00:00:00, from each channel.
NDP messages are sent at the highest transmit power and at the lowest data rate supported for the channel being transmitted on. The transmit power and data rate selection is not configurable by the end-user and is hardcoded.
Cisco Neighbor Discovery Protocol forms the basis of many algorithms within Cisco RRM. Because of that, it goes without saying, if NDP doesn’t work neither does RRM.
Learn more RRM from the white paper.
NDP is used by the following
RF Grouping Algorithm
Transmit Power Control (TPC – basis calculation for TPCv2)
Flexible Radio Architecture (FRA – the basis for coverage overlap factor)
Rogue detection (If AP isn’t sending NDPs or unintelligible NDP then it is a rogue)
CleanAir (Used for interference reports)
CMX (For AP RF distance and path loss measurements)
Campus Fabric
Ideas
If we can “break the dependency between IP addresses and policies”
Then we can greatly simplify the network and make the network more functional.
We can make the IP address your locator and provide other ways to
Group users/devices to apply policies?
Solution: Fabric
• Fabric provides an Overlay network • Overlay network is a logical topology for virtual connection devices, built on top of some arbitrary physical underlying topology
• Overlay networks usually use alternate forwarding attributes to provide additional services rather than the services provided by the bottom layer
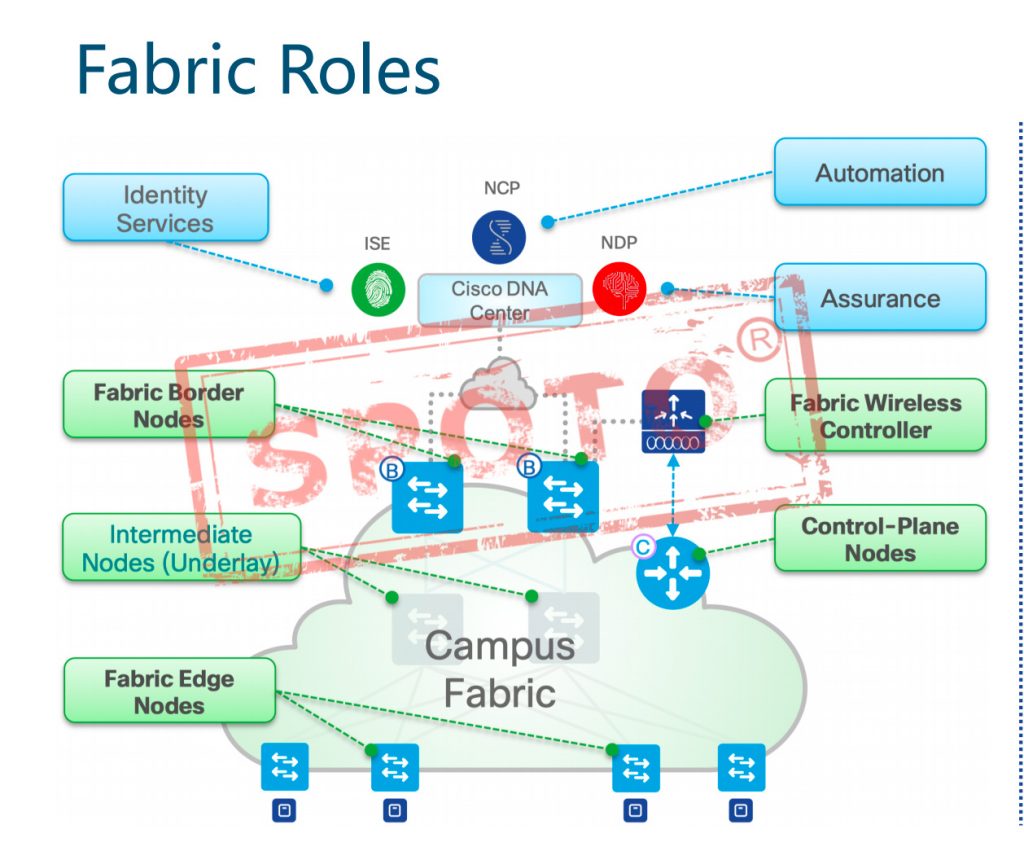
Control-Plane Nodes
Control-Plane Node runs a Host Tracking Database to map location information
• A simple host database that maps terminal ID and other attributes to the current location
• The host database supports multiple types of terminal ID lookup types (IPv4, IPv6 or MAC)
• Receive terminal ID mapping registration for “known” IP prefixes from the edge and/or border nodes
• Solve the search request from the edge and / or border node to find the target terminal ID












Comments